Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):596-600
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000005
PURPOSE: To analyze gestation evolution and deliveries after myoma treatment by embolization of the uterine arteries. METHODS: In the initial evaluation, 112 patients submitted to embolization of uterine arteries were included for treatment of myoma. From those, only nine wanted to be submitted to conservative treatment in order to keep their reproductive capacity. This procedure was indicated to the nine patients, since they were not susceptible to a conservative surgical treatment. They were submitted to embolization of the uterine arteries with particles of polyvinyl alcohol or embospheres with diameters ranging from 500 to 700 µm, and they have evolved without intercurrence. RESULTS: During the follow-up of these patients, there was a good clinical response with significant reduction in the uterus and myoma volumes. Four of them got pregnant, two had an early abortion and two evolved normally till the end of gestation with a term delivery. One of these had twins. CONCLUSION: Embolization of the uterine arteries is an option for the treatment of uterine myoma, and presents good clinical and anatomical results, allowing patients to preserve their reproductive capacity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):278-284
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500003
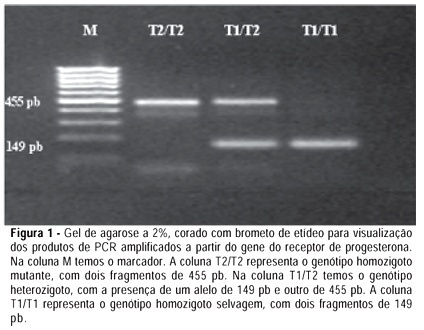
PURPOSE: to analyze race, parity and presence of the progesterone receptor polymorphism, named PROGINS, as factors related to uterine leiomyoma occurrence in Brazilian women. METHODS: we carried out a case-control study, composed of 122 patients with the diagnosis of uterine fibroid and 125 women without the disease. After recording the clinical data, we collected biological material for DNA extraction, polymerase chain reaction and agarose gel electrophoresis in order to identify the presence of PROGINS polymorphism. Statistical analysis was performed using the non-parametric Mann-Whitney test or the chi2 test, depending on the studied variable. The risk for the occurrence of the disease was calculated by the logistic regression model, providing the odds ratio (OR). The adopted significance level was 5% (p<0.05) and the confidence interval was 95% (95% CI). RESULTS: we observed a higher prevalence of "non-white"women - mulatto and black - (50 vs 22.4%) and nulliparas (23.8 vs 11.2%) in the cases, while the progesterone receptor genotype was more often PROGINS positive - heterozygous or mutant homozygous - among the controls (21.6 vs 10.7%). The OR indicated an elevated risk for leiomyoma related to the "non-white"race (OR=3.46; 95% CI: 2.0-6.0) and the nulliparity (OR=3.30; 95% CI: 1.9-5.6), with reduction in the presence of PROGINS-positive genotypes (OR=0.43; 95% CI: 0.2-0.9). CONCLUSIONS: the "non-white"race and nulliparity were considered risk factors for the occurrence of uterine fibroid in the studied population, while PROGINS polymorphism showed to be a protective factor.