Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):449-455
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004946
To assess cardiometabolic risk factors during normal pregnancy and the influence of maternal obesity on them.
This study included 25 healthy pregnant women with a single pregnancy and a gestational age of less than twenty weeks. Longitudinal analysis of blood pressure, body weight, body mass index (BMI), serum concentrations of leptin, adiponectin, cortisol, total cholesterol and fractions, triglycerides, uric acid, fasting glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, HOMA-IR and insulin/glucose ratio was performed each trimester during pregnancy. In order to evaluate the impact of obesity, pregnant women were divided into two groups based on BMI for the first quarter of pregnancy: Gpn for pregnant women with BMI<25 kg/m2 and Gso for BMI≥25 kg/m2. One-Way ANOVA for repeated measurements or Friedman test and Student-t or Mann-Whitney tests for statistical comparisons and Pearson correlations test were used for statistical analysis.
The mean values for the first quarter of pregnancy for the following parameters were: age: 22 years; weight: 66.3 kg and BMI 26.4 kg/m2, with 20.2 and 30.7 kg/m2 for the Gpn and Gso groups, respectively. Mean weight gain during pregnancy was ±12.7 kg with 10.3 kg for the Gso group and 15.2 kg for the Gpn group. Regarding plasma determinations, cortisol, uric acid and lipid profile increased during all trimesters of pregnancy, except for HDL-cholesterol, which did not change. Blood pressure, insulin and HOMA-IR only increased in the third quarter of pregnancy. The Gso group tended to gain more weight and to show higher concentrations of leptin, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, VLDL-cholesterol, TG, glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR, besides lower HDL-cholesterol and greater diastolic blood pressure in the 3rdquarter of pregnancy. Three pregnant women developed gestational hypertension, presented prepregnancy obesity, excessive weight gain, hyperleptinemia and an insulin/glucose ratio greater than two. Weight and BMI were positively correlated with total cholesterol and its LDL fraction, TG, uric acid, fasting blood glucose, insulin and HOMA-IR; and were negatively correlated with adiponectin and HDL-cholesterol. Leptin level was positively correlated with blood pressure.
The metabolic changes in pregnancy are more significant in obese women, suggesting, as expected, an increased risk of cardiometabolic complications. During their first visit for prenatal care, obese women should be informed about these risks, have their BMI and insulin/glucose ratio calculated along with their lipid profile to identify pregnant women at higher risk for cardiovascular diseases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):315-319
DOI 10.159/S0100-720320140004977
To analyze associations between mammographic arterial mammary calcifications in menopausal women and risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
This was a cross-sectional retrospective study, in which we analyzed the mammograms and medical records of 197 patients treated between 2004 and 2005. Study variables were: breast arterial calcifications, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, age, obesity, diabetes mellitus, smoking, and hypertension. For statistical analysis, we used the Mann-Whitney, χ2 and Cochran-Armitage tests, and also evaluated the prevalence ratios between these variables and mammary artery calcifications. Data were analyzed with the SAS version 9.1 software.
In the group of 197 women, there was a prevalence of 36.6% of arterial calcifications on mammograms. Among the risk factors analyzed, the most frequent were hypertension (56.4%), obesity (31.9%), smoking (15.2%), and diabetes (14.7%). Acute coronary syndrome and stroke presented 5.6 and 2.0% of prevalence, respectively. Among the mammograms of women with diabetes, the odds ratio of mammary artery calcifications was 2.1 (95%CI 1.0-4.1), with p-value of 0.02. On the other hand, the mammograms of smokers showed the low occurrence of breast arterial calcification, with an odds ratio of 0.3 (95%CI 0.1-0.8). Hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus, stroke and acute coronary syndrome were not significantly associated with breast arterial calcification.
The occurrence of breast arterial calcification was associated with diabetes mellitus and was negatively associated with smoking. The presence of calcification was independent of the other risk factors for cardiovascular disease analyzed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):328-333
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005014
The prevalence of urinary incontinence in diabetic pregnant women is significantly high two years after cesarean section. Incontinence can be the most common consequence of hyperglycemia compared to other complications. Thus, identifying the risk factors for the development of urinary incontinence in diabetes is the major aim in the prevention of this very common condition. Recent surveys have shown that not only muscle but also the urethral extracellular matrix play an important role in the mechanism of urinary continence. Translational work on rats by our research group showed that diabetes during pregnancy damages the extracellular matrix and urethral striated muscle, a fact that may explain the high prevalence of urinary incontinence and pelvic floor dysfunction in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes affects the expression, organization and change in extracellular matrix components in different organs, and tissue remodeling and fibrosis appear to be a direct consequence of it. Therefore, understanding the impact of modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes, which involves using preventive strategies, can reduce the rates of urinary incontinence and the health care costs, and improve the quality of life of women, especially during pregnancy and postpartum.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):251-258
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004976
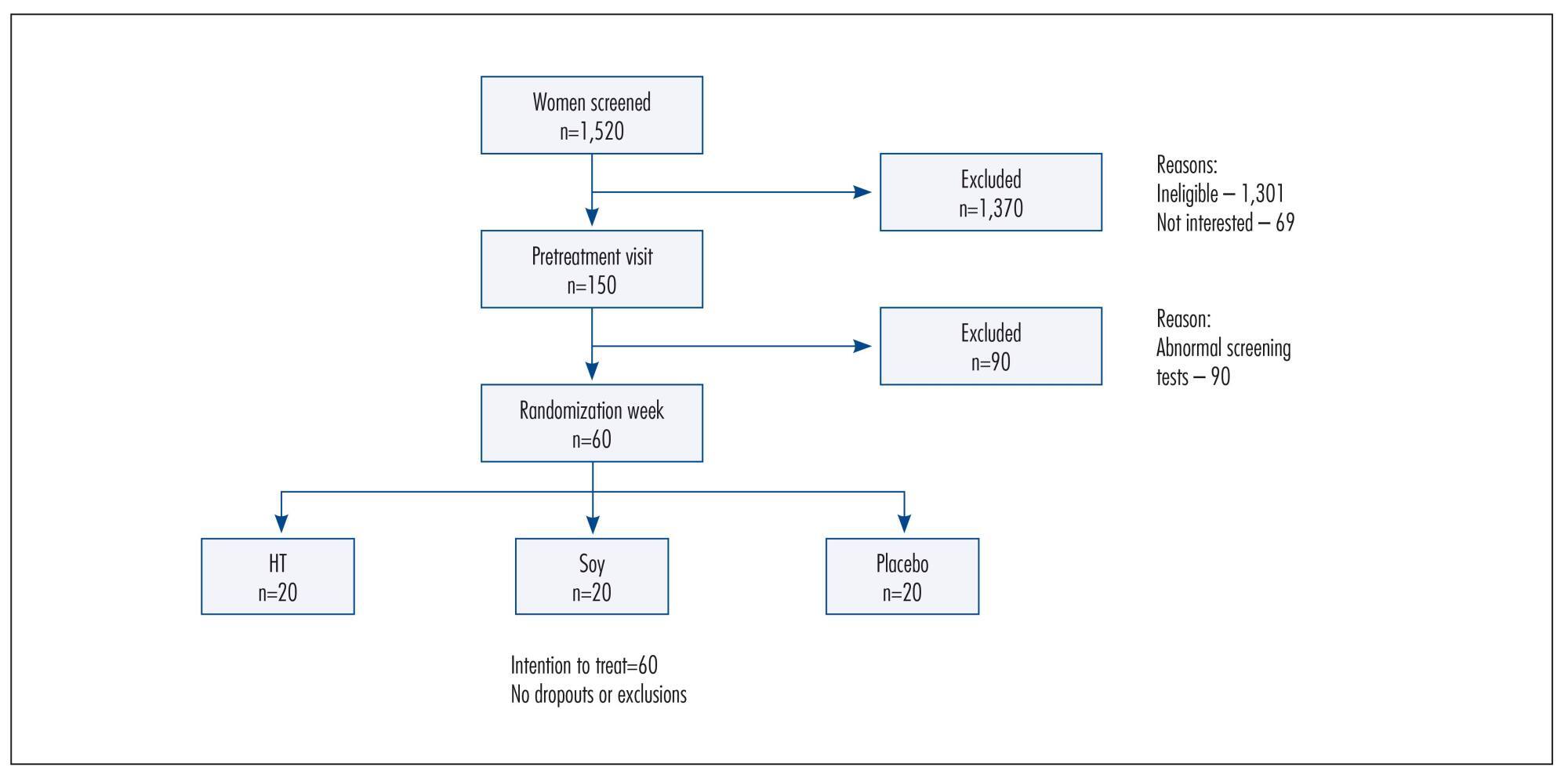
To assess the effects of a soy dietary supplement on the main biomarkers of cardiovascular health in postmenopausal women compared with the effects of low-dose hormone therapy (HT) and placebo.
Double-blind, randomized and controlled intention-to-treat trial. Sixty healthy postmenopausal women, aged 40-60 years, 4.1 years mean time since menopause were recruited and randomly assigned to 3 groups: a soy dietary supplement group (isoflavone 90mg), a low-dose HT group (estradiol 1 mg plus noretisterone 0.5 mg) and a placebo group. Lipid profile, glucose level, body mass index, blood pressure and abdominal/hip ratio were evaluated in all the participants at baseline and after 16 weeks. Statistical analyses were performed using the χ2 test, Fisher's exact test, Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric test, analysis of variance (ANOVA), paired Student's t-test and Wilcoxon test.
After a 16-week intervention period, total cholesterol decreased 11.3% and LDL-cholesterol decreased 18.6% in the HT group, but both did not change in the soy dietary supplement and placebo groups. Values for triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, glucose level, body mass index, blood pressure and abdominal/hip ratio did not change over time in any of the three groups.
The use of dietary soy supplement did not show any significant favorable effect on cardiovascular health biomarkers compared with HT. Clinical Trial Registry: The trial is registered at the Brazilian Clinical Trials Registry (Registro Brasileiro de Ensaios Clínicos - ReBEC), number RBR-76mm75.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):237-243
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005010
To assess the determinants of late stage in women with cervical cancer in Brazil.
A cross-sectional study of secondary basis. Women with invasive cervical cancer enrolled in the Cancer Hospital Registry between January 2000 and December 2009 were included. Late clinical stage (≥IIB) was the outcome considered. The following variables were studied: age at diagnosis, race or ethnicity, years of education, marital status, alcohol consumption, smoking status, place of residence, year of diagnosis, initial treatment received, and status after the first treatment. Odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) and a logistic regression model were used. P values<0.05 were considered statistically significant.
37,638 cases were included, with a mean age of 52.4±14.1 years. Late clinical stages were observed in 70.6% of cases and were associated with the presence of squamous cell carcinoma (OR=1.8; 95%CI 1.7-2.0), age ≥50 years (OR=1.5; 95%CI 1.4-1.6), living with a partner (OR=1.3; 95%CI 1.2-1.4), black skin color (OR=1.2; 95%CI 1.1-1.4), and low educational level (OR=1.2; 95%CI 1.1-1.3).
In Brazil, the diagnosis of cervical cancer is a delayed event. Although the main factor associated with late stage of cervical cancer identified in this study is a biological factors (histological type) and, consequently, not eligible for intervention, it was confirmed that socioeconomic disparities in the country are associated with late stage disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):222-227
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050007
To identify risk factors for weight retention in women after childbirth.
This was a prospective observational study that followed for six months adult women who delivered at a tertiary center. Were applied a structured questionnaire before hospital discharge and at six weeks and six months after childbirth, through home visits. The outcome was weight retention after childbirth (if risk >7.5 kg). The variables analyzed were: age, skin color, working during pregnancy, income, education, marital status, age at menarche, maternal age at first birth, parity, mode of delivery, birth interval, pre-pregnancy weight, gestational weight gain, percent body fat, and nutritional status. Data were first analyzed by bivariate analysis between prevalence of weight retention at six months and several covariates (p<0.2). We then calculated the Odds Ratio (OR) and their respective gross confidence intervals of 95% (95%CI) and finally performed multivariate logistic regression to control for confounding factors and to estimate the OR and 95%CI.
The frequency of weight retention >7.5 kg by 6 months after delivery was 15%. In bivariate analysis, weight retention was associated with the following variables: age at menarche <12 years (OR=3.7; 95%CI1.1-13.2), gestational weight gain ≥16 kg (OR=5.8; 95%CI 1.8-18.6), percent body fat at baseline >30% (OR=5.0; 95%CI 1.1-23.6), and nutritional status by 6 weeks postpartum >25 kg/m2 (OR=7.7; 95%CI1.6-36.1). In multivariate analysis, only excessive gestational weight gain (OR=74.1; 95%CI 9.0-609.6) remained as a risk factor.
Excessive weight gain during pregnancy should receive special attention in prenatal care in view of its association with weight retention and excess weight in women after childbirth.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):124-130
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300006
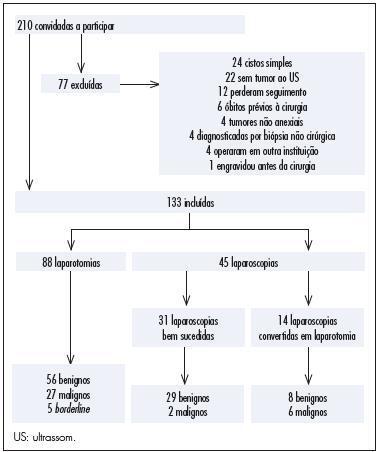
To assess clinical factors, histopathologic diagnoses, operative time and differences in complication rates between women undergoing laparoscopy or laparotomy to diagnose and treat an adnexal mass and their association with laparoscopy failure.
In this prospective study, 210 women were invited to participate and 133 of them were included. Eighty-eight women underwent laparotomy and 45 underwent laparoscopy. Fourteen of the 45 laparoscopies were converted to laparotomy intraoperatively. We assessed whether age, body mass index (BMI), previous abdominal surgeries, CA-125, Index of Risk of Malignancy (IRM), tumor diameter, histological diagnosis, operative time and surgical complication rates differed between the laparoscopy group and the group converted to laparotomy and whether those factors were associated with conversion of laparoscopy to laparotomy. We also assessed surgical logs to evaluate the reasons, as stated by the surgeons, to convert a laparoscopy to laparotomy.
In this research, 30% of the women had malignant tumors. CA-125, IRM, tumor diameter and operative times were higher for the laparotomy group than the laparoscopy group. Complication rates were similar for both groups and also for the successful laparoscopy and unsuccessful laparoscopy groups. The surgical complication rate in women with benign tumors was lower for the laparoscopy group than for the laparotomy group. The factors associated with conversion to laparotomy were tumor diameter and malignancy. During laparoscopy, adhesions a large tumor diameter were the principal causes of conversion.
This study suggests that laparoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of adnexal masses is safe and does not increase complication rates even in patients who need conversion to laparotomy. However, when doubt about the safety of the procedure and about the presence of malignancy persists, consultation with an expert gynecology-oncologist with experience in advanced laparoscopy is recommended. A large tumor diameter was associated with the necessity of conversion to laparotomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(12):536-540
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001200002
PURPOSE: To evaluate weight retention 12 months postpartum and factors associated among women who had received prenatal care at Health Care Centers in Porto Alegre, southern Brazil. METHODS: Pregnant women in the last trimester were identified at 20 Health Care Centers. Socioeconomic, demographic and anthropometrics data were obtained. Six and 12 months after delivery, the women received home visits for anthropometric measures. The gestational weight gain was defined by pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI). Weight retention was defined as the difference between pre-gestational weight and weight at postpartum. Data were analyzed using McNemar's Test, ANOVA with Bonferroni correction and multiple linear regression. RESULTS: Of the 715 pregnant women recruited, 545 were assessed 12 months after delivery. Women were more likely to be overweight 12 months postpartum compared to the pre-pregnancy period (52.9 versus 36.7%) and weight retention during the 12 months postpartum was more than 10 kg in 30.7% of the women. Weight retention in the postpartum period was higher among women who were overweight (9.9±7.7 kg) compared to those who were of normal weight during the pre-pregnancy period (7.6±6.2 kg). Pre-pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and maternal age were associated with gestational weight retention 12 months postpartum (p<0.001). CONCLUSION: Adequate prenatal care is necessary to minimize the adverse effects of excessive weight gain during pregnancy on women's health.