Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(2):77-81
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005199
To analyze the factors that might influence the recurrence of ovarian endometriomas after laparoscopic excision.
A retrospective cohort study. We evaluated 129 patients who underwent laparoscopic excision of ovarian endometriomas from 2003 to 2012 and who were followed up for at least two years after surgery. Vaginal ultrasound was repeated to exclude persistent lesion and to identify recurrence. The Student's t-test was used to compare continuous variables and the χ or Fischer exact test (for values of less than five) was used to test homogeneity between proportions. A logistic regression model for multivariate proportional hazards was used to analyze predictors of long-term outcome. The level of significance was set at 5% in all analyses.
The overall rate of ovarian endometrioma recurrence was 18.6%. Endometrioma diameter, surgical procedure techniques and demographic data such as age, presenting symptoms, body mass index, smoking and physical exercise habits were not associated with recurrence, whereas interruption of postoperative medical treatment was significantly correlated with a higher recurrence rate (OR 23.7; 95%CI 5.26-107.05; p=0.001).
Current oral contraceptive use appears to be associated with a dramatic reduction in the risk of recurrence of ovarian endometriotic cysts. Treatment interruption was associated with a higher recurrence rate of ovarian endometrioma after laparoscopic treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(2):64-70
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005115
To determine the prevalence of toxoplasmosis and to identify the main factors associated with seroreactivity in pregnant women cared for at two reference centers in a city in Northeast Brazil.
A cross-sectional study was conducted on 561 pregnant women at two high-risk prenatal reference centers in a city in Northeast Brazil. All women were interviewed using an epidemiological questionnaire and had their blood samples collected for the following serological tests: anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgG and IgM (ELISA), IgG avidity test, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS version 18.0 for Windows, calculating odds ratio, confidence interval of 95% and with the level of significance set at 5%.
Seroreactivity for toxoplasmosis was detected in 437 women (77.0%), susceptibility in 124 (22.1%) and active infection in 5 (0.9%). There was no significant association between seroreactivity for toxoplasmosis and age, location, income, education, availability of sewage, number of pregnancies or gestational age. The variables significantly associated (p≤0.05) with seroreactivity were multiparity (p=0.03) and living with stray dogs (p=0.01).
This study identified high seroreactivity for toxoplasmosis among patients seen during prenatal care, as well as factors associated with seroreactivity. Appropriate guidelines about primary preventive measures should be emphasized and quarterly serological monitoring is recommended for pregnant women in this city and elsewhere in the Northeast of Brazil.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(1):36-41
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005179
To evaluate the sparing of fertility and ovaries in women submitted to surgical treatment for benign adnexal tumors.
Between February 2010 and January 2014, 206 patients were included in this observational study as they were submitted to surgical treatment for benign ovarian tumors at CAISM, a tertiary hospital. Fertility sparing surgery was defined as tumorectomy or unilateral salpingoophorectomy without hysterectomy in premenopausal women. Preservation of the ovary occurred when at least one ovary or part of it was mantained.
Of the 206 women with benign tumors, 120 (58%) were premenopausal and 86 (42%) were postmenopausal. There were 36 (30%) ovarian germ cell tumors, 31 (26%) epithelial neoplasms and 11 (9%) sex-cord stromal tumors among premenopausal women. In the group of postmenopausal women, 35 (41%) epithelial neoplasms, 27 (31%) sex-cord stromal tumors and 8 (9%) ovarian germ cell tumors were identified. Among 36 women with non-neoplastic ovarian tumors, 21 (58%) had endometriomas and 8 (22%) functional cysts. Among 22 women with extra-ovarian tumors, uterine leiomyomatosis was the most frequent finding (50%). In the group of women who were ≤35 years old, 26 (57%) were treated by tumorectomy and 18 (39%) were submitted to unilateral salpingoophorectomy with sparing of the uterus and the contralateral ovary. Women who were ≤35 years old were more frequently operated by laparoscopy which was associated with a higher number of fertility sparing procedures when compared to laparotomy (p<0.01). Twenty-six (28%) women submitted to hysterectomy with bilateral salpingoophorectomy were premenopausal.
Although there is a trend to perform only tumorectomy in women who are ≤35 years old, a significant number of young women is still treated by salpingoophorectomy. Among 36- to 45-year-old women, only 70% had their fertility spared, while 20% had both ovaries removed. However, whenever possible, we must try to preserve the ovaries, mainly in premenopausal women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(1):30-35
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005134
To evaluate the prevalence of low bone mineral density (BMD) in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors.
In this cross-sectional study, 115 breast cancer survivors, seeking healthcare at a University Hospital in Brazil, were evaluated. Eligibility criteria included women with amenorrhea ≥12 months and age ≥45 years, treated for breast cancer and metastasis-free for at least five years. BMD was measured by DEXA at the lumbar spine (L1-L4) and femoral neck. Low BMD was considered when total-spine and/or femoral-neck T-score values were <-1.0 Delphi Score (DP) (osteopenia and osteoporosis). The risk factors for low BMD were assessed by interview. Data were analyzed statistically by the χ2 test and Fisher's exact test.
The mean age of breast cancer survivors was 61.6±10.1 years and time since menopause was 14.2±5.6 years, with a mean follow-up of 10.1±3.9 years. Considering spine and femoral neck, 60% of breast cancer survivors had low BMD. By evaluating the risk factors for low BMD, a significant difference was found in the percent distribution for age (higher % of women >50 years with low BMD), personal history of previous fracture (11.6% with low BMD versus 0% with normal BMD) and BMI. A higher frequency of obesity was observed among women with normal BMD (63%) compared to those with low BMD (26.1%) (p<0.05).
Postmenopausal breast cancer survivors had a high prevalence of osteopenia and osteoporosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(1):16-23
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005138
To evaluate eating in postmenopausal women and its relation to anthropometry, age and time since menopause in São Bernardo do Campo residents.
During the period from June to August of 2011, 148 postmenopausal women residents in state of São Paulo (Southeast region of Brazil) were evaluated using a structured questionnaire containing socioeconomic, clinical, anthropometric and food data. The level of physical activity, biochemical variables, Body Mass Index (BMI), abdominal circumference (AC) and dietary intake (energy, protein, carbohydrates and fats, fiber, cholesterol, vitamins A and C, minerals, calcium and iron) were analyzed according to age and time after menopause.
Mean BMI was 29.0≤5.6 kg/m2 and abdominal circumference was 95.7±12.9 cm. The average daily caloric consumption was 1,406.3±476.5 kcal. The calorie intake was significantly more appropriate in normal-weight women and women with AC<88 cm. The same was observed for protein intake (p<0.001 and p=0.006, respectively). No association was observed with age or duration of the postmenopausal period, except for average protein consumption that was higher in the group with five years or less of menopause (p=0.048).
The anthropometry of postmenopausal women showed a predominance of overweight and obesity. Dietary intake was adequate in relation to the percentage of calories and macronutrients and calories among most normal-weight women and women with AC<88 cm.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(1):10-15
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005202
To determine if the presence of infectious agents in vaginal or cervical content can alter the results of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) test and the measurement of cervical length (CC) by transvaginal ultrasonography.
A total of 107 pregnant women with a history of spontaneous preterm birth were submitted to the phIGFBP-1 test and to measurement of CC by transvaginal ultrasonography every 3 weeks, between 24 and 34 weeks of gestation. Genital infections were determined immediately before testing. The patients were distributed into four groups (GA, GB, GC, and GD) and the correlation between genital infection and changes in the tests was determined within each group based on the odds ratio (OR) and the Pearson correlation coefficient.
In each group, over 50% of the patients had genital infections (GA 10/17; GB 28/42; GC 15/24; GD 35/53), with bacterial vaginosis being the main alteration of the vaginal flora. Positive results for phIGFBP-1(GA 10/10; GB 18/28; GC 15/15; GD 19/35) and CC≤20 mm (GA 10/10; GB 20/28; GC 10/15; GD 20/35) were obtained more frequently in patients with genital infection in all groups. Nonetheless, when applying the Pearson correlation coefficient we detected a poor correlation between genital infection and positivity for markers.
The presence of changes in the vaginal flora and of other genital infections does not significantly alter the results of phIGFBP-1 and the measurement of cervical length when compared to cases without infection. However, more studies with larger samples are necessary to confirm these results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(12):555-561
DOI 10.1590/So100-720320140005155
To determine if illicit drug use increases the vertical transmission of HIV, to identify the risk factors involved in mother and child health and the prevalence of illicit drug use among these pregnant women.
Sixty-four (7.6%) of 845 pregnant women from the metropolitan region of Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil, attended in the service between October 1997 and February 2012 reported the use of illicit drugs. Cases were HIV-positive drug users (n=64) and controls were women who did not use drugs (n=192). Three controls were selected for each case. Several conditions of exposure were considered in the control group such as tobacco use, alcohol use, alcohol and tobacco use, maternal age, educational level, ethnicity, and marital status. Problems during the prenatal period, delivery and postpartum, vertical HIV transmission and neonatal outcomes were also investigated.
Univariate analysis showed as significant variables: maternal age, tobacco use, number of prenatal care visits, antiretroviral therapy, mode of infection, and viral load at delivery. Logistic regression revealed as significant variables: maternal age (less than 25 years); tobacco use, and number of prenatal care visits (less than 6). The vertical transmission of HIV was 4,8% (95%CI 1.7–13.3) among drug users and 2,1% (95%CI 0.8–5.2) in the control group, with no statistically significant difference between groups. Neonatal complications were more frequent among drug users, but also with no statistically significant difference between groups.
The use of illicit drug is frequent during pregnancy among HIV-infected women. The approach to illicit drug use should be routine during prenatal care visits. These women are more discriminated against and tend to deny their habits or do not seek prenatal care. There was no difference in vertical virus transmission between groups, probably indicating adherence to antiretroviral use for antiretroviral therapies during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(12):548-554
DOI 10.1590/So100-720320140005038
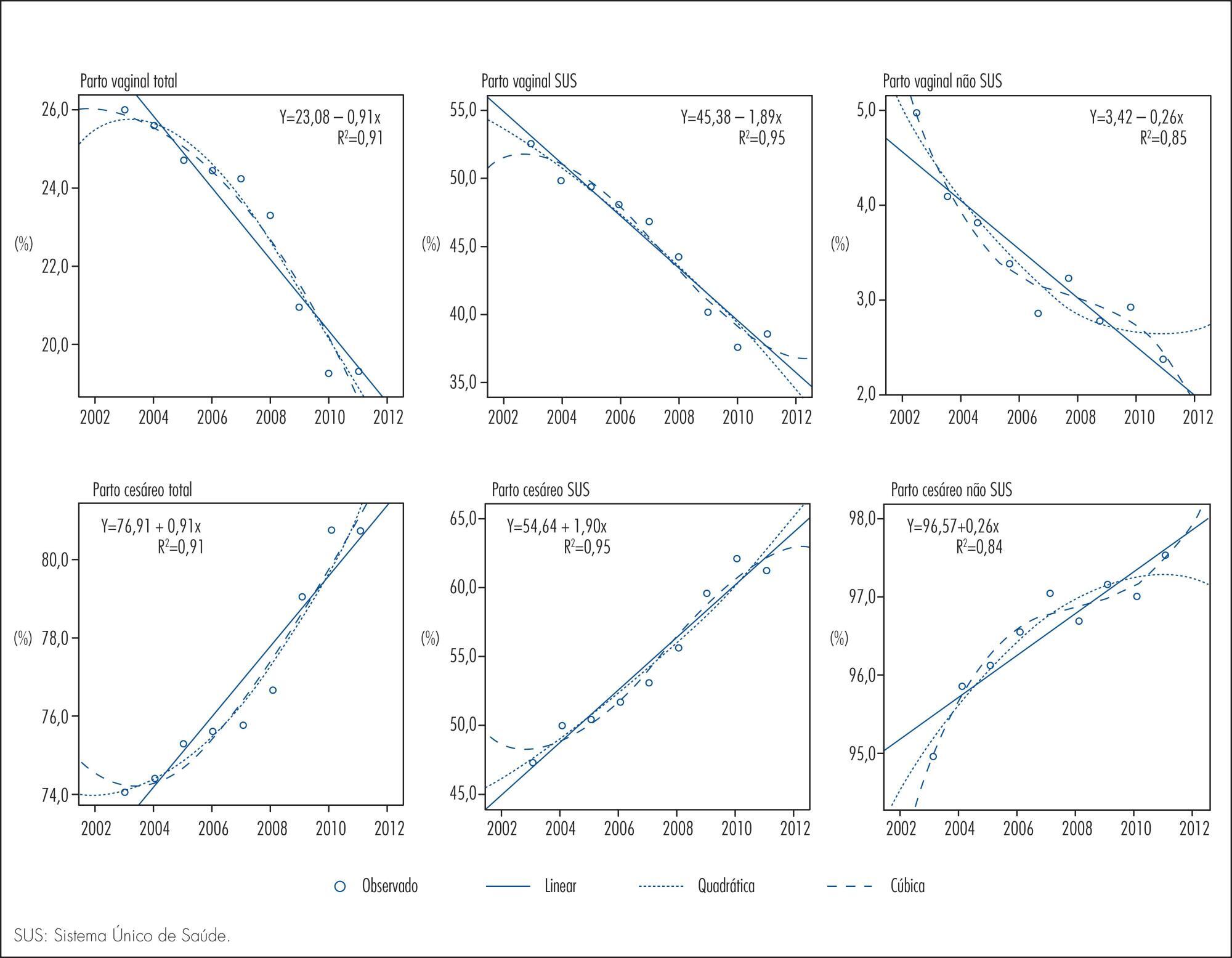
To analyze the time trend of the rates of cesarean and vaginal delivery according to the source of financing.
This was an ecological study of the time series analysis of cesarean and vaginal delivery rates according to the financing source, carried out in Maringá, Paraná State, Brazil, from 2002 to 2012. Information available at the System of Information on Live Births and at the System of Hospital Information of the Brazilian Unified Health System (SUS) was used for data collection. Moving averages were calculated for all mode of delivery rates in order to smooth random fluctuations in the series, dispersion diagrams were designed between the coefficients and years of the study, and polynomial regression models were estimated from the functional relation observed, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
Throughout the 11 years of the study there were 48,210 births, 77.1% by cesarean delivery and only 22.9% by vaginal delivery. A total of 22,366 procedures were financed by SUS, 54.6% of them being cesareans. Trend analysis was significant for all the regression models, demonstrating an ascending trend for cesarean delivery and a descending trend for vaginal delivery for both types of financing. The non-SUS cesarean rates always exceeded 90.0% and were more frequent than the SUS cesarean rates, even with a 36.0% increase of the latter during the study period.
Based on trend analysis, cesarean deliveries will continue to increase in both health financing sources unless new actions and strategies of reduction are implemented, involving the sociocultural, demographic and obstetric characteristics of women, the training and activity of professionals in the area of obstetrics and an adequate structure of health services for providing vaginal delivery.