Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):450-455
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800003
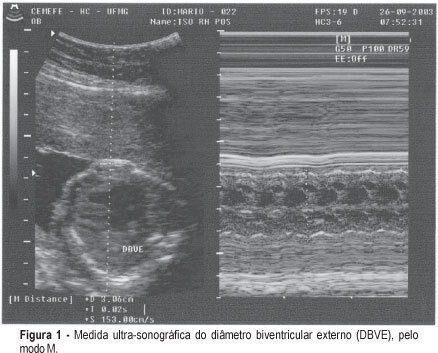
PURPOSE: to test a new, noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. METHODS: the index obtained by the ratio between the ultrasonographic measurement of the biventricular outer dimension (BVOD) and femur length (both in centimeters) was correlated with fetal hemoglobin values in a cross-sectional study. Fifty-nine fetuses of isoimmunized pregnancies selected for invasive treatment and submitted to 130 cordocenteses for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia were included in the study. The cardiofemoral index was obtained immediately before the cordocentesis and the fetal hemoglobin index was obtained from fetal blood samples. Linear regression was carried out to assess the correlation between the index and fetal hemoglobin; ROC curve was applied to determine the most accurate cutoff for the diagnosis of the fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl. RESULTS: BVOD measurement varied from 1.6 to 4.7 cm (average 2.5±1.3cm), and length of the femur, from 3.0 to 6.9 cm (average 4.3±0.9 cm). The cardiofemoral index varied from 0.4 to 1.0 (average 0.6±0.1). A significant inverse correlation between the cardiofemoral index and fetal hemoglobin (R²=0.37 and p<0.0001) was observed. The cutoff of 0.60 was the best to predict a level of fetal hemoglobin below or equal to 10.0g/dl: 80.85% sensitivity, 83.13% specificity, 73.8% positive predictive value, and 88.46% negative predictive value, in the diagnosis of fetuses anemia. CONCLUSION: the cardiofemoral index allows for good accuracy in the prediction of fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. It may thus be applied as a noninvasive method to the diagnosis of this pathology.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):442-449
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800002
PURPOSE: to establish the frequency of acute toxoplasmosis in pregnant women, vertical transmission rate and the perinatal results of the infected fetuses and also to evaluate the relationship between the most used maternal-fetal diagnostic tests for toxoplasmosis during pregnancy and the relationship between age and acute toxoplasmosis infection during pregnancy. METHODS: longitudinal prospective study of 32,512 pregnant women attended by The Pregnancy Protection Program of the State of Mato Grosso do Sul - Brazil, from November 2002 to October 2003. ELISA (IgG and IgM) and IgG avidity test were performed for maternal diagnosis and amniotic fluid PCR for fetal investigation of the infection. The relationship between data was analyzed statistically by the chi2 or two-sided Fisher's exact test in contingency tables. RESULTS: a 0.42% frequency of acute Toxoplasma gondii infection among pregnant population was found, where 92% were previously exposed and 8% were susceptible. Among IgM-positive pregnant women, the age ranged from 14 to 39 years, with a mean of 23±5.9 years. There was no statistically significant relationship between age and maternal acute T. gondii infection (p=0.73). The vertical transmission rate was 3.9%. A statistically significant relationship was shown (p=0.001) between a lower avidity IgG test (<30%) and the presence of fetal infection and a higher IgG avidity test (>60%) and the absence of fetal infection. There was a statistically significant association (p=0.001) between fetal infection (amniotic fluid PCR) and neonatal infection. CONCLUSIONS: maternal acute toxoplasmosis frequency was lower than the Brazilian national parameters, whereas vertical transmission rate did not differ from the rates found in other studies. The IgG avidity test, when associated with gestational age and the examination date, was useful to evaluate the therapeutical options and to consider the risk of vertical transmission when performed before 12 weeks. Positive PCR in amniotic fluid showed a positive relationship with the worst neonatal prognosis, being a specific method in diagnosing intrauterine fetal infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):415-420
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700008
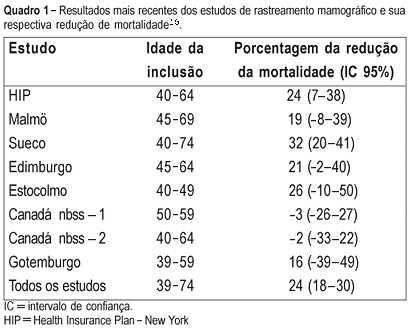
PURPOSE: to evaluate the cost of preventive mammographic screening in climacteric women, as compared to the cost of breast cancer treatment in more advanced stages. METHODS: one thousand and fourteen patients attended at the Climacteric outpatient service of the Gynecology Department, Federal University of São Paulo Paulista School of Medicine, were included in the study and submitted to mammographic test. All mammographic test's were analyzed by the same two physicians and classified according to the BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System American College of Radiology) categories. The detected lesions were submitted to cytological and histological examination. RESULTS: the final diagnostic impression of the 1014 examinations, according to the classification of BI-RADS categories was: 1=261, 2=671, 3=59, 4=22 and 5=1. The invasive procedures were performed through a needle guided by ultrasound or stereotactic examinations: 33 fine-needle aspiration biopsies, 6 core biopsies guided by ultrasound and 20 core biopsies guided by stereotactic examination. Five cancer diagnoses were established. The total cost of this screening based on Brazilian procedure values was R$ 76,593.79 (25,534 dollars). Therefore, the cost of the diagnosis of the five cases of cancer in this screening was R$ 15,318.75 (5,106 dollars) each. However, the average cost per patient screened was R$ 75.53 (25 dollars). CONCLUSIONS: considering that the total treatment cost of only one case of breast cancer in advanced stage including hospital costs, surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and hormonal treatment is similar to the cost of 1,000 mammographic screenings in climacteric women, it may be concluded that the cost of the early cancer diagnosis program is worth it and should be included in the public health program, as a way of lowering the public health expense.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):407-414
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of vulval squamous intraepithelial lesions and associated factors in HIV-infected patients attended at the public health services of Rio de Janeiro city. METHOD: a total of 374 HIV-infected patients were attended at public services in Rio de Janeiro city and submitted to gynecological examination, Pap smear and colposcopic examination of the cervix and vulva. The association of vulval intraepithelial lesion was analyzed according to the results of clinical (age and cervical lesions), laboratorial (CD4 count) and behavioral (number of partners and smoking habit) variables. The study (independent) variables were the epidemiological data, the immunologic status and the results of gynecological propaedeutic. Thus, age, the smoking habit, number of sexual partners, count of T CD4 lymphocites, and cervical intraepithelial lesion were selected. In the beginning, a bivariate analysis was performed, aiming at assessing the association between the presence of vulval intraepithelial lesion (ultimate variable) and the independent variables (age, smoking habits, number of sexual partners, cytology, colposcopy and CD4 count). Thereafter, the results with statistical significance (p<0.05) were submitted to a multiple logistic regression, and the probability ratio with the respective 95% confidence interval was established. RESULTS: the prevalence of vulval intraepithelial lesions was 40%. In the multivariate analysis CD4 count below 500 cells/mm³ OR=2.69 [IC 95%: 1.61-4.52], abnormal colposcopy OR=1.64 [IC 95%: 1.01-2.67] and age under 26 OR=1.98 [IC 95%: 1.18-3.30] were significant. In the vulval and cervical simultaneous lesion subgroup, age under 26 OR=3.30 [IC 95%: 1.65-6.59] and CD4 count below 500 cells/mm³ OR=4.15 [IC 95%: 1.92-8.96], were significant on analysis. CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of vulval squamous intraepithelial lesions in HIV-infected patients is high. Immunodeficiency, presence of cervical intraepithelial lesions and age under 26 were associated with the presence of vulval intraepithelial lesions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):401-406
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700006
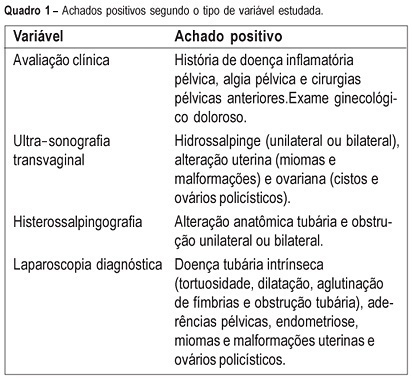
PURPOSE: to evaluate the agreement between noninvasive methods - pelvic pain, transvaginal ultrasound and hysterosalpingography - and the gynecologic endoscopy approach for the diagnosis of tuboperitoneal factors responsible for conjugal infertility. METHODS: this is a cross-sectional study including 149 infertile patients who were submitted to clinical evaluation, transvaginal ultrasound, hysterosalpingography, hysteroscopy, and laparoscopy. In the evaluation of pelvic pain, the following complaints were considered to be abnormal: pelvic pain of the dyspareunia type, dysmenorrhea or acyclic pain, and pain upon mobilization of the cervix and palpation of the adnexa. Ultrasonographic examination was considered to be altered when adnexal or uterine morphological changes (hydrosalpinx, myomas or uterine malformations) were detected. Hysterosalpingography was considered to be abnormal in the presence of anatomical tubal changes and unilateral or bilateral obstruction. The agreement between noninvasive methods and endoscopy was evaluated by kappa statistics. RESULTS: the agreements between pelvic pain, transvaginal ultrasound, and hysterosalpingography and the endoscopic approach were 46.3% (kappa=0.092; CI 95%: -0.043 to 0.228), 24% (kappa=-0.052; CI 95%: -0.148 to 0.043), and 46% (kappa=0.092; CI 95%: -0.043 to 0.228), respectively. When at least one alteration detected by noninvasive methods was considered, the agreement with endoscopic approach was 63% (kappa=-0.014; CI 95%: -0.227 to 0.199). Sensitivity and specificity in predicting alterations on endoscopic approach were 39.5 and 80% in the presence of pelvic pain, 14.5 and 72% in the presence of alteration on transvaginal ultrasound, 39.5 and 80% in the presence of alteration on hysterosalpingography, and 70.2 and 28% in the presence of at least one alteration by noninvasive methods. CONCLUSION: there is a poor diagnostic agreement between the several noninvasive methods and endoscopy in the investigation of conjugal infertility secondary to tuboperitoneal factors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):393-400
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700005
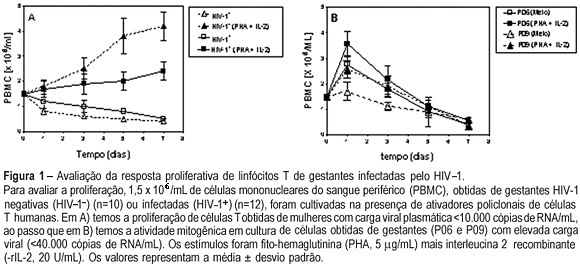
PURPOSE: to evaluate T cell proliferation and cytokine production in HIV-1-infected pregnant women and their impact on in vitro virus replication. METHODS: peripheral blood from 12 HIV-1-infected pregnant women and from their neonates was collected. As control, 10 samples from non-infected pregnants were also colleted. The CD4+ and CD8+ T cell counts were assayed by flow cytometry. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and plasma were obtained by centrifugation with and without Ficoll-Hypaque gradient, respectively. The freshly purified PBMC were kept in cultures for seven days with PHA plus r-IL-2, and the lymphoproliferative response was assayed by Trypan blue dye exclusion. In some experiments we added anti-IL-10 monoclonal antibody. The plasma samples and supernatants from cell cultures were stored to determine both peripheral cytokine levels, by ELISA sandwich, and viral load, by RT-PCR. RESULTS: the results showed that the lymphoproliferative response was smaller in cultures obtained from HIV-1-infected women than in control cultures [4.2±0.37 vs 2.4±0.56 (x 10(6) cell/mL), p<0.005]. In both control and infected pregnant women who had low plasma viral load, the level of IL-10 was higher than in those with high viral replication (9.790±3.224 vs 1.256±350 pg/mL, p=0.002). The elevated TNF-alpha production detected in serum (7.200±2.440 pg/mL) and supernatants (21.350±15.230 pg/mL) was associated with higher plasma viral loads and vertical infection. The IL-10 blockade by anti-IL-10 antibodies augmented viral replication in the cell cultures. CONCLUSION: these results indicate that IL-10 production exerts a negative influence on virus replication, diminishing the probability of intrauterine HIV-1 infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):387-392
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700004
PURPOSE: to assess peak systolic velocity (PSV) and the resistance index (RI) in the middle cerebral artery (MCA), suprarenal aorta (SRA) and infrarenal aorta (IRA) of the fetus and in the umbilical artery (UA) between the 22nd and 38th week of gestation. METHODS: a prospective study which evaluated the parameters of 33 normal fetuses in the 22nd, 26th, 30th, and 38th week of gestation. Pregnant women with a singleton fetus with no diseases or complications and who agreed to participate were included in the study. Exclusion criteria were fetal malformations, discontinuation of prenatal care visits and mothers who smoked, used alcohol or illicit drugs. Ultrasound examinations were performed by a single observer. For the acquisition of the Doppler velocimetry tracing in the MCA, SRA, IRA and UA, the sample volume was 1 to 2 mm, placed in the center of the arteries. The insonation angle was 5º to 19º in the MCA, below 45º in the SRA and IRA, and less than 60º in the UA. We used a wall filter of 50-100 Hz. The parameters were calculated automatically with the frozen image, three measurements being made. The final result was obtained by the arithmetic mean of the three values. Data were analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA), post hoc Bonferroni test, Pearson's correlation, and regression analysis. The level of significance was set at p<0.05 in all analyses. RESULTS: PSV increased from 26.3 to 57.7 cm/s in the MCA between the 22nd and the 38th week of gestation (p<0.05). In the SRA and in the IRA, PSV increased between the 22nd and 34th week of gestation, from 74.6 and 59.0 cm/s to 106.0 and 86.6 cm/s, respectively (p<0.05). In the UA, PSV increased between the 22nd and the 34th week of gestation, but decreased from 55.5 to 46.2 cm/s between the 34th and the 38th week of gestation. In the MCA, the RI was lower in the 22nd (0.81) and 38th week of gestation (0.75) and higher (0.85) in the 26th week (p<0.05). In the SRA, the RI values were stable in all weeks and in the IRA they were stable in most weeks (p>0.05). In the UA, RI decreased from 0.69 to 0.56 between the 22nd and 38th week of gestation (p<0.05). CONCLUSION: in normal fetuses, in the second half of gestation PSV increased in the MCA, SRA and IRA, decreasing in the UA between the 34th and 38th week of gestation. RI was lower in the 22nd and 38th weeks of gestation in the MCA, decreased between the 22nd and the 38th week in the UA, and was constant in most of the gestational weeks in the SRA and IRA.