Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):28-34
To determine embryo quality (mean graduated embryo score [GES]) in infertile patients with endometriosis undergoing in vitro fertilization with embryo transfer (IVF-ET) compared with infertile patients without endometriosis.
A case-control study was performed comparing 706 embryos (162 patients) divided into 2 groups: 472 embryos derived from patients without endometriosis (n= 109, infertile patients with tubal infertility) and 234 embryos from patients in the study group (n= 53, infertile patients with peritoneal endometriosis). All patients were subjected to IVF using an oestradiol-antagonist-recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) protocol for ovarian stimulation. Themean GESwas performed to evaluate all embryos at 3 points in time: 16 to 18 hours, 25 to 27 hours, and 64 to 67 hours. Embryo evaluation was performed according to the following parameters: fragmentation, nucleolar alignment, polar body apposition, blastomere number/morphology, and symmetry. The primary outcomemeasure was the mean GES score.We also compared fertilization, implantation, and pregnancy rates.
Although the number of embryos transferred was greater in patients with endometriosis than in the control group (2.38 ± 0.66 versus 2.15 ± 0.54; p= 0.001), the meanGESwas similar inbothgroups (71 ± 19.8 versus 71.9 ± 23.5; p= 0.881). Likewise, the fertilization ratewas similar in all groups, being 61% in patients with endometriosis and 59% in the control group (p= 0.511). No significant differences were observed in the implantation (21% versus 22%; [p= 0.989]) and pregnancy rates (26.4% versus 28.4%; p= 0.989).
Embryo quality measured by the mean GES was not influenced by peritoneal endometriosis. Likewise, the evaluated reproductive outcomes were similar between infertile patients with and without endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):20-27
To analyze the agreement, in relation to the 90th percentile, of ultrasound measurements of abdominal circumference (AC) and estimated fetal weight (EFW), between the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium for the 21st Century (intergrowth-21st) tables, as well as regarding birth weight in fetuses/newborns of diabetic mothers.
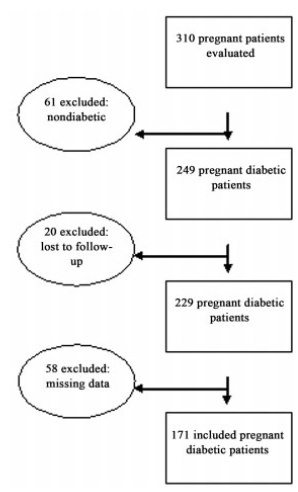
Retrospective study with data from medical records of 171 diabetic pregnant women, single pregnancies, followed between January 2017 and June 2018. Abdominal circumference and EFW data at admission (from 22 weeks) and predelivery (up to 3 weeks) were analyzed. These measures were classified in relation to the 90th percentile. The Kappa coefficient was used to analyze the agreement of these ultrasound variables between the WHO and intergrowth-21st tables, as well as, by reference table, these measurements and birth weight.
The WHO study reported 21.6% large-for-gestational-age (LGA) newborns while the intergrowth-21st reported 32.2%. Both tables had strong concordances in the assessment of initial AC, final AC, and initial EFW (Kappa = 0.66, 0.72 and 0.63, respectively) and almost perfect concordance in relation to final EFW (Kappa = 0.91). Regarding birth weight, the best concordances were found for initial AC (WHO: Kappa = 0.35; intergrowth-21st: Kappa= 0.42) and with the final EFW (WHO: Kappa = 0.33; intergrowth- 21st: Kappa = 0.35).
The initial AC and final EFW were the parameters of best agreement regarding birth weight classification. The WHO and intergrowth-21st tables showed high agreement in the classification of ultrasound measurements in relation to the 90th
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):14-19
Considering the increased frequency of maternal deaths reported from 2001 to 2005 for Indigenous andmestizo women from the Ecuadorian rural area ofOtavalo,where the Kichwa people has lived for centuries, the objective of the present article is to describehow the efforts of the local health community and hospital workers together with a propitious political environment facilitated the implementation of intercultural childbirth,which is a strategy that respects the Andean childbirth worldview.
We evaluated a 3-year follow-up (2014-16) of the maternal mortality and the childbirth features (4,213 deliveries).
Although the Western-style (lying down position) childbirth was adopted by 80.6% of the pregnant women, 19.4% of bothmestizo and Indigenous women adopted the intercultural delivery (squatting and kneeling positions). Both intercultural (42.2%) and Western-style (57.8%) childbirths were similarly adopted by Kichwa women, whereas Western-style childbirth predominated among mestizo women (94.0%). After the implementation of the intercultural strategy in 2008, a dramatic decrease of maternal deaths has been observed until now in both rural and urban Otavalo regions.
This scenario reveals that the intermingling of cultures and respect for childbirth traditions have decreased maternal mortality in this World Health Organization- awarded program.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):9-13
We evaluated risk factors to determine if there were specific risk factors that could predict massive bleeding in nulliparous women with placenta previa.
The participants were classified into two groups. Women with a calculated blood loss ≥ 1,000mL were included in the massive bleeding group. Women without any signs or symptoms related with hypovolemia or with a calculated bleeding volume < 1,000 mL were categorized into the non-massive bleeding group.
There were 28 patients (40.6%) with massive bleeding and 41 cases (59.4%) with non-massive bleeding. The calculated blood loss and number of cases that required red cell transfusions were statistically different between the groups (< 0.005 and 0.002, respectively). There were no statistically significant differences in terms of maternal or fetal factors, placental location, or delivery characteristics between the two groups.
We could not determine the predictive features for massive hemorrhage based on clinical features, delivery features, or placental location.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):46-53
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been considered another tool for use during the pre- and postoperative periods of the management of pelvic-organ prolapse (POP). However, there is little consensus regarding its practical use for POP and the association betweenMRI lines of reference and physical examination.We aimedto evaluate the mid- to long-term results of two surgical techniques for apical prolapse.
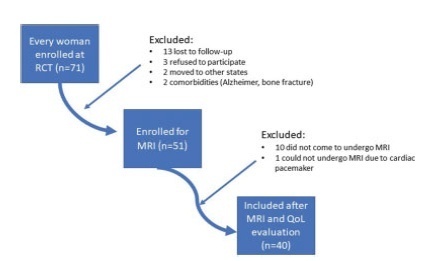
In total, 40 women with apical POP randomized from 2014 to 2016 underwent abdominal sacrocolpopexy (ASC group; n = 20) or bilateral vaginal sacrospinous fixation with an anterior mesh (VSF-AM group; n = 20). A physical examination using the POP Quantification System (POP-Q) for staging (objective cure) and the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire-Vaginal Symptoms (ICIQ-VS: subjective cure), were applied and analyzed before and one year after surgery respectively. All MRI variables (pubococcigeous line [PCL], bladder base [BB], anorectal junction [ARJ], and the estimated levator ani subtended volume [eLASV]) were investigated one year after surgery. Significance was established at p < 0.05.
After a mean 27-month follow-up, according to the MRI criteria, 60% of the women were cured in the VSF-AM group versus 45% in ASC group (p= 0.52). The POP-Q and objective cure rates by MRI were correlated in the anterior vaginal wall (p= 0.007), but no correlationwas foundwith the subjective cure. The eLASVwas largeramongthe patients with surgical failure, and a cutoff of ≥ 33.5mm3 was associated with postoperative failure (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [ROC]: 0.813; p= 0.002).
Both surgeries for prolapse were similar regarding theobjective variables (POP-Q measurements and MRI cure rates). Larger eLASV areas were associated with surgical failure.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):41-45
The aim of the present study was to analyze relapse rates and patterns in patients with endometrial cancer with the aim of evaluating the effectiveness of current follow-up procedures in terms of patient survival, as well as the convenience of modifying the surveillance strategy.
Retrospective descriptive study including all patients diagnosed with endometrial cancer relapse at the Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics of the Complejo Hospitalario Insular-Materno Infantil de Canarias, between 2005 and 2014.
Recurrence was observed in 81 patients (10.04% of the sample); 66.7% of them suffered relapse within 2 years and 80.2% within 3 years after the termination of the primary treatment; 41.9% showed distant metastases while the rest corresponded to local-regional (40.7%) or ganglionar (17.4%) relapse; 42% of these were symptomatic; 14 patients showed more than 1 site of relapse. Relapse was detected mainly through symptoms and physical examination findings (54.3%), followed by elevated serummarker levels (29.6%), computed tomography (CT) images (9.9%) and abnormal vaginal cytology findings (6.2%). No differences in global survival were found between patients with symptomatic or asymptomatic relapse.
Taking into account that the recurrence rate of endometrial cancer is low, that relapse occurs mainly within the first 3 years post-treatment and that symptom evaluation and physical examination are the most effective follow-up methods, we postulate that a modification of the current model of hospital follow-up should be considered.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):158-164
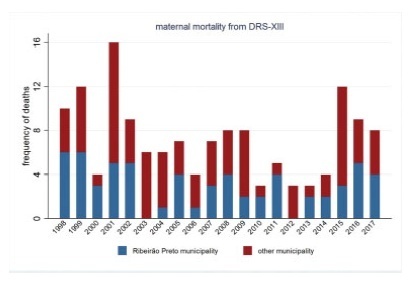
To describe the evolution of maternal mortality right after the establishment of maternal death committees in the region of the city of Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil.
The present study describes the spatial and temporal distribution of maternal mortality frequencies and rates, using data from the state of São Paulo, the municipality of Ribeirão Preto, and its Regional Health Department (DRS-XIII) from 1998 to 2017. The present ecological study considered the maternal mortality and live birth frequencies made available by the Computer Science Department of the Brazilian Unified Health System (Departamento de Informática do Sistema Único de Saúde, DATASUS, in the Portuguese acronym)/Ministry of Health, which were grouped by year and political-administrative division (the state of São Paulo, the DRS-XIII, and the city of Ribeirão Preto). The maternal mortality rate (MMR) was calculated and presented through descriptive measures, graphs, and cartograms.
The overall MMR observed for the city of Ribeirão Preto was of 39.1; for the DRS-XIII, it was of of 40.4; and for the state of São Paulo, it was of 43.8 for every 100 thousand live birhts. During this period, the MMR for the city of Ribeirão Preto ranged from 0% to 80% of the total maternal mortalities, and from 40.7% to 47.2% of live births in the DRS-XIII. The city of Ribeirao Preto had an MMR of 76.5 in 1998and 1999, which decreased progressively to 12.1 until the years of 2012 and 2013, and increased to 54.3 for every 100 thousand live births over the past 4 years. The state of São Paulo State had an MMR of 54.0 in 1998-1999, which varied throughout the study period, with values pregnancy of 48.0 in 2008-2009, and 54.1 for every 100 thousand live births in 2016-2017. Several times before 2015, the city of Ribeirão Preto and the DRS-XIII reached the Millennium Goals. Recently, however, the MMR increased, which can be explained by the improvement in the surveillance of maternal mortality.
The present study describes a sharp decline in maternal death in the region of Ribeirão Preto by the end of 2012-2013, and a subsequent and distressing increase in recent years that needs to be fully faced.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(2):119-125
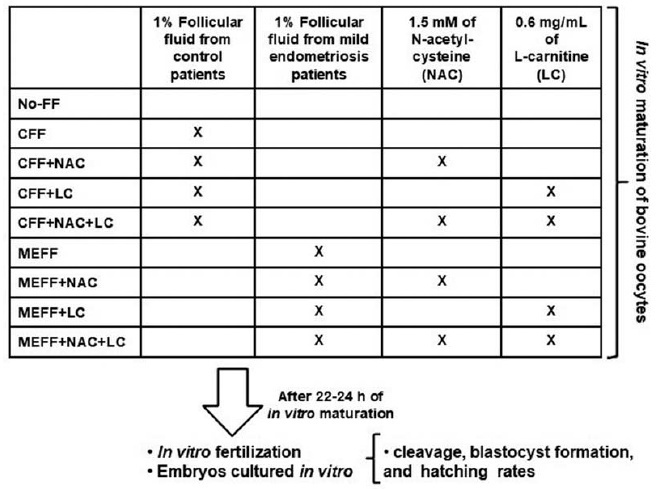
To investigate whether follicular fluid (FF) from infertile women with mild endometriosis (ME) alters in vitro bovine embryo development, and whether the antioxidants N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) and/or L-carnitine (LC) could prevent such damages.
Follicular fluid was obtained from infertile women (11 with ME and 11 control). Bovine oocytes were matured in vitro divided in: No-FF, with 1% of FF from control women (CFF) or ME women (MEFF); with 1.5mM NAC (CFF + NAC, MEFF + NAC), with 0.6mg/mL LC (CFF + LC, MEFF + LC), or both antioxidants (CFF + NAC + LC, MEFF + NAC + LC). After in vitro fertilization, in vitro embryo culture was performed for 9 days.
A total of 883 presumptive zygotes were cultured in vitro. No differences were observed in cleavage rate (p = 0.5376) and blastocyst formation rate (p = 0.4249). However, the MEFF group (12.5%) had lower hatching rate than the No-FF (42.1%, p = 0.029) and CFF (42.9%, p = 0.036) groups. Addition of antioxidants in the group with CFF did not alter hatching rate (p ≥ 0.56), and in groups with MEFF, just NAC increased the hatching rate [(MEFF: 12.5% versus MEFF + NAC: 44.4% (p = 0.02); vs MEFF + LC: 18.8% (p = 0.79); versus MEFF + NAC + LC: 30.8% (p = 0.22)].
Therefore, FF from infertile women with ME added to medium of in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes impairs hatching rate, and NAC prevented these damages, suggesting involvement of oxidative stress in worst of oocyte and embryo quality of women with ME.