Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(6):324-328
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000600008
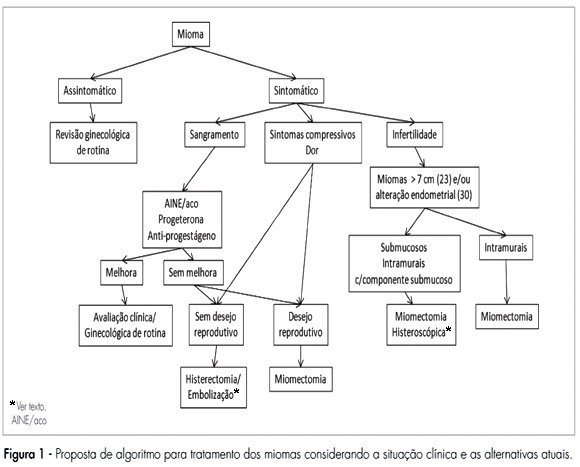
Leiomyomas are benign tumors. They appear in the myometrium and present a variable amount of fibrous conjunctive tissue. About 75% of the cases are not symptomatic and are usually found during abdominal, bimanual pelvic examination or during ultrasonography. The symptoms are directly related to the size, number and localization of the myomas. In the present review, the current clinical therapeutic procedures (oral anti-conceptive drugs, progestins and anti-progestins, analogues of the gonadothrophins’ releasing hormone (GnRH), and non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs), and also the surgical procedures (hysterectomy, myomectomy, embolization) are presented for the treatment of leiomyomas.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):267-275
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500008
Sweeteners are frequently used by women of reproductive age. This is a narrative review about the sweeteners currently sold in the Brazilian commerce. There is a few information on the use of saccharin and cyclamates in pregnancy and their effects on the fetus. Due to the limited information available and their carcinogenic potential in animal species, saccharin and cyclamates should be avoided during pregnancy (risk C). Aspartame has been extensively studied in animals and it is considered safe for use during pregnancy (risk B), except by women homozygous for phenylketonuria (risk C). Sucralose and acessulfame-K are not toxic, carcinogenic or mutagenic in animals, but there are no controlled studies in humans. However, since these two sweeteners are not metabolized, it is unlikely that their use during pregnancy could be harmful (risk B). Stevia, a substance extracted from a native Brazilian plant, is innocuous in animal pregnancies, but there are no controlled studies in humans (risk B). Body agents found in the composition of artificial sweeteners (mannitol, sorbitol, xylitol, erithrol, lactilol, isomalt, maltilol, lactose, fructose, maltodextrin, dextrin, and inverted sugar) are substances generally regarded as safe for human consumption. In conclusion, according to the currently available evidence, aspartame, sucralose, acessulfame-K and stevia can be safely used during pregnancy.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):211-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400008
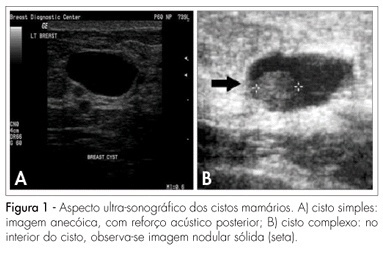
The benign mammary tumors are responsible for up to 80% of the clinical masses. Its differential diagnosis is wide, involving mammary cysts, fibroadenomas, phyllodes tumors, papillomas, hamartomas, and adenomas, among others. The fibroadenoma is the most common mammary neoplasia in patients under 35 years old, while the cysts are more frequent in the perimenopause. The differential diagnosis among solid or cystic nodules can be made through the fine-needle aspiration or by ultrasound, being therapeutic for the last ones. In this article, the differential diagnostic aspects will be revised between these tumors, as well as the new therapeutic approaches.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):158-164
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300008
Axillary nodal metastasis is still the most important breast cancer prognostic factor. As in approximately 80% of the patients with tumors measuring less than 2 cm the axillary lymph nodes are negative, it has been proposed sentinel lymph node biopsy, reducing surgical morbidity in the patients with negative result. Recently, this technique has been widely used in Brazil, but there are two questions that need to be answered: what is the probability of a false-negative result (not diagnosing a positive lymph node) and if the understaging by false-negative result exposes the patient to the risk of axillary recurrence or even distant metastases, due to less effective surgical and adjuvant therapy. The literature shows that the false-negative rate varies from 5 to 10%, being the surgeon's experience the major factor that contributes to improved results. Although axillary relapse is rare, it is not yet possible to evaluate the long term effect of not removing positive lymph nodes, due to short follow-up. The recommendation is that sentinel lymph node biopsy should only be performed by surgeons with experience confirmed by a low false-negative rate.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):103-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200008
Male infertility affects 10% of couples in the reproductive age worldwide and is treatable in many cases. In addition to other well-described etiologies, genetic causes of male infertility are now more commonly diagnosed. In men with prior vasectomy or varicocele, microsurgical reconstruction of the reproductive tract or varicocelectomy is more cost-effective than sperm retrieval with in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection if no female fertility risk factors are present. If epididymal obstruction after vasectomy is detected or advanced female age is present, the decision to use either microsurgical reconstruction or sperm retrieval with in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection should be individualized. Sperm retrieval with in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection is preferred to surgical treatment when female factors requiring in vitro fertilization are present or when the chance for success with sperm retrieval and intracytoplasmic sperm injection exceeds the chance for success with surgical treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(1):48-55
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000100008
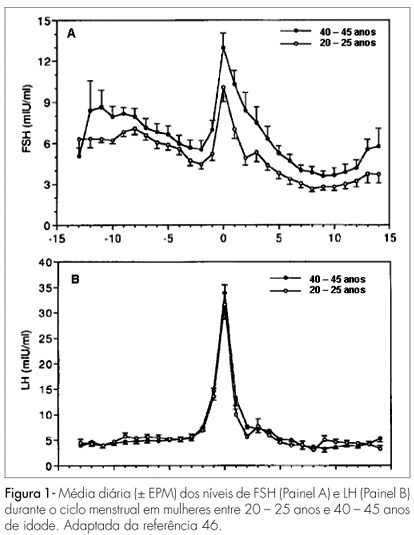
Changes in the levels of gonadotropins throughout the reproductive life depend on a fine tuned functional development of neural pathways and GnRH-neurones, pituitary gonadotrophs and granulosa-theca cells of the follicular wall. Both, LH and FSH levels change according to the day-time, menstrual cycle phase, and gynecological age. Initiating the puberty, changes in LH pulses are remarkable, showing higher frequency and amplitude at night. Later in puberty, the pulses of LH are also maintained during the day, remaining its levels with very little variation within the 24 hours period. During the menstrual cycle, the FSH levels increase at the end of the luteal phase, decrease during the medium and late follicular phase, increase rapidly in the ovulatory phase and remain at low basal levels until the late luteal phase. The levels of LH remain unaltered during the whole follicular phase, increase in the ovulatory surge, and decrease to the basal levels in the luteal phase. At the forth decade of life, the GnRH secretion changes, with hypothalamic loss of sensitivy to the estradiol positive feedback and decrease in frequency and prolongation of the GnRH pulses. The pituitary response is atenuated due to decrease in the density of GnRH receptors on gonadotroph cells, loss of gonadotroph sensitivity, secretion of more basic FSH and LH molecules, decrease in frequency and increase in amplitude of LH and FSH pulses. These modifications result in monotropic increase of the FSH secretion. Current studies show that the selective increase in the FSH levels in the early follicular phase is gradual, beginning as early as the third decade of life. These alterations in FSH are associated with an accelerated follicular depletion in women after 37-38 years old. On the other side, the LH levels remain almost constant up to the end of reproductive life. The different levels of FSH and LH seen throughout the reproductive years may be due to yet unknown regulatory mechanisms in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis.