Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):162-168
To assess ovarian reserve (OVR) by means of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), and antral follicle count (AFC) measurement in eumenorrheic women with breast cancer, exposed to gonadotoxic chemotherapy.
Fifty-two women (35.3 ± 3.8 years old) with breast cancer and undergoing cyclophosphamide-containing chemotherapy were enrolled. The assessment was performed before chemotherapy (T1) and after 2 (T2) and 6 months (T3).
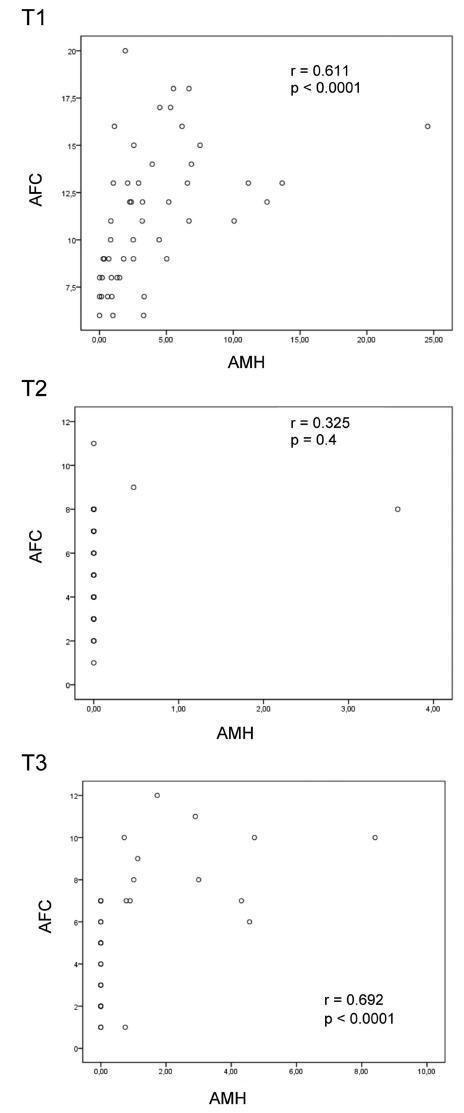
Six months after chemotherapy, the prevalence of regular cycles was 60%. Anti-Müllerian hormone decreased down to undetectable levels at T2 and T3 (T1: 2.53 [1.00–5.31]; T2 < 0.08; T3: < 0.08 [< 0.08–1.07] ng/mL), (p< 0.0001). Antral follicle count was 11 [8.0–13.5] follicles at T1 and lower at T2 (5.50 [3.75–8.0] and T3 (5.0 [2.5–7.0]) (p< 0.0001). In patients who remained with regular cycles during chemotherapy or resumed normal menses, FSH and estradiol levels remained unchanged.
Anti-Müllerian hormone and AFC are useful as markers of OVR decline in women exposed to chemotherapy. Follicle-stimulating hormone is only adequate in women who become amenorrheic.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):155-161
To evaluate whether the presence of maternal blood pressure reduces the risks of morbidity, perinatal mortality and morbidity at 24 months of age in very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) compared with a control group.
A retrospective, observational, case-control study. Total 49 VLBWIs were allocated to the study group, called the maternal arterial hypertension group (AHG), and matched with 44 in the control group (CG). The infants were assessed during hospitalization and at 12 and 24 months corrected age at a specialized clinic. For the assessment of growth, the World Health Organization (WHO) Anthro software (Geneva, 2006) was used, and for the psychomotor assessment, the Denver II test was used.
In relation to the antenatal variables, the infants of the AHG had more centralized circulation assessed by Doppler, received more corticosteroids and magnesium sulfate, and were born by cesarean section more frequently. In terms of the postnatal and in-hospital outcomes, the AHG had a higher gestational age at birth (30.7 versus 29.6 weeks) and a lower frequency of 5-minute Apgar scores of less than 7 (26.5% versus 52.3%). The CG had a higher rate of pulmonary dysplasia (30.2% versus 8.3%). There were no differences in terms of hospital mortality, complications, somatic growth and functional problems at 24 months of corrected age.
The presence of maternal hypertension, especially preeclampsia, was not a protective factor against morbidity, mortality and evolution in VLBWIs aged up to 24 months. Therefore, the clinical practice should be focused on prolonging the pregnancy for as long as possible in these conditions as well.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):149-154
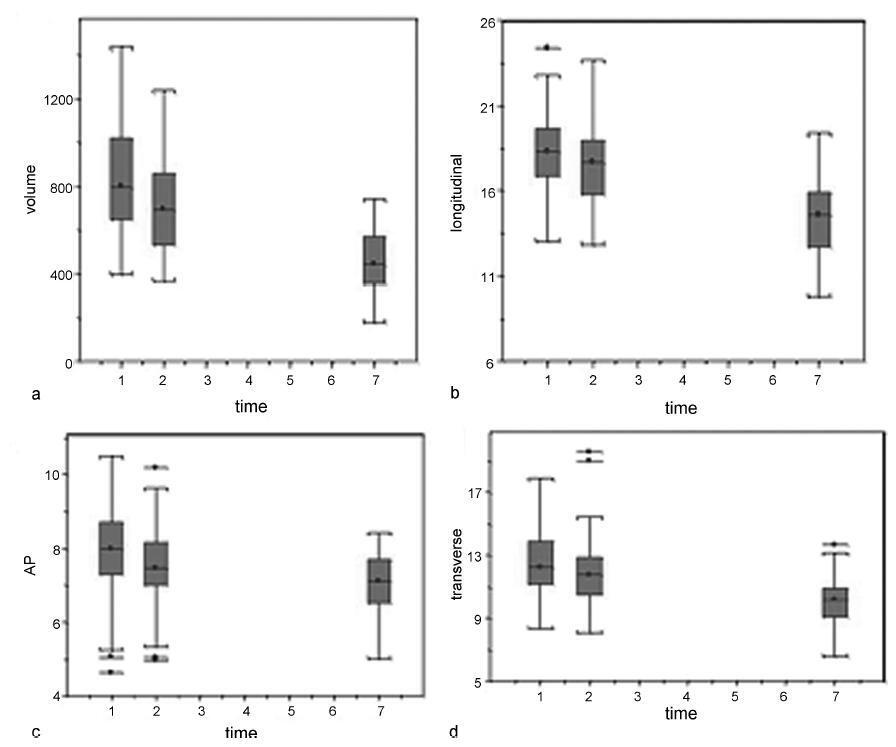
Our aim was to describe the changes observed by ultrasonography in uterine dimensions during the early puerperium among women who experienced an uncomplicated puerperium. Additionally, the influence of parity, mode of delivery, breastfeeding and birth weight on uterine involution was evaluated.
Ninety-one patients underwent an ultrasound examination on days 1 (D1), 2 (D2) and 7 (D7) of the postpartum period. The longitudinal, anteroposterior and transverse uterine diameters were measured, and the uterine volume was calculated by the formula: longitudinal diameter (LD) X anteroposterior diameter (APD) X transverse diameter (TD) X 0.45. The thickness and length of the uterine cavity were also measured.
The uterine volume and the LD, APD and TD decreased by 44.8%, 20.9%, 11.8% and 20.0% respectively. The uterine cavity thickness was reduced by 23%, and the length of the cavity was reduced by 27.2% on D7. Uterine involution was correlated inversely with parity when the day of the postpartum period was not taken into account (p= 0.01). However, when the uterine involution was correlated to parity separately, with D1, D2 or D3, no correlations were found. A significant difference occurred at D2, when it was found that the uterus had a smaller volume following cesarean section compared with vaginal delivery (p= 0.04). The high birth weight and breastfeeding were significantly related to uterine involution (p ≤ 0.01 and p= 0.04).
The sonographic evaluation of the uterus in the early puerperium should consider birth weight, breastfeeding and parity, as well as the delivery route on D2, to identify abnormalities related to uterine involution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):94-101
Anemia is a very frequent event among pregnant women. There are evidences of differences in the incidence of dental caries between pregnant and nonpregnant women, but the relationship between salivary iron (Fe) and serummarkers of anemia and caries development has not been investigated.
To evaluate the correlation between salivary (Fe) and serum iron (Fe, ferritin and hemoglobin) parameters in pregnant women with the development of dental caries.
A prospective cohort was conducted with 59 women. The outcome of interest was represented by new dental caries lesions during pregnancy, using the Nyvad criteria. Pregnant women were evaluated at three clinical times: up to the 16th week of gestational age (GA) (T1), in the last trimester of pregnancy (T2), and postpartum (T3), at the Mother and Child Unit ofUniversityHospital of the Universidade Federal doMaranhão.A stimulated saliva sample was collected for biochemical analysis of salivary Fe, and a blood sample was collected early in the morning. The correlation between salivary and serum Fe was evaluated through the Pearson correlation test. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Kruskal-Wallis were used to compare the means of anemia parameters at different times. The Student's t and Mann-Whitney tests were used to compare the anemia parameters between the groups of pregnant women (with and without new caries lesions).
SerumFe concentrationswere higher in the first trimester of pregnancy and lower after delivery (p = 0.036). It was also observed that the ferritin concentrations were higher in the first trimester and lower at the end of gestation (p = 0.011). Therewas no association between the expositions of salivary iron and anemia, and the development of dental caries. There was a positive correlation between serum Fe in T1 and salivary Fe in T2 (p < 0.05).
The serummarkers of anemiaweremore prevalent in the last trimester of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):123-127
Expectant follow-up for biopsy-proven cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 1 is the current recommendation for the management of this lesion. Nevertheless, the performance of the biopsy guided by colposcopy might not be optimal. Therefore, this study aimed to calculate the rate of underdiagnoses of more severe lesions in women with CIN 1 diagnosis and to evaluate whether age, lesion extent and biopsy site are factors associated with diagnostic failure.
Eighty women with a diagnosis of CIN 1 obtained by colposcopy-guided biopsy were selected for this study. These women were herein submitted to large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ). The prevalence of lesions more severe than CIN 1 was calculated, and the histological diagnoses of the LLETZ specimens were grouped into two categories: "CIN 1 or less" and "CIN 2 or worse."
The prevalence of lesions diagnosed as CIN 2 or worse in the LLETZ specimens was of 19% (15/80). Three women revealed CIN 3, and 1 woman revealed a sclerosing adenocarcinoma stage I-a, a rare type of malignant neoplasia of low proliferation, which was not detected by either colposcopy or previous biopsy. The underdiagnosis of CIN 2 was not associated with the women's age, lesion extension and biopsy site.
The standard methods used for the diagnosis of CIN 1 may underestimate the severity of the true lesion and, therefore, women undergoing expectant management must have an adequate follow-up.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):115-122
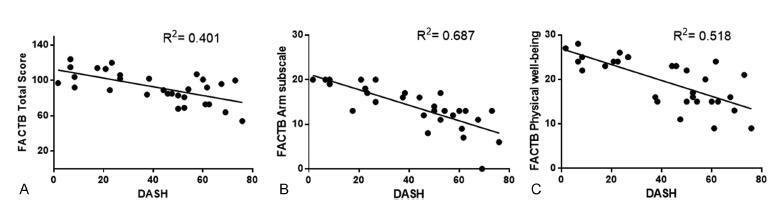
To evaluate the correlation between upper limb functionality and quality of life in women with five-year survival following breast cancer surgical treatment. The secondary objective was to evaluate the function of the ipsilateral upper limb and the quality of life in relation to the type of surgery and the presence of pain.
The Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH), and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy - Breast plus Arm Morbidity (FACTB + 4) questionnaires were used to evaluate upper limb function and quality of life respectively. Data distribution was verified by the Shapiro-Wilk test. Pearson's correlation coefficient was used for the parametric variables, and Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was used for the distribution of non-parametric variables. The statistical significance was set at 5% (p < 0.05).
The study included 30 patients, with a mean age of 51.23 (±8.72) years. The most common complications were: pain (50%), adherence (33.3%), and nerve lesion (20.0%). There was a moderate negative correlation between the instruments DASH and FACTB + 4 (total score), r = -0.634, and a strong negative correlation between the DASH and the FACTB + 4 armsubscale, r = -0.829. The scores of both questionnaires showed significant difference on the manifestation of pain. However, there was no significant difference found when comparing the scores considering the type of surgery performed.
Five years after surgery, the patients showed regular functionality levels on the ipsilateral upper limb and decreased quality of life, especially in the group manifesting pain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):110-114
To describe the frequencies of chromosomal abnormalities found in abortion material, and to observe its correlation to maternal age.
A retrospective study was conducted based on data obtained from the databank of a medical genetics laboratory in Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. A total of 884 results from products of conception analysis were included, 204 of which were analyzed by cytogenetics, and 680bymolecular biology basedon quantitative fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (QF-PCR). The frequency of individual chromosomal aberrations and the relationship between the presence of anomalies and maternal age were also evaluated.
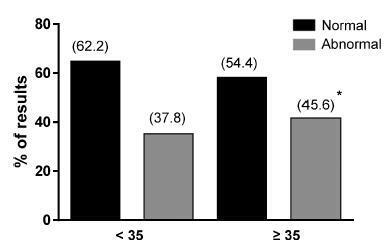
The conventional cytogenetics technique was able to detect 52% of normal and 48% of abnormal results in the analyzed material. Quantitative fluorescence polymerase chain reaction revealed 60% of normal and 40% of abnormal results from the samples evaluated by this method. The presence of trisomy 15 was detected only by cytogenetics, as it was not included in the QF-PCR routine investigation in the laboratory. A significant increase in abnormal results was observed among women aged 35 years or older compared with younger women (p = 0.02).
Chromosomal aberrations are still a major cause of spontaneous abortion, and the conventional cytogenetics technique is efficient for miscarriage material analysis, but molecular methods such as QF-PCR are adequate complementary strategies to detect the major chromosomal anomalies, leading to technical reports with reliable results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):102-109
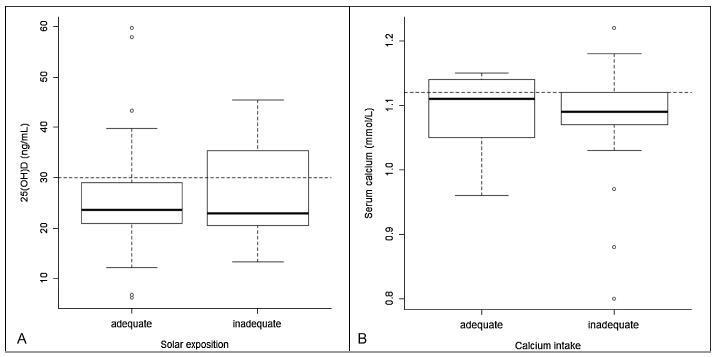
To assess the prevalence of hypovitaminosis D, altered arterial blood pressure, and serum levels of glucose and lipids in community-dwelling women in the city of Ribeirão Preto, in the southeast of Brazil.
Thiswas a cross-sectional studyof women aged40-70years old.Calciumintake and level of sun exposure were assessed by means of a questionnaire. A blood sample was used to determine glucose, lipid profile and 25-hydroxyvitaminD(25[OH]D) concentration.
Ninety-one women were enrolled (age = 54.2 ± 7.1 years). Themean serum 25(OH)D concentration was 25.7 ± 8.9 ng/mL. A total of 24 (26.4%) women had 25 (OH)D levels < 20 ng/mL. Seventy women (76.9%) had 25(OH)D levels < 30 ng/mL. Seventy-five women (90.4%) had inadequate calcium intake, and 61 women (67%) had appropriate sun exposure, 49 of whom (80.3%) had serum 25(OH)D levels < 30 ng/mL.
This study indicates that even in community-dwelling women, living in a city with high sun exposure, serum levels of 25(OH)D > 30 ng/ml are hardly reached. Thus, it is probable that other intrinsic factors besides sun exposure may regulate the levels of vitamin D.