Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):411-416
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500011
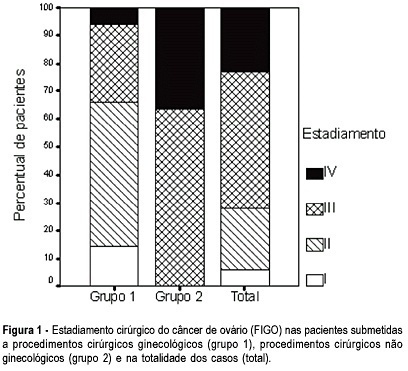
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the incidence of non-gynecological surgical procedures used in the treatment of ovarian cancer, as well to describe their complications. METHODS: eighty-two patients with ages from 22 to 89 (mean = 54.1 ± 15.1 years), submitted to laparotomy for surgical treatment of ovarian cancer from February 1999 to October 2003 were retrospectively evaluated. This study included only patients with epithelial ovary carcinoma. The patients were divided into 2 groups, patients submitted exclusively to gynecological procedures and patients submitted to non-gynecological procedures. Statistical analysis was made with the Student's t-test or the chi-square test. RESULTS: 5 patients (6.1%) were in stage (FIGO) I, 18 (21.9%) in stage II, 40 (48.8%) in stage III, and 19 (23.2%) in stage IV. Non-gynecological procedures were done in 35 cases (42.7%), including: 17 colostomies, 16 enterectomies, 8 peritonectomies, 7 colectomies, 5 partial diaphragm resections, 4 partial cystectomies, 4 splenectomies, 2 ileostomies, and 1 hepatectomy. All patients submitted to non-gynecological procedures were included in stages III and IV. This group of patients underwent longer-lasting surgeries (5.3 ± 1.4 versus 3.1 + 0,0 h; p < 0.001). There was no significant difference between these two groups regarding hemotransfusion requirement (42,2 versus 40%; p = 0.512) and hospitalization time (11.5 ± 7.2 versus 10 ± 9.9 days; p = 0.454). Patients submitted to non-gynecological surgeries developed higher rates of postoperative complications (37 versus 17.1%; p = 0.042), and two of them (2.4%) died. CONCLUSION: non-gynecological surgical procedures are frequently used in the treatment of patients with ovarian cancer. These procedures are associated with a longer-lasting surgery and higher rates of postoperative complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):405-410
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500010
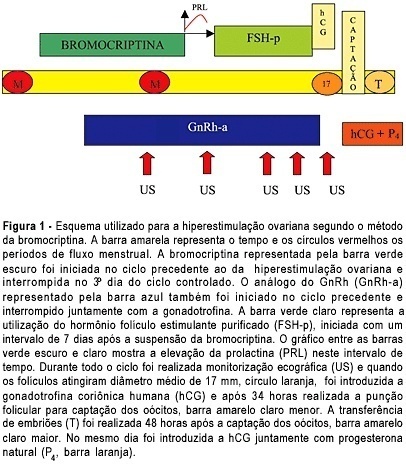
OBJECTIVE: to assess the ovarian response of poor responsive patients, submitted to the bromocriptine method. PACIENTS AND METHODS: a prospective clinical trial for the in vitro fertilization (IVF) program was performed in 10 poor responsive patients. Endocrinologically normal ovulatory women under 38 years old, who had previously failed in IVF due to poor response to ovarian stimulation with the traditional protocol, were submitted to the bromocriptine method in 12 cycles. They were given bromocriptine, a dopaminergic agonist, in the preceding cycle in order to stop the prolactin production. When the medication was removed at the beginning of the stimulation cycle, an elevation of seric prolactin by a rebound phenomenon was found. This optimized its seric concentration, improving the quality of oocytes and embryos. Serum prolactin and estradiol concentrations, number of follicles, number and quality of oocytes and cleaved embryos, fertilization and pregnancy rates were analyzed. RESULTS: there was a reduction in the dose of gonadotropin administered and in the duration of ovarian stimulation and an improvement in follicular recruitment, oocyte retrieval, embryo morphology, fertilization, and ongoing pregnancy rates. Fertilization rate was 77.7%, pregnancy rate was 44.4% and live baby rate was 25%. CONCLUSION: this study suggests that the bromocriptine method enhanced follicular recruitment and embryonic development, resulting in increased fertilization and pregnancy rates when compared with the traditional protocol for poor responsive patients. Studies with a large number of patients are necessary to confirm these results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):355-361
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500003
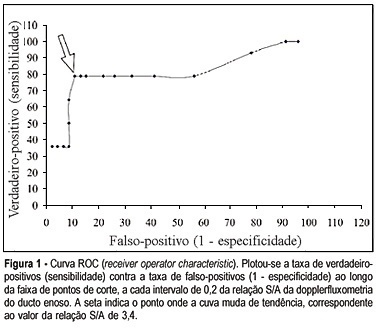
OBJECTIVE: to assess through Dopllerfluxometry the S/A ratio of the ductus venosus and determine the cut-off point to identify preterm fetuses with the 'brain sparing phenomenon". METHOD: a cross-sectional study was performed in 60 pregnant women that presented the "brain sparing phenomenon" (umbilical cerebral ratio >1) and gestational age between 25 and 33 weeks. The following parameters were studied: S/A ratio of the ductus venosus, pH and base excess (BE) of a fetal blood sample collected from the umbilical vein immediately after birth. The fetuses were classified according to the gas analysis result. They were considered abnormal when pH <7.20 and BE < -6 mmol/l. A receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to examine the relationship between S/A ratio and fetal acidemia. RESULTS: sixty pregnant women in the period of January 1998 to January 2003 were selected. In the moment of the study the gestational age varied from 25 to 33 weeks, with an average of 29.7 weeks (±1.8 weeks). All of the fetuses presented the "brain sparing phenomenon". Among them 14 presented abnormal gas analysis at birth and 46 presented normal gas analysis. The prevalence of fetuses with abnormal gas analysis in the studied material was 23.33%. Significant association was observed between the abnormal ductus venosus velocimetry and abnormal gas analysis at birth (chi2 = 784.44, p < 0.00001) in preterm fetuses with "brain sparing phenomenon". The best cut-off point of the S/A ratio (where the ROC curves bent) was 3.4. CONCLUSION: fetal acidemia in preterm fetuses with "brain sparing phenomenon" may be noninvasively identified by Doppler measurement of the ductus venosus when the S/A rises above 3.4.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):349-354
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500002
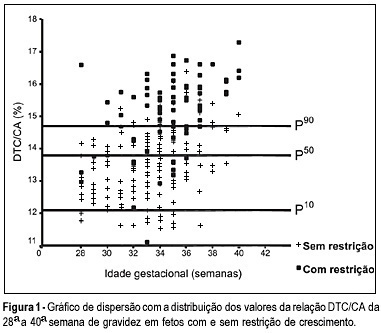
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the accuracy of both the transverse diameter of the cerebellum (TDC) and of the transverse diameter/abdominal circumference (TDC/AC) ratio in the detection of fetal growth restriction (FGR), in high-risk pregnancies. METHOD: a prospective cross-sectional study was carried out in 260 patients with gestational age between 28 and 40 weeks. The TDC and AC of fetuses were measured through ultrasound and the fetuses with TDC below the 10th percentile or TDC/AC ratio above the 90th percentile (>14.6) were classified as FGR suspects. After birth, the accuracy of the TDC and TDC/AC was evaluated using the neonatal diagnosis of FGR as the gold standard (birth weight <10th percentile). RESULTS: after birth, 79 newborns (30.4%) were classified as small for gestational age. The TDC was appropriate in 74 (93.7%) of these fetuses and small in only 5 (6.3%). The sensitivity (SE), specificity (SP), positive (PPV) and negative (NPV) predictive values and accuracy of the TDC in the prediction of FGR were 6.3, 93.4, 29.4, 69.5, and 67%, respectively. The TDC/AC >14.6 correctly identified 59 of the 79 growth-restricted fetuses, with 27 false-positives and 20 false-negatives, SE of 74.5%, SP of 85.1%, PPV of 68.6%, NPV of 88.5% and 81.9% accuracy. CONCLUSION: the TDC is not a good screening parameter for the detection of FGR while the TDC/AC ratio above the 90th percentile is effective in this detection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):325-328
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400010
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of a rapid antibody HIV test (DetermineTM - Abott) for women in labor between August 1, 2001, and October 5, 2002. METHODS: all parturient women who had not been tested for the detection of HIV during pregnancy or had the result of an HIV test not available at admission were included in the present study. Blood samples were collected at the moment of admission, and the rapid test was carried out and compared with the gold standard (ELISA and Western blot). RESULTS: in 298 pregnant women assessed, the rapid test was positive in 16 (5.3%), and the results were confirmed by ELISA and Western blot in 12 cases (4%). All negative results were confirmed by the ELISA and Western blot tests. CONCLUSIONS: the test presented 100% sensitivity, 98% specificity, 75% positive predictive value, and 100% negative predictive value. These data show the importance of the rapid test for the detection of HIV infection in emergencies, such as imminent delivery of non-previously tested pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):311-316
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400008
OBJECTIVE: to assess the concordance of different urodynamic parameters with simplified cystometry, thus improving the cost-benefit relationship for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) diagnosis in woman. METHODS: we evaluated retrospectively the medical records of thirty patients treated, from January 2000 to March 2001. All patients had been submitted to physical and gynecological examinations. A conventional urodynamic study had been made using a Dynograph R-611 recorder. Simplified cystometry had used a saline tube with "Y" connector, connected to a Foley 14 Fr catheter, which allowed measurement of intra-vesical pressure at the same time as physiological saline infusion. The following parameters were analyzed: residual volume, bladder capacity, complacency, involuntary detrusor contractions, and abdominal leak-point pressure. The Pearson test of agreement and the Wilcoxon signed rank test were used to verify the concordance between related samples, with p < 0,05. RESULTS: the average age was 50 years old (28-70). Concordance between studies for stress urinary losses was 67%, and for detrusor involuntary contractions, 90%. The average residual volume was significantly different: by simplified cystometry it was 16.8 ml versus 2 ml by conventional urodynamics (p < 0.01). The average maximum vesical capacity by urodynamic study was 440.5 ml, and by simplified cystometry, 387 ml (p < 0.05). Vesical complacency was on average, significantly larger in simplified cystometry (43.0 ml/cmH2O) than in the urodynamic study (31.5 ml/cmH2O), with p < 0.01. CONCLUSION: preliminary evaluations suggest that the urogynecologic propedeutic associated with cystometry is an option to be considered in the clinical and preoperative assessment of patients with SUI instead of conventional urodynamics, particularly when the latter is not available. Simplified cystometry is an accessible exam that grants comparable results for the detection of involuntary detrusor contractions and for the identification of urinary loss, providing the examiner with trustworthy data on vesical behavior.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):317-323
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400009
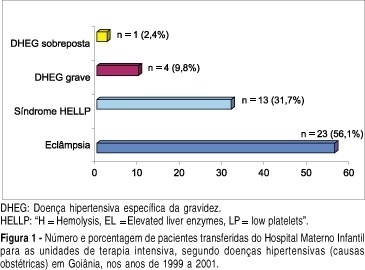
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the epidemiological and parturitional aspects of obstetric patients admitted to intensive care units (ICU), and analyze the frequency of intensive support needed by them. METHODS: observational and descriptive study of all obstetric patients' transfers to ICU from the Hospital Materno Infantil of Goiânia-Go, from January 1999 to December 2001. The analysis has included variables as maternal age, parity, obstetric and non-obstetric indications for ICU admissions, moment of transfer, mode of delivery, maternal death, and the frequency of ICU utilization per 1,000 deliveries (IDR - imminent death ratio). The statistical analysis was performed by the chi2 test or the Fisher exact test and a significant difference was set at a level of 5%. RESULTS: over the 36-month period analyzed, 86 pregnancy-associated ICU admissions were identified (among 4,560 deliveries). Of the 86 patients, 52.33% (n=45) were nulliparae and 63 (73.26%) were between 19 and 35 years old. Hypertensive disorders accounted for 41 (57.75%) of the admissions and hemorrhage for 14 (19.72%). Eclampsia (n=23), HELLP syndrome (n=13) and premature abruptio placentae (n=5) were the most common obstetric indications for ICU admissions. Maternal cardiac disorders accounted for 4 cases of non-obstetric indications. There was a predominance of postpartum transfers (82.35%). Fifty-five (72.37%) patients needed delivery by caesarian section. The average time spent in the UCI by those patients was 5.1 days. Maternal mortality found in this study was 24.29%, hypertensive disorders being responsible for 52.94% (9/17) of all obstetric-associated deaths. There were no significant statistical differences (p=0.81) regarding these obstetric-associated deaths and their causes (hypertensive disorders, hemorrhage or infections) or even regarding maternal deaths and duration of stay (< or > 48 hours) in the ICU (p=0.08). The IDR found was 18.8 per 1,000 deliveries. CONCLUSIONS: the need of intensive care estimated by IDR was 18.8 per 1,000 deliveries, the pregnancy-induced hypertension being responsible for the majority of the indications for maternal transfers.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):305-309
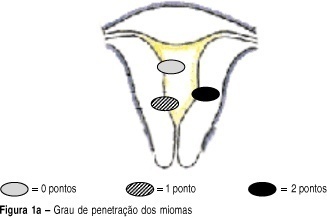
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400007
OBJECTIVE: to develop a new preoperative classification of submucous myomas to evaluate the viability and the degree of difficulty of hysteroscopic myomectomy. METHODS: forty-four patients were submitted to hysteroscopic resection of submucous myomas. The possibility of total resection of the myoma, the surgery duration, the fluid deficit, and the incidence of complications were evaluated. The myomas were classified by the Classification of the European Society of Endoscopic Surgery (CESES) and by the classification proposed (CP) by our group, that besides the degree of penetration of the myoma in the myometrium, adds the parameters: extent of the base of the myoma as related to the uterine wall, the size of the myoma in centimeters and its topography at the uterine cavity. For statistical analysis the Fisher test, the Student t test and the analysis of variance were used. Statistic significance was considered when the p-value was smaller than 0.05 in the bicaudal test. RESULTS: in 47 myomas the hysteroscopic surgery was considered complete. There was no significant difference among the three levels (0, 1 and 2) by CESES. By CP, the difference among the number of complete surgeries was significant (p=0.001) between the two levels (groups I and II). The difference between the surgery duration was significant when the two classifications were compared. In relation to the fluid deficit, just CP presented significant differences among the levels (p=0,02). CONCLUSIONS: the proposed classification includes more clues about the difficulties of the hysteroscopic myomectomy than the standard classification. It should be noted that the number of hysteroscopic myomectomies used for that analysis was modest, being interesting to evaluate the performance of the proposed classification in larger series of cases.