Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(3):147-151
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000300003
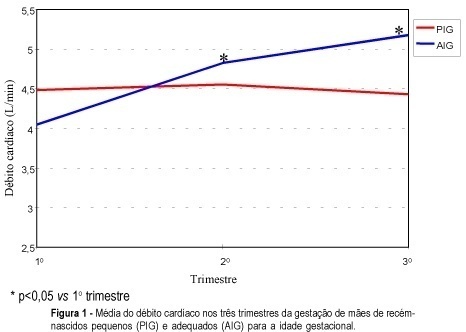
Purpose: to evaluate maternal hemodynamic and cardiac structural changes during the three trimesters of pregnancy and to relate them to the weight/gestational age of the newborn. Methods: twenty-two healthy pregnant women were submitted to echocardiography for the study of cardiac output, mean arterial pressure, left atrium diameter, and peripheral resistance during three periods of pregnancy, i.e., before the 12th week and at the 26thand 36th weeks of pregnancy. Seventeen pregnant women gave birth to infants with adequate weight for gestational age, four gave birth to small for gestational age newborns and one gave birth to a large for gestational age infant. Results: among mothers of low weight newborns, cardiac output and left atrium diameter remained constant, mean arterial pressure showed a tendency to increase and peripheral resistance was significantly increased (28%), during the gestation. Among the mothers of adequate weight newborns there was an increase in cardiac output of 19% in the second trimester and 8% in the third. The left atrial diameter increased approximately 9% during the gestation, with maintenance of mean arterial pressure and a tendency to a decrease in peripheral resistance. Conclusion: the present results support an association between hemodynamic adaptation and weight newborn.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(3):137-143
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000300002
Purpose: to study, in high risk pregnancies with cerebral redistribution of blood flow, the fetal surveillance and perinatal outcome, according to umbilical artery dopplervelocimetry. Methods: a total of 717 high-risk pregnancies attended at the Fetal Surveillance Unit were included. The last examination performed until 72 h prior to delivery was taken into account. Multiple gestations and fetal anomalies were excluded. The redistribution of blood flow was diagnosed if the pulsatility index of middle cerebral artery was below the 5th percentile for gestational age. The umbilical artery dopplervelocimetry was abnormal when A/B ratio was more than the 95th p. Results: in the group with normal umbilical artery dopplervelocimetry (560 cases -- 78.1%), significant correlation was found only between redistribution of blood flow and suspected or abnormal cardiotocography (17.1%). In the group with abnormal umbilical artery dopplervelocimetry (157 cases -- 21.9%) we found significant correlation between redistribution of blood flow (105 cases -- 66.9%) and cardiotocography abnormalities (57.2%), abnormal 1st(43.8%) and 5th (12.4%) minute Apgar scores. In these cases, the mean values of gestational age at delivery (34.4 ± 3.6 weeks), birth weight (1,810.5 ± 769.3 g), and pH at birth (7.20 ± 0.1) were significantly lower. Conclusion: The redistribution of fetal blood flow characterized by means of middle cerebral artery dopplervelocimetry is related to perinatal results when some level of placental insufficiency occurs, and does not present association to perinatal outcome when pregnancy shows normal fetal-placental blood flow.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(3):181-186
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000300008
Purpose: to evaluate the incidence of side effects and acceptance (continuity rate) of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) as an injectable three-monthly contraceptive given to adolescents in our milien. Method: forty adolescents (70% lactating) started to use DMPA and were followed-up for a mean of 14.2 months. Spontaneous complaints, menstrual changes, physical examination and laboratory data were collected and studied using Wilcoxon or McNemar tests. Results: the most frequent complaints were abdominal pain (16.6%) and headache (15.2%). Predominant menstrual patterns were spotting and oligomenorrhea. Significant variation of the systolic blood pressure was not observed during the follow-up. There was a slight fall in the levels of diastolic blood pressure, at the limit of significance. Significant deviations from baseline regarding fasting glucose were not noted, but the mean hemoglobin concentration tended to increase. Weight gain (mean 3.9 kg at 12 months) and menstrual irregularity (occurred in more than 70% of all visits) were the main reasons for discontinuation of the method. Twenty-seven patients were accompanied during 12 months and the continuity rate at that time was 81.5%. Conclusion: depot medroxyprogesterone acetate is a satisfactory contraceptive method for adolescents.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(3):175-179
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000300007
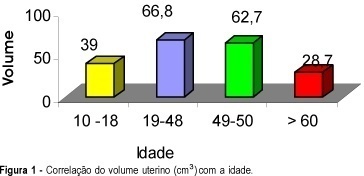
Purpose: to determine the accuracy of transabdominal ultrasound (TAUS) in revealing physiological and pathological changes in uterine volume, and to compare uterine volume detected by TAUS and by transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) in an attempt to determine the relationship between the two methods. Methods: a total of 1,186 pelvic echographic examinations (TAUS and TVUS) were first reviewed retrospectively in terms of the major diseases and indications for the examinations. A total of 480 TAUS examinations without uterine disease were then selected and uterine volume was correlated with age and parity. Finally, a retrospective study was conducted to compare the uterine volume of 50 women obtained by TAUS and TVUS. Data were analyzed statistically by Student's t-test and Spearman and Pearson correlation. Results: correlating with parity, volume was 44.4 cm³ for P = 0 (n = 99), 58.5 cm³ for P = 1 (n = 72), 75.8 cm³ for P = 2-3 (n = 137), 88cm³ for P = 4-5 (n = 56), and 105cm³ for P = 6 or more (n = 26), showing a positive correlation between parity and uterine volume. Calculation of Spearman's correlation coefficient yielded r = 0.59 and p = 0.001 and calculation of Pearson's correlation coefficient yielded r = 0.55 and the same p value. There were no significant differences between the uterine volumes detected by TAUS and TVUS. Conclusions: the volume increases with parity and changes with age, and these modifications are detected by TAUS. The two methods (TAUS and TVUS) are equivalent in determining the uterine volume; however, when TAUS is used, bladder filling allows a better evaluation of the uterine length.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(2):113-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000200009
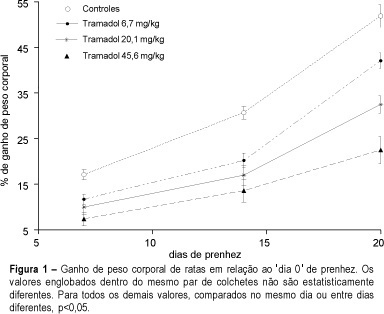
Purpose: to examine the effects of tramadol hydrochloride on rat pregnancy. Methods: five groups of 10 pregnant albino rats each were treated from the 1st up to the 20th day of pregnancy as follows: GI = intact controls; GII = controls which received 0.5 ml of distilled water (drug vehicle) once a day by gavage; GIII, GIV and GV = groups treated respectively with 6.7, 20.1 or 45.6 mg/kg of tramadol hydrochloride once a day by gavage in a final volume of 0.5 mL. Body weight gain was monitored by weighing at the beginning and on the 7th, 14th and 20th day of pregnancy. At term the animals were killed under deep ether anesthesia and the following parameters were evaluated: number of implantations, of resorptions, of viable fetuses and of placentae; presence of major malformations; maternal and fetal mortality and weights of fetuses and placentae. Results: tramadol significantly affected maternal body weight gain, this effect being more apparent in groups IV and V (mean reductions of weight gain of 41 and 56%, respectively). In group III the weight gain was affected more at days 7 and 14 (33% mean gain reductions) than at day 20 (19%). Drug treatment affected significantly and in a dose-dependent fashion the following parameters: individual weight of fetuses (GV = -39.2%), offspring weight (GIV = -51.7%; GV = -44.2%), number of placentae (GIV = -28.4%; GV = -11.6%), individual weight of placentae (GV = -10%) and the total weight of placentae (GIV = -28.4%; GV = -16.8%). Though among the treated animals there was an increase in resorptions and deaths at birth, these events were not significantly different from those found in controls. Conclusions: Tramadol showed definite deleterious effects on albino rat pregnancy, and these effects were exerted not only on the maternal but also the on fetal organisms. Overall, the effects were more pronounced at the 14th than at the 20th day of pregnancy, thus suggesting that the organogenic phase of the fetus is more susceptible than its initial (embryogenic) or final (term) phases. The results call attention to the care which is to be taken when the use of this opioid is considered during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(2):101-105
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000200007
Purpose: to study the changes in amniotic fluid index (AFI) measured by ultrasonography, mean arterial pressure (MAP) and pulse rate in normal pregnant women submitted to subtotal body immersion in water for different periods of time, and to standardize the technique. Methods: AFI values were studied as recommended by Phelan et al.¹ in a group of 52 pregnant women with gestational age of 28 weeks or more considered to be clinically normal, before and after exposure to subtotal immersion in water heated to 32 to 34ºC for 30, 45 and 60 min. The patients were seen at the Ultrasonography and Medical Updating School of Ribeirão Preto and in the Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics of the Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo. Results: before and after immersion, the average of MAP was 87.8 and 87.1 in the group of 30 min, 76.7 and 66.6 in the group of 45 min and 77.4 and 60.7 in the group of 60 min, with statistical significance. Before and after immersion, the means of pulse rates were 74.9 and 78.7 in the group of 30 min, 83.6 and 85.2 in the group of 45 min and 84.9 and 90.6 in the group of 60 min, with statistical significance. The mean of AFI also showed statistical significance. When submitted to 30-min immersion the means of AFI were 11.7 cm before and 16.8 cm after. In the group of 45 min, the averages were 9.7 cm before and 13.8 cm after immersion. In the group of 60 min, the averages were 9.5 cm before and 13.6 cm after immersion. The time of immersion of 30-min was as effective and ample as 45 or 60 min. Conclusions: subtotal immersion in water is a safe and practical procedure that can mobilize fluids during pregnancy, increasing amniotic fluid volume.
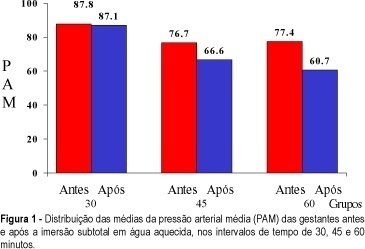
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(2):93-97
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000200006
Purpose: to analyze the effect of betamethasone on the pregnancy of rats. Methods: thirty pregnant rats were divided into three groups of ten animals each. Group I -- the animals received betamethasone IM (1 mg/kg body weight, in 0.5 ml distilled water) on the 11th, 12th, 18th and 19th day of pregnancy. Group II -- the rats received distilled water (0.5 ml) IM on the 11th, 12th, 18th and 19th day of pregnancy. Group III - the rats did not receive any drug or vehicle. The animals were weighed on days 0, 7, 14 and on the 20th of pregnancy, and on the last day of weighing, the animals were sacrificed. The number of implantations, resorptions, fetuses, placentas, malformations, maternal and fetal mortality as well as the weight of the fetuses and placentas were obtained and analyzed. Results: our results show that the rats treated with betamethasone gained significantly less weight. Their fetuses had an average weight of 3.2 g compared with 3.75 g in the control group. The results regarding placental weight were 0.36 g vs 0.48 g, respectively. All these differences were statistically significant. Conclusions: betamethasone had a negative effect on the gain of weight of matrices, fetuses and placentas when administered repeatedly and continuousy after the second half of pregnancy.
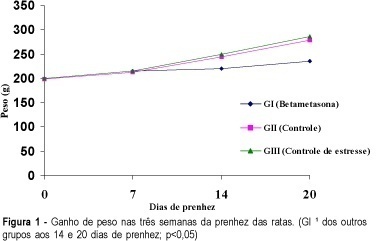
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(2):77-82
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000200003
Purpose: to evaluate the nonpharmacologic treatment (reassurance) as a first line therapy for women with cyclical mastalgia, and to observe if a prolonged course of pain alters the outcome. Methods: we conducted a noncontrolled experimental study with a sample of 128 eligible women with a clear history of cyclical mastalgia treated with reassurance. A visual linear analogical scale of the pain was used before and after treatment in order to assess its severity and the mastalgias were classified into degrees I (mild), II (moderate) and III (severe) according to the intensity of pain. We also used a modified Cardiff Breast Score (CBS) to assess the clinical response. The data analysis was performed using the chi² test (Epi-Info 6.04 software). Results: we verified a success rate of 59.4% with reassurance, but there was no significant statistical difference between the groups (p = 0.16) with different degrees of mastalgia. The less satisfactory response to the nonpharmacologic treatment in those pacients with a prolonged course of pain was only apparent, since there was no significant statistical difference (p = 0.14). Conclusion: reassurance should be always tried as the first choice treatment for women with cyclical mastalgia, independently of pain intensity. Prolonged course of pain did not alter the outcome.