Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1040-1046
The purpose was to assess the rates of postoperative complications and the need of temporary stoma of laparoscopic surgical treatment for bowel endometriosis in a referral center.
The surgical indication, type of operation, operative time, length of hospital stay, need for a temporary stoma, rate of conversion to open surgery, postoperative complications were evaluated.
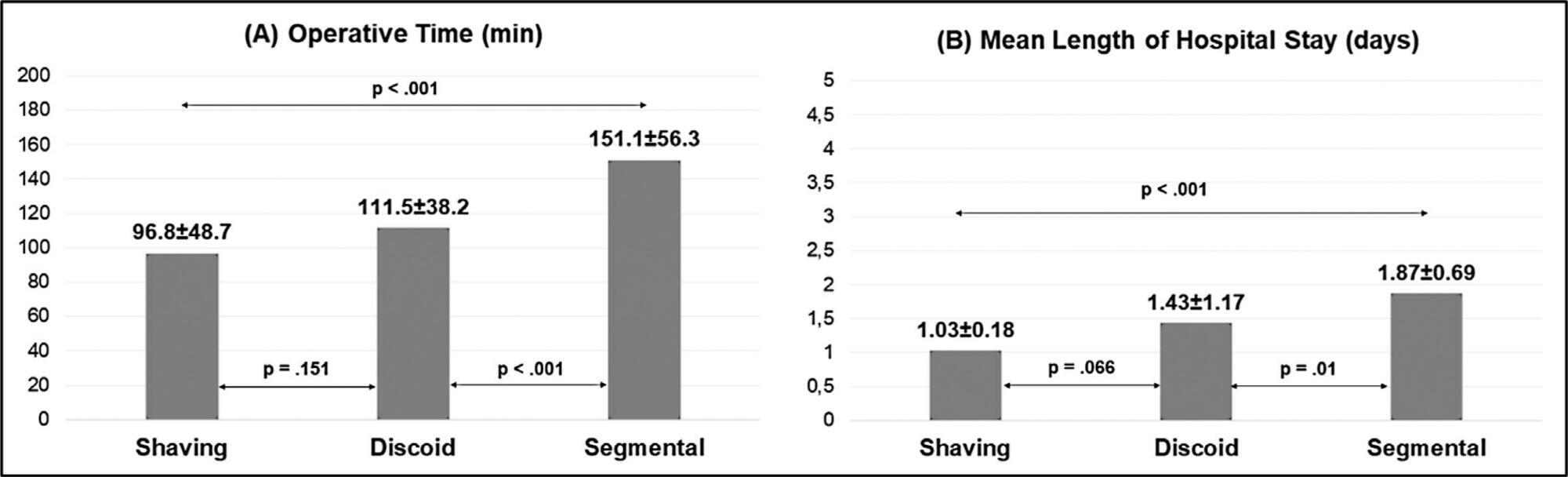
One-hundred and fifty patients were included. The average duration of surgery was significantly longer for segmental resection (151 minutes) than for disc excision (111.5 minutes, p < 0.001) and shaving (96.8 minutes, p < 0.001). Patients with segmental resection had longer postoperative lengths of hospital stay (1.87 days) compared with patients with disc excision (1.43 days, p < 0.001) and shaving (1.03 days, p < 0.001). A temporary stoma was performed in 2.7% of patients. Grade II and III postoperative complications occurred in 6.7% and 4.7% patients, respectively.
Laparoscopic intestinal resection has an acceptable postoperative complication rate and a low need for a temporary stoma.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):769-771
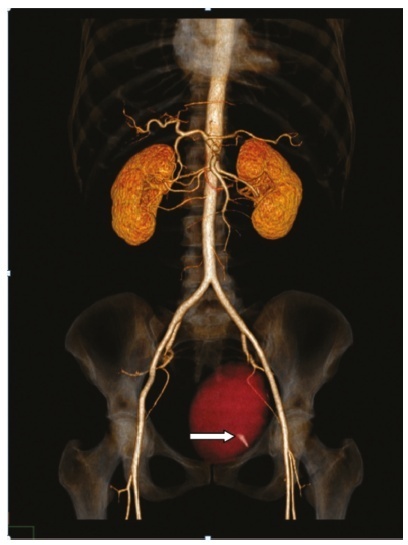
The placement of a suburethral sling is standard treatment for stress urinary incontinence. The transobturator technique (TOT) emerged as an alternative to minimize the risks of the blind insertion of needles, leading to a lower rate of perforation complications compared with the retropubic approach. We present a case of injury to a branch of the left obturator artery following the placement of a urethral sling using TOT, followed by intense bleeding and hemodynamic instability, which was treated with embolization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(7):361-366
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000700007
PURPOSE: to identify sensitivity alteration in the intercostal brachial nerve pathway using an extensiometer, and to observe the measurement reproducibility of the apparatus. METHODS: the Semmes-Weinstein extensiometer was used to evaluate the sensitivity along the intercostal brachial nerve pathway. Ninety-four women have participated in the study, divided into two groups: a CA Group composed of 47 women submitted to breast cancer axillary lymphadenectomy, and a comparative group composed of 47 women without breast cancer, who had not been submitted to any kind of axillary surgery. Each participant underwent anamnesis and two consecutive applications of the extensiometer. The Control Group responses to the extensiometer test were used as normality reference values. RESULTS: based on Control Group responses, the prevalence of sensitivity changes was 85.1% in the CA Group. Reproducibility of the extensiometer application was confirmed in the CA Group through the Kappa's test (p=0.8). CONCLUSIONS: in this studied sample, sensitivity alterations had high prevalence; evaluations made with the extensiometer were reproducible, and thus we consider the equipment reliable to evaluate sensitivity along the intercostal brachial nerve pathway.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(4):182-188
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000400005
PURPOSE: to observe the impact of obesity and other risk factors on the rate of failure in patients submitted to Burch's surgery for the treatment of urinary incontinence. METHODS: cases study of patients submitted to Burch's surgery, from 1992 to 2003. Patients were evaluated at the second post-surgery appointment (average 66 days) and after one-year follow-up, and classified in two groups: Continent and Non-continent. Variables analyzed were: age, parity, body mass index (BMI), menopause duration, duration of hormonal therapy, urodynamic evaluation, history of urinary tract infection, previous urinary incontinence surgery, diabetes, cystocele and uterine prolapse, time spent in hospital, necessity of self-probing, post-surgical spontaneous micturition, and surgical wound. Data were analyzed with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences 14.0 statistical package. For the comparison of continuous variables, Student's t-test or Mann-Whitney test were used, and Fisher exact and χ2 tests, for the categorical variables (p<0.05). RESULTS: at the second post-surgical evaluation, there was no significant difference between the two groups, concerning the variables analyzed. After one-year follow-up, from a total of 97 patients, 81 were continent and 16, non-continent, BMI and height being different between the groups. In the continent group, average BMI was 27.1 and height, 1.57 m, and, among the non-continent, 30.8 (p=0.02) and 1.52 m (p=0.01). The BMI>30 Odds Ratio was 3.7 (CI95%=1.2-11.5). CONCLUSIONS: obesity has shown to be an important risk factor for the surgery failure in the first follow-up year. Results show that patients with BMI>30 have 3.7 times more chance of being non-continent one-year after Burch's surgery than non-obese patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(1):22-27
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000100005
PURPOSE: to analyze complications, morbidity, mortality and survival rate in a group of patients with cervical cancer with central pelvic relapse after primary radiotherapy treatment. METHODS: retrospective study of a series of 16 cases of pelvic exenteration after primary radiotherapy treatment. Descriptive statistics, survival curve through Kaplan-Meier's method, and regression analysis to evaluate prognosis were performed. RESULTS: sixteen patients have undergone pelvic exenteration. Epidermoid carcinoma, IIb stage and undifferentiated grade were the most frequent conditions. Post-operatory tumor relapse occurred in half the cases. Eleven patients presented peri or post-surgical complications, the most frequent being pelvic infection, that of the surgical wound, and urinary fistulae. Global survival rate was 64.3%, with average follow-up of 11 months. Regression analysis did not detect any significant prognosis factor for the patient survival. CONCLUSIONS: the survival rate was 64.3%. No particular factor associated to poor prognosis has been found in the present series of cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(8):423-427
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000800007
PURPOSE: to identify the incidence and associated factors of surgical scar endometriosis. METHODS: a retrospective cohort observational study performed from the medical records of female patients attended at the Clinical Hospital of Univesidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG) with histopathological diagnosis of scar endometriosis from May 1978 to December 2003. RESULTS: a total of 72 patients were included in the study. The incidence of scar endometriosis after cesarean section was significantly higher than after episiotomy (0.2% and 0.06%, respectively; p<0.00001) with relative risk of 3.3. The women’s age, when diagnosed, ranged from 16 to 48 years old, (mean=30.8 years old). The scar location varied according to the previous surgery: 46 scars after cesarean sections, one after hysterectomy and one after abdominal surgery (48 lesions in the abdominal wall); 19 scars after episiotomy, one because of relapse and two after pelvic floor surgeries (22 pelvic wounds); two women had not been submitted to previous gynecological surgery (one umbilical endometrioma and one lesion in the posterior vaginal wall). Pain was the most frequent symptom (80%), followed by a node (79%) and, in more than 40%, the pain and the node suffered modification with menstruation. Other less frequent complaints were: dyspareunia, secondary infertility, pelvic pain, dysmenorrhoea, scar secretion, menorrhagia pain when evacuating. The mean time observed between the surgery and the beginning of the symptoms was of 3.7 years. The average size of the endometriomas was 3.07 cm. The diagnosis based on clinic evaluation was correct in 71% of the cases. The choice of treatment in all the cases was the surgical excision. In only one incident there was relapse and new intervention. CONCLUSIONS: scar endometriosis is a rare situation originated, in most cases, after obstetrical surgical procedure, with higher risk after cesarean section. It is a highly suggestive clinical condition, with a rare necessity of complementary diagnostic procedures, and the best treatment choice is the surgical excision.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(6):291-296
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000600003
PURPOSE: loss of cutaneous sensitivity has been related to lesions of the intercostobrachial nerve (ICBN) during the axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer treatment. We evaluated pain and cutaneous sensitivity in the ICBN dermatome of patients in which the nerve was preserved during the axillary dissection. METHODS: we carried out a prospective cohort study of 77 patients divided into: NP group (n=34), patients without ICBN preservation, and ICB group (n=43), patients in which the nerve was preserved. Cutaneous sensitivity was evaluated one year after surgery using 1) a modified McGill Pain Questionnaire; 2) clinical examination including brachial perimetry and evaluation of pain and tactile sensitivity; 3) Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments which allow an objective, qualitative, and quantitative evaluation of peripheral nerve lesions. RESULTS: pain was more frequently reported in the NP group (23/33) than in patients from the ICB group (17/42); p=0,012. Painful sensitivity was preserved in the majority of patients from the ICB group (38/42) but in only 11/33 patients from the NP group (p<0,01). There was no significant difference in the number of lymph nodes dissected between the two groups (p=0,06). CONCLUSIONS: patients with ICBN preservation had less pain and more preservation of cutaneous sensitivity, with no decreased number of axillary lymph nodes removed during the axillary dissection.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):289-292
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500009
Pneumoperitoneum, abdominal pain and paralytic ileus in the postoperative period are usually related to perforation of the gastrointestinal tract. The authors present a case of a patient submitted to cesarean section (abruptio placentae) who had a postoperative course of abdominal distention and abdominal pain. Abdominal X-ray showed important dilatation of the colon and small bowel. Pneumoperitoneum was seen on chest X-ray. An exploratory laparotomy was performed because of suspicion of intestinal perforation. The operation showed a marked dilatation of bowel, pneumoperitoneum, and infected hemoperitoneum and subaponeurotic hematoma (Escherichia coli), without any perforation. Postoperative recovery was good and antibiotics were given for 4 days (ceftriaxone + metronidazole). The patient was diseharged from hospital on the 7th day after laparotomy. After review of the literature the authors concluded that this case of pneumoperitoneum was probably related to infection by a gas-producing bacterium in a patient with clinical findings of paralytic ileus.