Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):653-658
To identify the prevalence of pyelonephritis during pregnancy and to analyze the clinical and laboratorial aspects, perinatal results and complications.
A transversal study of 203 pregnant women who had pyelonephritis during pregnancy and whose labor took place between 2010 and 2016 at a hospital in the state of Santa Catarina, Brazil. The analysis was based on medical records as well as on the hospital’s database. Clinical and laboratory conditions, antibiotics, bacterial resistance, perinatal outcomes and complications were all taken into account. The data was compared using the Mann-Whitney test and the Chi-square test.
A prevalence of 1.97% with pyelonephritis was evidenced, with most patients having it during the second trimester of gestation. The bacteriamost commonly found in the urine cultures was Escherichia coli, in 76.6% of cases, followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae (8.7%). Ceftriaxone had the lowest bacterial resistance (only 3.5% of the cases). On the other hand, ampicillin and cephalothin presented higher bacterial resistance, 52% and 36.2%, respectively. The risk of very premature delivery was more than 50% higher in patients with pyelonephritis.
Ampicillin and first-generation cephalosporins are associated with a higher bacterial resistance while ceftriaxone proved to have a high efficacy for the treatment of pyelonephritis due to low bacterial resistance. Patients with pyelonephritis showed a higher risk for very premature delivery (< 32 weeks). In this casuistry, there were no others significant differences in the overall perinatal outcomes when compared with the routine service series.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):647-652
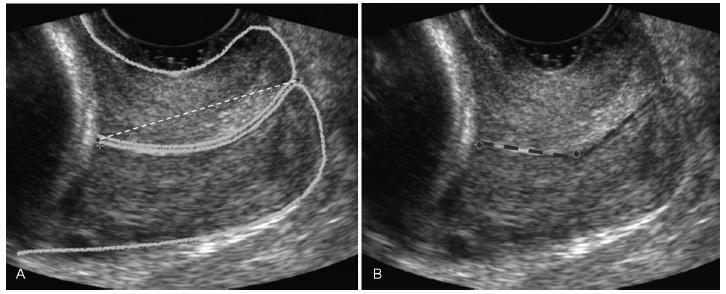
To determine cervical biometry in pregnant women between 18 and 24 weeks of gestation and the ideal mode of measurement of cervical length in cases of curved and straight cervical morphology.
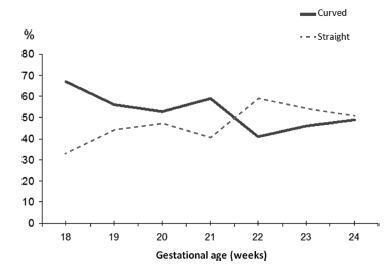
The uterine cervices of 752 low-risk pregnant women were assessed using transvaginal ultrasound in a prospective cross-sectional study. In women with straight uterine cervices, cervical biometry was performed in a continuous manner. In women with curved uterine cervices, the biometry was performed using both the continuous and segmented techniques (in segments joining the cervical os). Polynomial regression models were created to assess the correlation between the cervical length and gestational age. The paired Student t-test was used to comparemeasuring techniques.
The cervical biometry results did not vary significantly with the gestational age and were best represented by linear regression (R2 = 0.0075 with the continuous technique, and R2 = 0.0017 with the segmented technique). Up to the 21st week of gestation, there was a predominance of curved uterine cervix morphology (58.9%), whereas the straight morphology predominated after this gestational age (54.2%). There was a significant difference between the continuous and the segmented measuring methods in all the assessed gestational ages (p < 0.001).
Cervical biometry in pregnant women between 18 and 24 weeks was represented by a linear regression, independently of the measuring mode. The ideal measuring technique was the transvaginal ultrasound performed at a gestational age 21 weeks.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):670-675
To describe the experience of a distance education course on sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth for residents.
This prospective educational intervention study was conducted by investigators from the Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil, between April and September 2014. The participants were 219 physicians (residents from the 1st to the 6th years). The duration of the course was of 24 hours (10 video lectures and online chats). At baseline, the participants answered questions about their training, attitude and experience regarding sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth; before and after the course, they answered questions to assess their knowledge about the topic; at the end of the course, they answered questions on the quality of the course. The Student t-test was used to compare the before and after scores of the knowledge tests; values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
A total of 143 residents concluded the course; most were in their 1st (27.2%) or 3rd (29.4%) years of residency. There was a significant increase in themean scores of the questionnaires that assessed the knowledge of the topic: 4.4 (1.6) versus 6.0 (1.3; maximum score: 10), before and after the course respectively (p < 0.0001). Most of the participants (74.1%) declared that the quality of the course as a whole reached their expectations, and 81.1% would recommend the course to a friend.
The online Sexology course for Obstetrics and Gynecology residents increased their knowledge about the sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth, and fulfilled the participants’ expectations. The experience described heremay serve as a model for other sexuality courses targeting similar audiences.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):663-669
To examine the role of the panoramic mandibular radiograph in the diagnosis of low bone mineral density (BMD) in postmenopausal women.
A cross-sectional study including volunteer women aged over 40 years in amenorrhea due to ovarian failure for at least 12 months, who were cared for at the climacteric outpatient clinic of a university hospital in the city of Cuiabá, in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. The panoramic radiographs were evaluated using a specific software. Two aspects were analyzed in the mandibular panoramic radiograph: a qualitative aspect regarding the shape of the mandibular cortical bone, and a quantitative aspect regarding thewidth of themandibular cortical bone. Themorphology of themandibular cortical bone in the digital panoramic radiograph was determined bilaterally by the observation of the bone structure between the mental foramen and the base of the jaw. The mandibular cortical bonewas categorized into three groups. Themental index (MI)was used to evaluate the thickness of themandibular cortical bone through a perpendicular line drawn fromthe base of the mandible at the height of the center of the mental foramen, with another line drawn tangent to the inferior border of the mandible, and a third line parallel to the line at the superior border of themandible. The MI data are expressed in millimeters, with a normal value of 3.0 mm. The densities of the lumbar spine and femur, expressed in g/cm2, were categorized as normal, osteopenia or osteoporosis.
The agreement index between the MI and the BMD of the lumbar spine was good (Kappa = 0.718), but the same index between the MI and the BMD of the femoral neck was poor (Kappa = 0.443). An excellent agreement occurred when the mandibular cortical index (MCI) was compared with the BMD of the lumbar spine (Kappa = 0.912). The agreement between MCI and the BMD in the femur was moderated (Kappa = 0.579).
The radiomorphometric indices evaluated in the mandibular panoramic radiograph are capable of identifying postmenopausal women with low mineral density in the mandible, and the results can be used to refer these women to appropriate medical investigation and/or treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):614-621
The present study aimed to evaluate the impact of vitrification on the viability of follicles using a three-dimensional (3D) in vitro culture.
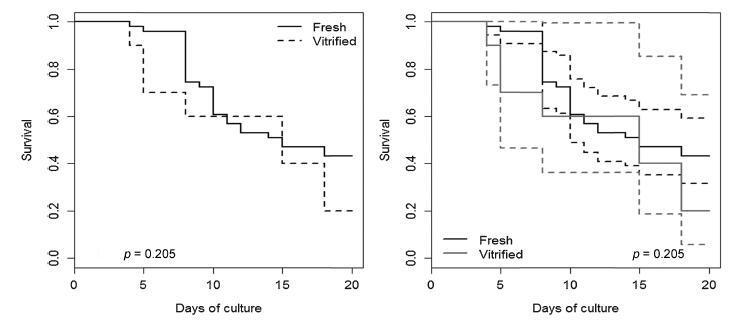
Bovine ovarian tissue samples (n = 5) obtained from slaughterhouses were utilized. The cortex was cut into small fragments of 2 x 3 x 0.5 mm using a tissue slicer. From these fragments, secondary follicles were first isolated by mechanical and enzymatic methods, then encapsulated in alginate gel and individually cultured for 20 days. Additional fragments of the same ovarian tissue were vitrified in a solution containing 25% glycerol and 25% ethylene glycol. After warming, the follicles underwent the same follicular isolation process that was performed for the fresh follicles.
A total of 61 follicles were isolated, 51 from fresh ovarian tissue, and 10 from vitrified tissue. After the culture, the vitrified and fresh follicles showed 20% and 43.1% survival rates respectively (p = 0.290),with no significant differences. At the end of the culture, therewere no significant differences in follicular diameter between the vitrified (422.93 ± 85.05 μm) and fresh (412.99 ± 102.55 μm) groups (p = 0.725). Fresh follicles showed higher mean rate of antrum formation when compared with vitrified follicles (47.1% and 20.0% respectively), but without significant difference (p = 0.167).
The follicles were able to develop, grow and form antrum in the 3D system after vitrification, despite the lower results obtained with the fresh tissue.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):608-613
The aim of this study was to evaluate the health aspects of Brazilian women older than 65 years of age.
This was a retrospective study that included 1,001 Brazilian women cared for in the gynecological geriatric outpatient office of our institution. We report a crosssectional analysis of female adults aged over 65 years, including data on demographics, clinical symptoms such as vasomotor symptoms, associated morbidities, physical examination and sexual intercourse. We used the chi-squared test to assess the data.
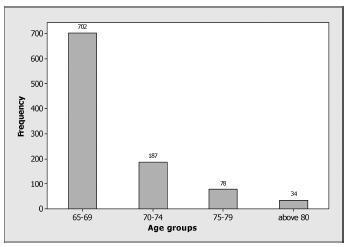
The age of the patients on their first clinic visit ranged from65 to 98 years, with a mean age of 68.56 ± 4.47 years; their mean age at the time of natural menopause was 48.76 ± 5.07 years. The most frequent clinical symptoms reported during the analyzed period were hot flashes (n = 188), followed by arthropathy, asthenia, and dry vagina. The most frequent associated morbidities after 65 years of age were systemic arterial hypertension, gastrointestinal disturbance, diabetes mellitus, and depression, among others. The assessment of the bodymass index (BMI) found decreases inBMIwith increased age. At the time of the visit, 78 patients reported sexual intercourse. The majority of women reporting sexual intercourse (89.75%, n = 70) were between 65 and 69 years of age, 8.97% (n = 7) were between 70 and 74 years of age, and only 1.28% (n = 1) of those were aged older than 75 years.
Our findings suggested that vasomotor symptoms can persist after 65 years of age. There was a significant decrease in sexual intercourse with increased age. The cardiovascular disturbances in our study are health concerns in these women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):602-607
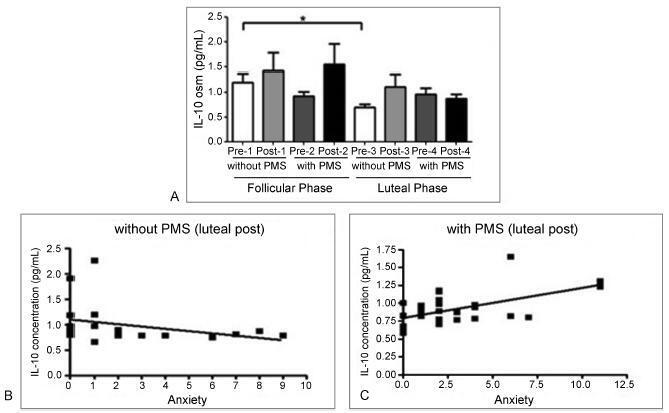
To investigate the level of anxiety and its relationship with interleukin (IL)- 10 (anti inflammatory cytokine that modulates mood swings) in a group of female soccer players.
Fifty-two eumenorrheic soccer players were evaluated (age 19.8 ± 4.7 years). The presence of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and phases of the menstrual cycle were determined by a daily symptomreport (DSR) kept for 3 consecutivemonths. The concentration of cytokine IL-10 was determined from urine samples collected at four moments: at the follicular and luteal phases of the menstrual cycle, and before (pre) and after (post) the simulated game, and it was quantified by flow cytometry (Luminex xMAP - EMDMillipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The level of anxietywas determined through the BAI anxiety questionnaire answered by all athletes at the same time of the urine collection. The Student t-test, analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Pearson correlation with significance level at 5% were used for data analysis.
We showed that the prevalence of PMS among female soccer players is similar to that reported in the literature. In addition,we showed that the group withPMS has a higher level of anxiety compared with group without PMS (p = 0.002). Interleukin-10 analysis in players without PMS revealed that there was a significant decrease in the level of this cytokine before the game during the luteal phase when compared with the follicular phase (p < 0.05). The correlation analysis between IL-10 and anxiety showed a negative correlation post-game in the luteal phase in the group without PMS (p = 0.02; r = -0.50) and a positive correlation post-game in the luteal phase in PMS group (p = 0.04; r = 0.36).
Our results suggest that IL-10 may contribute to reduce anxiety in the group without PMS. This could be attributed to the fact that no IL-10 variation was observed in the group with PMS, which presented higher anxiety symptoms when compared with the group without PMS.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):596-601
To investigate the clinical and sonographic parameters associated with adverse fetal outcomes in patients with congenital parvovirus B19 infection managed by intrauterine transfusion.
This was a single-center retrospective study conducted from January 2005 to December 2016 that assessed patients with singleton pregnancies with fetal parvovirus infection confirmed by a polymerase chain reaction of the amniotic fluid or fetal blood samples who underwent at least one intrauterine transfusion. The maternal characteristics, sonographic findings and parameters related to intrauterine transfusion were compared between the two groups (recovery/non-recovery), who were categorized based on fetal response after in-utero transfusions. Progression to fetal death or delivery without fetal recovery after the transfusions was considered nonrecovery and categorized as an adverse outcome.
The final analysis included ten singleton pregnancies: seven of which were categorized into the recovery group and three of which into the non-recovery group. The baseline characteristics were similar between the groups. All fetuses were hydropic at the time of diagnosis. No significant differences related to sonographic or intrauterine transfusion parameters were identified between the groups; however, the nonrecovery group tended to have an increased number of sonographic markers and lower fetal hemoglobin and platelet levels before the transfusion.
We were unable to firmly establish the clinical or sonographic parameters associated with adverse fetal outcomes in patients with parvovirus infection managed with intrauterine transfusions; however, edema, placental thickening and oligohydramnios may indicate greater fetal compromise and, subsequently, adverse outcomes. However, further studies are necessary, mainly due to the small number of cases analyzed in the present study.