Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):163-167
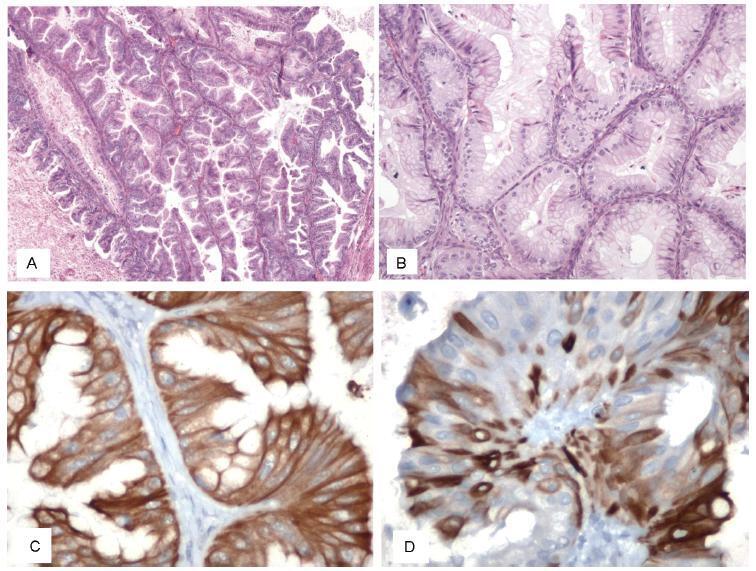
Melanomas of the female genital tract may occur in the vulva, the vagina, the ovary or the cervix.Pregnancy has been considered an aggravating factor in the evolution and prognosis of melanoma. A 35-year-old female presented with vaginal bleeding 2 months after a term cesarean delivery. An endovaginal ultrasound revealed a lesion in the uterine cervix. The pathological report revealed a small round-cell neoplasm, and the immunohistochemistry confirmed the diagnosis of malignant melanoma. A positron emission tomography revealed an expansive hypermetabolic lesion centered on the cervix, and hypermetabolic lesions in the liver and right kidney. Non-surgical treatment was provided, with biochemotherapy followed by ipilimumab and nivolumab. The patient died one year later. Postpartum vaginal bleeding, even if late-onset, should be investigated, as it may be a pregnancy-associated malignant melanoma, which has a poor prognosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):92-95
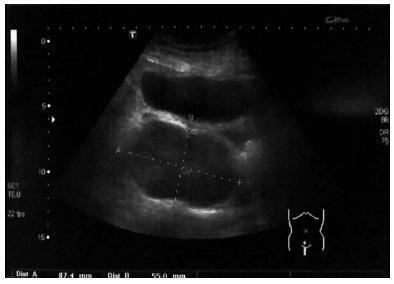
Nowadays, postpartum hemorrhage is the major cause of maternal mortality and morbidity worldwide. Uterine atony is its main cause; thus, prophylactic measures, as well as medical and surgical fast approaches, have been developed to manage it. The uterine compression sutures are a possible treatment that preserves the uterus and, consequently, the fertility potential. Bearing that in mind, we report two cases of postpartum hemorrhage after caesarean section, successfully treated with a new modification of Pereira suture - longitudinal and transverse uterine sutures were applied after no response was registered to the first-line therapies. Both women recovered, and the postpartum evaluation revealed a normal uterus with an adequate blood supply, suggesting potential fertility, as described in the literature regarding this kind of therapeutic approach.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):47-52
Vaginal cancer is a rare entity. The evidence on its management resides mostly in clinical cases or small case series. Of the histological types, the most frequent is the squamous cell carcinoma, followed by adenocarcinoma. But what to do when identifying an even more infrequent sarcoma in a premenopausal woman? In this study, we describe the case of a 53-year-old woman presenting with metrorrhagia for two months, who was evaluated after an intense episode. A necrotic and ulcerative vaginal swelling was documented and then submitted to biopsy, which revealed a vaginal sarcoma. The patient was referred to radiation therapy with 50 Gy (aiming to control the symptoms and to cause tumor reduction for posterior pelvic exenteration with intraoperative radiotherapy) and developed an extra-pelvic metastization at the end of the treatment, which caused a fast negative outcome. Despite the initial poor prognosis, a chemo-irradiation or primary surgery regimen might have achieved (although with greater side effects) a better survival. This case-report entails a discussion about the strategies to manage vaginal sarcoma in advanced stage and in premenopausal women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):640-644
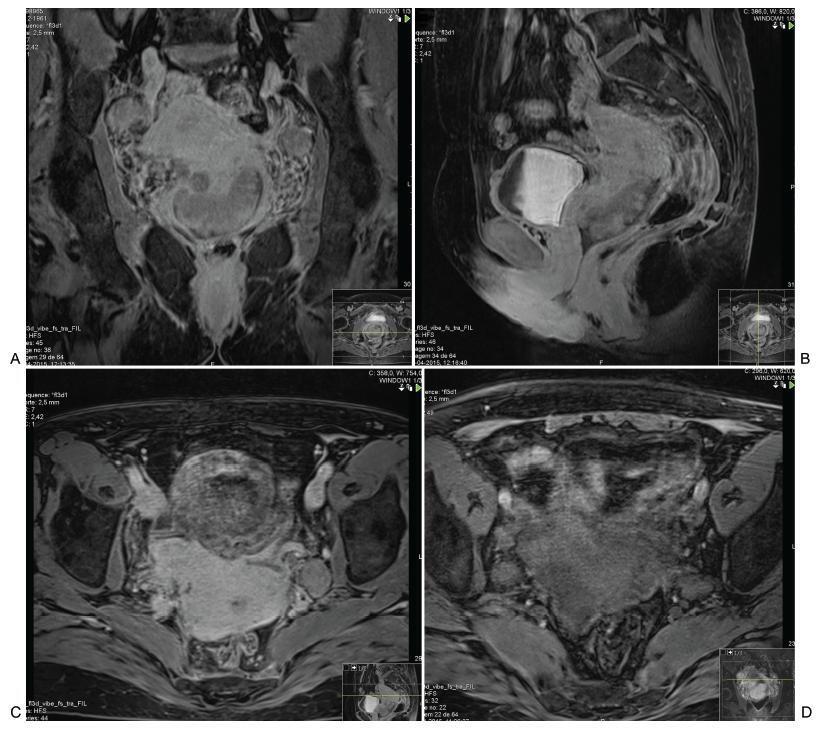
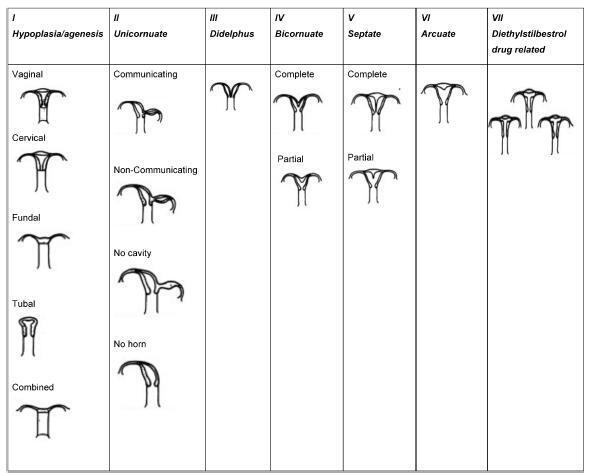
Approximately 1 in every 76,000 pregnancies develops within a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn.Müllerian uterus anomalies are often asymptomatic, thus, the diagnosis is a challenge, and it is usually made during the gestation or due to its complications, such as uterine rupture, pregnancy-induced hypertension, antepartum, postpartum bleeding and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). In order to avoid unnecessary cesarean sections and the risks they involve, the physicians should consider the several approaches and for how long it is feasible to perform labor induction in suspected cases of pregnancy in a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn, despite the rarity of the anomaly. This report describes a case of a unicornuate uterus in which a pregnancy developed in the non-communicating rudimentary horn and the consequences of the delayed diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):576-582
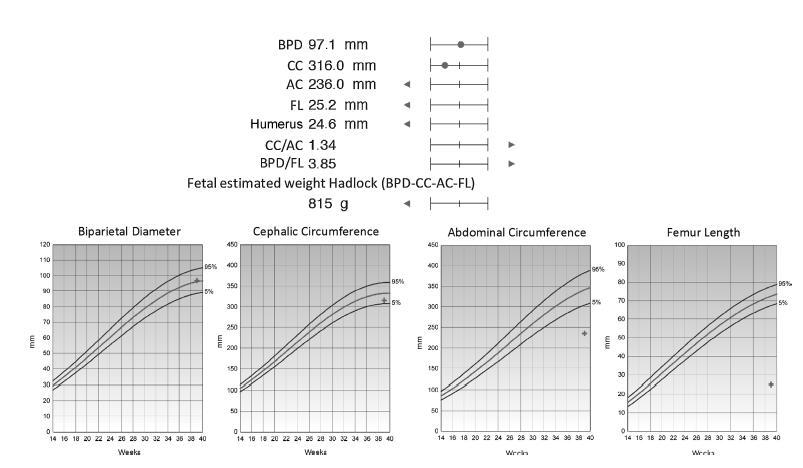
The clinical management and decision-making in pregnancies in which there is suspicion of lethal fetal malformations during the prenatal period, such as lethal skeletal dysplasia (SD), demand a multidisciplinary approach coordinated by an experienced physician. Based on the presentation of a case of osteogenesis imperfecta type IIA, we offer and discuss recommendations with the intention of organizing clinical and laboratory investigations aiming toward the clinical management, prognosis, and etiological diagnosis of these malformations, as well as genetic counselling to patients who wish to become pregnant.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):516-520
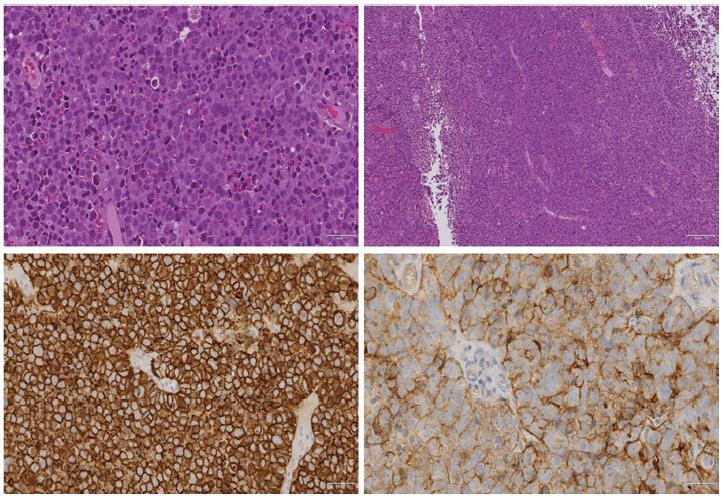
The association between plasmacytomas and multiple myeloma (MM) is well-described, and in about one third of the cases of plasmacytoma the additional study will lead to the diagnosis of MM. The finding of plasmacytomas in the genital tract is extremely rare, with sparse cases described in the literature, and these cases pose a challenge regarding the optimal guidance and treatment. This paper describes a case of uterine extramedullary plasmacytoma in a 79-year-old woman with complaints of postmenopausal abnormal uterine bleeding. The complementary study led to the diagnosis of uterine plasmacytoma and, subsequently, of MM. Despite the unfavorable outcome of this case, we consider pertinent to report it because it constitutes a differential diagnosis to be taken into account in the approach of pelvic masses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):513-515
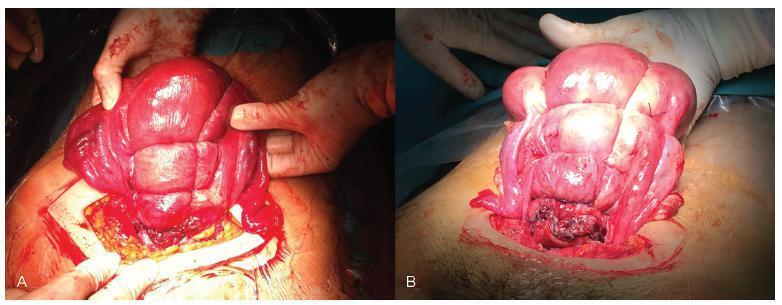
Acute abdomen secondary to epithelial ovarian cancer rupture during pregnancy is a rare event. Our aim is to present how the work of a coordinated multidisciplinary team in a case of ruptured epithelial ovarian cancer during pregnancy is feasible to obtain the best results possible. A 34-year-old woman during the 37th week of her first gestation presented with an acute abdomen. During laparotomy, a ruptured 16.5-cm left ovarian tumor was detected; the tumor was extirpated and sent to pathologic evaluation. In the meantime, a Kerr cesarean section was performed, and a healthy female neonate was born. The tumor was diagnosed as a cystadenocarcinoma; therefore, the family and the combined surgical team (obstetricians and a surgical oncologist) decided to complete a definitive radical ovarian cancer surgery: hysterectomy, right salpingooophorectomy, lymphadenectomy, omentectomy and appendectomy. The patient’s postoperative evolution was uneventful, and she was sent to adjuvant chemotherapy.