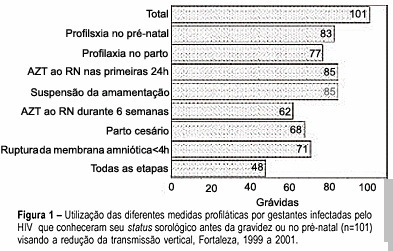
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):131-138
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200008
PURPOSE: to analyze the management for reduction of HIV transmission from mother to infant in infected pregnant women who delivered in public maternity hospitals of the municipality of Fortaleza, Ceará, from 1999 to 2001. METHODS: a descriptive study where data of SINASC, SINAN and LACEN data bank systems were cross-checked looking for HIV-infected pregnant women, followed by an active search for complementary information on the subject through medical records of the maternity hospitals. RESULTS: a hundred and thirty-eight pregnant women infected with HIV were identified. It was observed that 35.5% knew their serum status before pregnancy and 48.6% (67/138) were diagnosed during the prenatal visits. Of those 101 women that knew their serum status before or during pregnancy, only 47.5% followed all steps of prophylaxis, including the management of the newborns. The previous knowledge of the serum status was found to be significantly related to following the correct steps of prophylaxis (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: an increasing number of women who had no access to the different strategies for the reduction of vertical transmission were found in Fortaleza, Ceará, especially among those who became pregnant without knowing their serum status. Continuous awareness and training are very important for all health care providers involved in attending the pregnant women for the application of correct management in order to reduce HIV transmission from mother to infant.
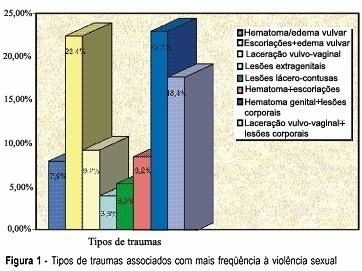
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):111-116
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the characteristics of sexual violence against women, the types of sexual crimes and resulting body lesions. METHODS: descriptive study based on the information obtained from the medical records of 102 victims of sexual violence who were seen at the Maria-Maria project from March 2002 to March 2003 and who fulfilled the eligibility criteria. The characteristics of the violence, the types of crimes and the body injuries are described. For calculation and analysis of the data, the Epi-Info, version 6.04, program, for simple percentages and frequency distribution were used. RESULTS: ages of the victims ranged from 1 to 68 years, 65.7% were younger than 20 years and one in four was younger than 9 years. The majority were single (78.3%) and with a low educational level (74.2%). The crime predominated at night (64.7%), in a secluded area (39.2%), followed by the victim's home (34.3%), and at the location of the attack (67.6%). Among the adolescent victims, the unknown attacker predominated, while among the children the attackers were men known to the victims. In the case of the children younger than 10 years, indecent assault was the most frequent crime (73.8%) while rape was the most frequent crime among the adolescents (66.4%). Body trauma occurred in 76.7% of the cases, mainly hematomas, vulva edema and abrasions. CONCLUSION: sexual violence predominated among children and adolescents, single women and with low educational level. The aggression happened more frequently during the night, by an unknown person, in a secluded area, in the case of adolescents, and by a known person (mainly neighbour), in the victim's home, in the case of children. Rape was the most frequent kind of crime among adolescents and among children it was indecent assault, usually associated with genital and corporeal trauma.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):105-110
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the high-risk oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV) detection rate of patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), checking the association between high-risk HPV, viral load and severity of the lesion, as well as the best viral load cutoff to predict lesion severity. METHODS: this is a cross-sectional study. One hundred and ten patients were selected by cytology and/or biopsy with CIN diagnosis. All of them were submitted to a new oncologic cytology, hybrid capture II (HC II), colposcopy, and loop electrosurgical excision and fulguration procedures (LEEP). RESULTS: the global detection rate of high-risk oncogenic HPV in these women was 77.3%. Eighty-one women (73.7%) had CIN with a detection rate of HPV-DNA of 87.6%. In women with CIN 2 or 3 the detection rate was 85.9%. HC II had a sensitivity of 87.8%, specificity of 56.0%, predictive positive value of 86.6% and predictive negative value of 58.3%, with an odds ratio of 7.76 (2.47 < OR < 25.15) for CIN 2 or 3 diagnosis. Using a receiver operator characteristic curve a viral load cutoff was set at 20 pg/mL in this population, with a predictive positive value of 81.3%. CONCLUSIONS: HPV DNA detection rate of patients with CIN was 77.3%. In women with CIN 2/3 it was 85.9%. The best viral load cutoff to predict cervical lesion severity was 20 pg/ml. Above this level the probability of high-risk oncogenic HPV detection is greater than 80%.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):89-96
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200002
PURPOSE: to evaluate knowledge, opinion and practice of gynecologists/obstetricians regarding induction of abortion. Method: a pretested, structured questionnaire was sent to gynecologists/obstetricians affiliated to FEBRASGO. They were asked to answer and return the questionnaire in a self-addressed, prepaid envelope, without identification of the respondent so as to preserve anonymity. Knowledge about the legal situation of abortion in Brazil, opinion about it and practice if confronted with abortion requests were questioned. RESULTS: approximately 90% of the respondents believed that abortion is legal for pregnancy resulting from rape or in case of risk to a woman's life and for 31.8% in case of severe fetal malformation. In their opinion abortion should be permitted in the case that pregnancy is a risk for a woman's life (79.3%), fetal malformation (77.0%) and after rape (76.6%), added to 9.9% who expressed that abortion should be permitted in all circumstances. Two thirds wrongly thought that a judicial order is required to practice a legal abortion and only 27.4% knew that a written request by the woman is required. Confronted with unwanted pregnancy, 77.6% of female gynecologists/obstetricians and 79.9% of partners of male respondents had an abortion, 40% would help a client and 48.5% a relative in the same situation. CONCLUSION: gynecologists/obstetricians lack knowledge on the legal situation of abortion although their opinion and practice are favorable.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):97-102
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200003
PURPOSE: to correlate the type of cervical lesion diagnosed by Pap smear with CD4 cell counts and HIV-RNA viral load in HIV-positive patients. METHODS: one hundred and fifteen HIV patients were evaluated retrospectively in the present study, during the period from January 2002 to April 2003, at a university hospital. Eighty-three patients presented cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in Pap smear, in comparison with thirty-two with no lesions. Patients were divided into three groups, according to CD4 counts: CD4 more than 500 cells/mm³, between 200 and 500 cells/mm³, and less than 200 cells/mm³, and other three groups, according to HIV viral load: less than 10,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL, between 10,000 and 100,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL, or more than 100,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL. Correlation was investigated by the Fisher test. RESULTS: of the eighty-three patients with CIN, 73% presented CD4 counts less than 500 cells/mm³. In all CD4 groups, more than 50% of the patients presented CIN. According to the viral load, 71.7% of the patients with less than 10,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL presented CIN I, compared with 11.3% that showed CIN III. In the group with higher viral load (>100.000 HIV-RNA copies/mL), 61.5% showed CIN I and 30.8% presented CIN III. CONCLUSION: association between viral load and CIN was established (p=0.013), which was not observed with CD4 cell counts and CIN. Concomitant cervicovaginal infection was considered a potential confounding factor.
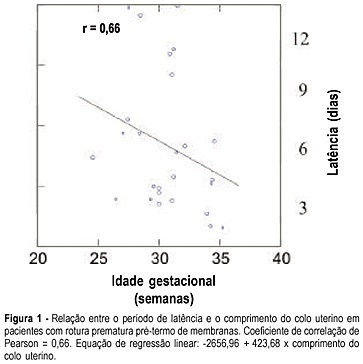
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):147-151
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200010
PURPOSE: to assess the length of the uterine cervix by transvaginal ultrasonography in pregnant women with preterm premature rupture of membranes. METHODS: the study group (Ge) consisted of 26 pregnant women with gestational age between 24 and 36 weeks and the control group (Gc) of 49 clinically normal patients at the same gestational age. The patients were evaluated between the 24th to 28th, 28th to 32th and 32th to 36th weeks. The groups were divided into subgroups Ge24-28, Ge28-32, Ge32-36 and Gc24-28, Gc28-32, Gc32-36, according to the study or control group. The cervix length was measured by transvaginal ultrasonography as the linear distance between the internal and external cervical os. RESULTS: we observed significant differences in cervix length between Ge24-28 and Gc24-28 groups whose values were, respectively, 24.3 and 33.0 mm (p=0.04), and between Ge32-36 and Gc32-36, 20.1 and 28.0 mm, respectively (p=0.005). The latency periods of Ge24-28, Ge28-32 and Ge32-36 were, respectively, seven, five and three days, showing a positive correlation with cervix length (r=0.66) and a negative correlation with gestational age (r=-0.27). CONCLUSIONS: the length of the uterine cervix varied with the gestational age when premature preterm rupture of the membranes was detected, with the length being shorter in the study group than in the control group betweeen the 24th and 28th and 32th and 36th weeks. In addition, it was demonstrated that, the shorter the cervix length, the shorter the latency time, with a reduction in the latency period with increasing gestational age at the time of rupture.
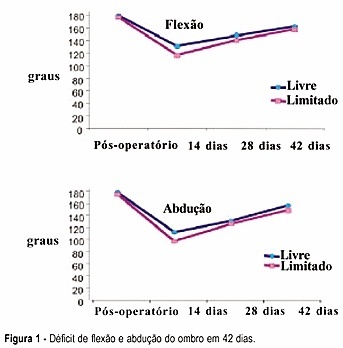
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):125-130
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the efficacy of a physical exercise protocol in the recovery of shoulder movement in women who underwent complete axillary lymph node dissection due to breast carcinoma, comparing free and restricted amplitude movements. METHODS: 59 women who underwent complete axillary lymph node dissection associated with modified mastectomy (46) or quadrantectomy (13) were included in this clinical, prospective and randomized study. On the first day after surgery 30 women were randomized to do the shoulder movement with free amplitude and 29 women had this amplitude restricted to 90º in the first 15 days. Nineteen exercises were done, three sessions per week, for six weeks. Mean (± standard error) deficits of shoulder flexion and abduction were compared, as well as gross and adjusted incidence rates of seroma and dehiscence. RESULTS: 42 days after surgery, flexion and abduction means were similar in the two groups. Both presented a mean flexion deficit (17.2º and 21.6º, respectively), and abduction deficit (19.7º and 26.6º, respectively). The incidence rates of seroma and dehiscence were neither related to exercise nor to the type of surgery, time of drain permanence, number of dissected or compromised lymph nodes, age or obesity. CONCLUSION: early physiotherapy with free movement of the women's shoulder was associated neither with functional capacity nor with postsurgical complications.