Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):525-531
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000900006
Purpose: to calculate sensitivity, specificity and positive and negative predictive values for multiparameter ultrasound scores for Down's syndrome. Patients and Methods: sensitivity and specificity for Down syndrome were calculated for ultrasound scores in a prospective study of ultrasound signs from 16 to 24 weeks in a high-risk population who denied invasive procedures after genetic counselling. The signs and scores were: femur/foot length < 0,9 (1), nuchal fold > 5 mm (2), pyelocaliceal diameter > 5 mm (1), nasal bones < 6 mm (1), absent or hypoplastic fifth median phalanx (1) and major structural malformations (2). Complete follow-up was obtained in each case. Genetic amniocentesis was proposed in the case of score 2 or more. Results: a total of 963 patients were examined from October 93 to December 97 at a mean gestational age of 19.6 (range 16 -24) weeks. Women's age ranged from 35 to 47 years (mean 38.8) and 18 Down syndrome cases were observed (1.8%). Sensitivity was 94.5% (17/18) for score 1 and 73% (13/18) for score 2 (false positive rate of 9.8% for score 1 and 4.1% for score 2). Individual sign sensitivity and specificity were: femur/foot = 16.7% (3/18) and 96.8% (915/945); nasal bones = 22.2% (4/18) and 92.1% (870/945); nuchal fold = 44.4% (8/18) and 96.5% (912/945); pyelic diameter = 38.9% (7/18) and 94.3% (891/945); absent phalanx = 22.2% (4/18) and 98.5% (912/945); malformation = 22.2% (4/18) and 98.2% (928/945). Conclusions: the overall sensitivity for score 1 was high but false positive rates were also high. For score 2, sensibility was still good (73%) and false positive rate was acceptable (4.1%). Positive and negative predictive values can be calculated for each prevalence (women's age). More cases are needed to reach final conclusions about this screening method (specially in a low-risk population) although this system has been useful for high-risk patients who deny invasive procedures.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):481-484
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800009
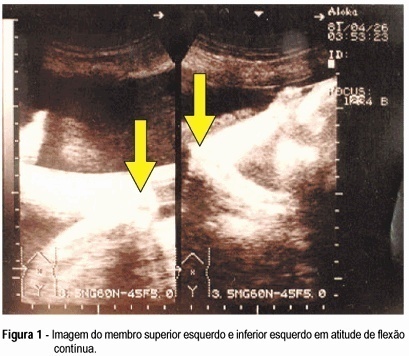
Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita is characterized by multiple joint contractures present at birth. Prenatal diagnosis is difficult. There are few reports in the literature. Fetal akinesia, abnormal limb position, intrauterine growth retardation, and polyhydramnios are the main findings of the ultrasonographic diagnosis. The authors describe a case of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita ultrasonographically diagnosed in the third gestational trimester. The main findings were absence of fetal movements, polyhydramnios, symmetrical and non-symmetrical fetal growth retardation with marked decrease of abdominal and thoracic circumference, low-set ears, micrognathia, continuous flexure contracture of limbs, internal rotation of the femur, and clubfoot on the right.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):416-423
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700007
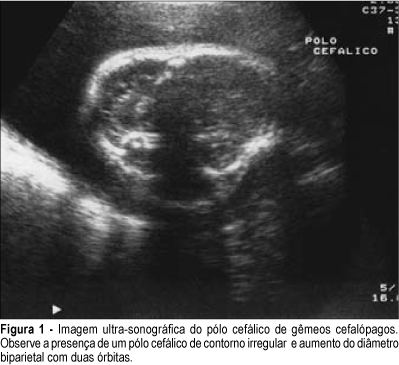
Conjoined twins have a rare prevalence and special curiosity among physicians and the general population. The reported frequency varies from 1:50,000 to 1:200,000 pregnancies. Its early diagnosis becomes very important when we think about pregnancy management, method of delivery and neonatal care. We describe two cases of conjoined twins diagnosed by ultrasound and magnetic resonance during prenatal care with the aim to better studying the fetus anatomy. The first conjoined twins were cephalopagus sharing head, thorax and abdominal wall and with two pelvis and four arms and four legs. The second were thoracopagus, united by thorax and part of abdomen. Magnetic resonance imaging contribution was not important to diagnose conjoined twins. However, it was useful to describe the shared organs, contributing to define fetal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):304-309
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500007
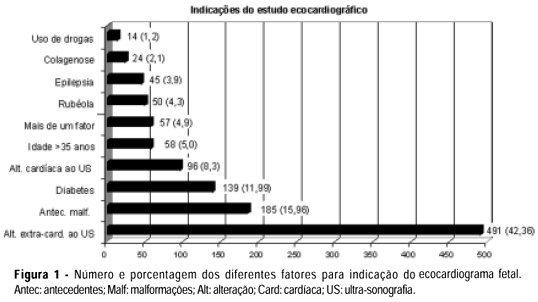
PURPOSE: to analyze the results of a screening and diagnostic program of arrhythmias and congenital heart disease in a reference hospital and the relevance of early diagnosis in the fetal and neonate evolution. METHODS: cardiac evaluation of 1159 fetuses was done in two different levels. Level I: by morphological ultrasound examination with the objective to detect the existence of either arrhythmias or structural cardiac malformations. Level II: by fetal echocardiography to establish the differential diagnosis. The results of level I in the arrhythmia group were compared with those of level II, and in the group with malformations the results of both levels were confronted with the neonate echocardiogram or necropsy. The kappa index was calculated to evaluate the concordance between the two levels. RESULTS: all detected arrhythmias in level I were confirmed in level II, there were no false negative cases and five patients with severe arrhythmia required pharmacological therapy. The diagnosis of structural malformation by level I had sensitivity of 72% and specificity of 98% and there were 28% of false-positive cases. In level II, the sensitivity and specificity of the diagnosis of congenital heart disease were 100 and 99%, respectively. The kappa index was 57% and indicated a moderate degree of concordance between the two levels. Fifty-one percent of the fetuses with diagnosis of cardiac malformations required pharmacological or invasive intervention immediately after birth. CONCLUSION: morphological ultrasound examination is a important tool in the screening of arrhythmias and congenital heart defects during fetal life. The sensitivity and specificity of the fetal echocardiogram were very high and the early diagnosis made it possible to treat the fetus with severe cardiac disease either during pregnancy or immediately after birth.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):244-250
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400007
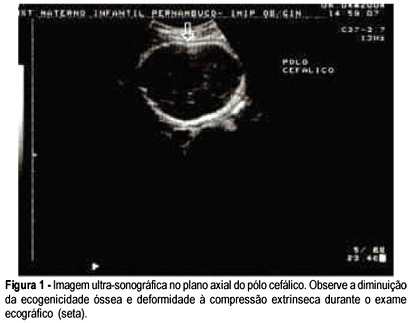
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a connective tissue disorder due to quantitative and qualitative anomalies in type 1 collagen, genetically transmitted by a dominant or recessive autosomal gene, leading to bone fragility. We report a case of a 19-year-old G1 PO patient referred to our institution following a screening ultrasound that demonstrated short limb fetal extremities. A level 3 scan was performed which evidenced an irregular cranial shape and compression of the cephalic pole with moderate transducer pressure. Limb shortening, decreased echoes and fractures of long bones were found on our scan evaluation. A vaginal delivery occurred at 35 weeks of gestation. The male newborn, weighing 1.990 grams had 6 and 8 in Apgar scores. The neonate was clearly abnormal, presenting irregular cranial shape, with poor ossification on X-ray, blue sclera, fractures and limb deformities. Postnatal evaluation was satisfactory and the neonate was discharged in good conditions. Prenatal diagnosis is important for an adequate pregnancy follow-up. Postnatal outcome was not related to vaginal delivery, as there were no recent fractures in the newborn.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(6):353-357
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000600009
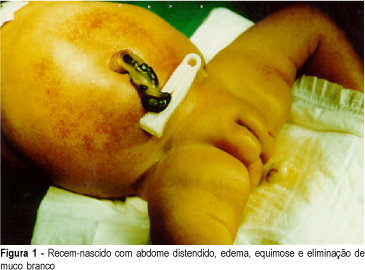
Introduction: meconium peritonitis as result of fetal intestinal perforation has a low incidence (1:30,000 deliveries) and high mortality (50% or more). Prenatal ultrasound findings include fetal ascites and intra-abdominal calcifications. Evidence suggests that prenatal diagnosis can improve postnatal prognosis. Case Report: R.C.M.S., 22 years, II pregnancy O para, presented ultrasound (12/02/98) with diagnosis of fetal ascites. Investigation for hydrops fetalis was performed and immune and nonimmune causes were excluded. Severe fetal ascites persisted on subsequent ultrasound examinations, without calcifications. Vaginal delivery occurred at 36 weeks (01/02/99), with polyhydramnios. Female neonate weighing 2,670 g, with signs of respiratory distress, abdominal distension and petechiae. Abdominal distension worsened progressively, with palpation of a petrous tumor in the right upper quadrant and elimination of white mucus at rectal examination. Radiological findings (01/04/99) were disseminated abdominal calcifications, intestinal dilatation and absence of gas at rectal ampulla. Exploratory laparotomy was indicated with diagnosis of meconium peritonitis. A giant meconium cyst and ileal atresia were observed and lysis of adhesions and ileostomy were performed. Initial postoperative evolution was satisfactory but was subsequently complicated by sepsis and neonatal death occurred (01/09/99). Conclusion: meconium peritonitis should be remembered at differential diagnosis of fetal ascites. In the present case, surgical indication could be anticipated if prenatal diagnosis were established, with improvement of neonatal evolution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(8):475-479
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000800008
SUMMARY Purpose: to evaluate the role of prenatal diagnosis of gastroschisis in the quality of assistance to and in the evolution of neonates with gastroschisis. Methods: a retrospective survey of 25 charts of neonates with gastroschisis treated at the State University of Campinas, between January 1989 and June 1998. Results: comparing the groups with prenatal (PN) and neonatal (NN) diagnosis, no differences regarding incidence of prematurity, birth weight and relations hip between weight and gestational age were observed. The median time from birth to surgery was 5 h. Such interval was shorter in the PN than the NN group (2.25 h versus 13 h; p<0.05). Primary closure of the defect was achieved in 17 neonates (68%) of both groups. Although this difference was not statistically significant, survival was higher among infants of the PN group (85.7% versus 45.5%). Conclusions: prenatal diagnosis of gastroschisis contributes favorably to improve perinatal assistance, resulting in reduced mortality of these children.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(12):750-758
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001200008
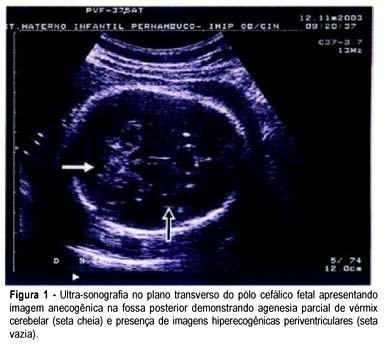
Congenital cytomegalovirus infection is an important clinical entity, due to its sonographic symptomatology. In Brazil, in utero diagnosis is not accomplished despite the improvements in diagnostic methods. We report a congenital infection including: splenomegaly and hepatomegaly, hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis, intracranial calcifications, hyperechoic kidneys, hyperechoic bowel, cardiomegaly, lung hypoplasia, ascites, and pericardial effusion. Fetal magnetic resonance imaging confirmed the sonographic findings. Amniocentesis was performed for cytomegalovirus PCR in amniotic fluid, which confirmed fetal infection. Fetal loss occurred in the 31st week of pregnancy. Necropsy studies confirmed the sonographic findings. The diagnostic methods have been useful to confirm congenital cytomegalovirus infection and to establish fetal outcome.