Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):507-512
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of osteoporosis in climacteric women and analyze the influence of general and reproductive risk factors on bone mineral density. METHODS: a cross-sectional study with the evaluation of the 473 hospital records of climacteric women followed up at the Menopause Outpatient Facility of CAISM/Unicamp, between 03/28/2000 and 04/17/2001. These women were at least 12 months in amenorrhea and presented the results of a bone densitometry study performed at the Nuclear Medicine Department of HC/Unicamp. The following variables were evaluated: age, color, body mass index, level of education, smoking, use of medication, age at menopause, parity, use and length of hormone replacement therapy and its effect on bone mineral density. Statistical analyses were performed using logistic regression ajusted by age and hormone replacement therapy use. RESULTS: the mean age of the studied women was 53.9 years (± 7.1 SD) with mean age at menopause being 45.9 years (± 6.9 SD). Osteoporosis occurred in 14.7% and osteopenia in 38% of the cases in the lumbar vertebrae (L2-L4 interspace) and in 3.8 and 32.7% in the femur, respectively. Logistic regression adjusted to age and hormone therapy showed an association between the following variables: level of education, age at menopause and body mass index. CONCLUSION: there was a high prevalence of osteoporosis and osteopenia in the studied population. Advanced age, lower level of education, late menarche, early menopause and lower body mass index were identified as risk factors for developing decreased bone mass in the studied population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):435-441
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700006
Purpose: to describe sociodemographic characteristics of a group of climacteric women in order to discover the frequency and the variables associated with obesity and android profile of body fat distribution. Methods: an observational study was carried out in 518 patients aged 45 to 65 years, in a climacterium outpatient clinic. Age, color, menopausal status, duration of menopause, physical activity, smoking status, diet, alcohol intake, personal and family antecedents of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, dyslipidemia and obesity were considered. Body mass index and the waist/hip ratio were the dependent variables. For the statistical analysis Wilcoxon test, Pearson's correlation coefficient, with a 5% level of significance, and multivariate analysis using regression model were used. Results: more than two thirds of the participants were nonobese with an android profile and postmenopausal. One fourth had physical activity and were smokers; half reported an inadequate diet and one fifth were alcoholics. Patients with an android profile presented higher mean age than women with gynecoid pattern. Personal antecedents of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes and family history of diabetes were related to obesity and android pattern. Postmenopausal status was significantly associated with the android profile. Conclusions: the majority of the participants were nonobese with an android profile, white, postmenopausal, sedentary, neither smokers nor alcoholics. The main factors related to obesity and android pattern were personal antecedents of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes, family history of diabetes and particularly, postmenopausal status with android profile.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(5):337-343
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500006
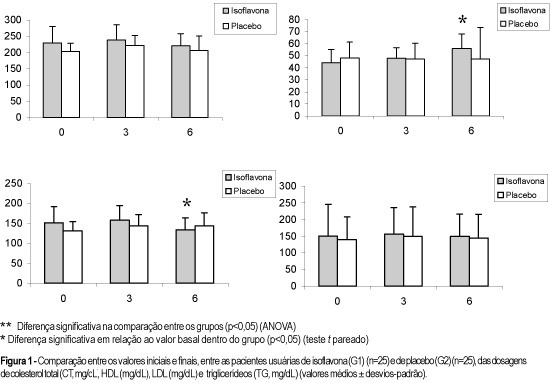
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of soy germ isoflavone on menopausal symptoms and blood lipids in postmenopausal women. METHODS: a prospective study was performed on 50 women, randomly divided into two groups: 25 women on soy germ isoflavones (60 mg/day, capsules) (G1) and 25 women on placebo (G2). Inclusion criteria: women with hot flushes and FSH >40 mIU/mL, non-vegetarian, non-smoker, non-Asiatic, not in use of hormone replacement therapy and without disease of the gastrointestinal tract. For six months, the menopausal Kupperman index (MKI) and hormonal and lipid profiles were assessed. For statistical analysis, ANOVA, t test and the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests were used. RESULTS: the median MKI values, initially similar in both groups, decreased in G1 at two and four months (MKI = 14 and 9, respectively), and in G2 at two months (MKI = 15) (p<0.01). At six months, isoflavone was significantly superior to placebo in reducing hot flushes (44 versus 12%, respectively). At the end of the study, in the isoflavone group, an increase in estradiol levels (from 16,8±7.3 to 18,0±6.7 ng/dL) (p<0.05) was observed, with no alteration in FSH, LH and vaginal cytology; there was also a reduction of 11.8% in LDL (from 151.5±39.2 for 133,6±26.4 mg/dL) and a HDL increase of 27.3% (from 44.0±11.3 to 56.0±11.9 mg/dL) (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: soy germ isoflavone induced favorable effects on menopausal symptoms and lipid profile, showing to be an interesting option for alternative therapy in postmenopausal women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(4):237-241
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000400003
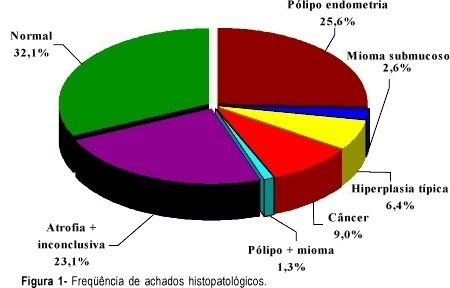
PURPOSE: to investigate the accuracy of hysteroscopy as a method for the evaluation of the uterine cavity in women with postmenopausal bleeding. METHODS: a cross-sectional study that consisted of the evaluation of 78 women with postmenopausal bleeding submitled to histeroscopy and directed biopsy in the period from January 2000 to June 2002 in the Bahia State Oncology Center. Hysteroscopy findings were classified as benign (leiomyoma, polyp, atrophy, normal) and suspect (hyperplasia, thickening, cancer) and the histopathologic findings as benign (leiomyoma, polyp, non-atypical hyperplasia, atrophy) and malignant (cancer and atypical hyperplasia). The results of hysteroscopy were compared with the pathologic findings. RESULTS: in relation to the suspect results (thickening, hyperplasia and cancer) hysteroscopy sensitivity and specificity were 85.7 and 88.7%, respectively. Positive and negative predictive values were 42.83 and 98.4%. Likelihood ratios of positive and negative tests were 7.6 and 0.16. Accuracy was 88.4% and kappa index, 0.5. CONCLUSION: hysteroscopy alone did not show an acceptable accuracy in the study, reinforcing the idea that its main advantage is to direct the biopsy, and it must always be associated with the histological diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):481-487
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800003
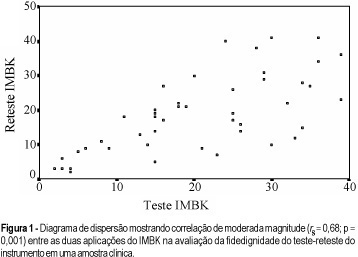
Purpose: based on the knowledge that the reliability of an instrument is essential for a correct interpretation of the results of research, the purpose of the present study is to evaluate the reliability of one of the menopausal indexes more often used in clinical practice and research, the Blatt and Kupperman Menopausal Index (BKMI). Methods: the population consisted of 60 climacteric patients attended at the Gynecology Outpatient Clinic of the Lauro Wanderley University Hospital of the Federal University of Paraíba in João Pessoa city. The reliability coefficient was analyzed by the test-retest method, whose application was done on two different occasions with an interval of four weeks, without administration of medicines. Results: the variation of the score observed with the application of BKMI at the first measurement was 2 to 41, with a median of 18 and mean of 18.8 (± 10.76), while at the second measurement, the menopausal index was 20.2 (± 10.51), median 19, and values ranging from 2 to 39. Despite these results, a Speaman (r s) coefficient of 0.68 (p = 0.001), which is a coefficient of only moderate intensity, was observed. Conclusions: the test-retest reliability in the application of the BKMI shows that, although this instrument presented a statistically moderate reliability, the intensity observed does not represent a reliable measurement. Considering that a correlational study is only a type of screening of the quality of a measurement method, we concluded that other studies must be performed with the purpose of evaluating the reliability and the validity of the BKMI. It is possible that the attribuition of different values to the items of BKMI and the inclusion of symptoms directly related to the estrogenic defficiency, like symptoms of vaginal atrophy, would make the instrument more reliable.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):475-479
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800002
Purpose: to evaluate the bone mineral density of postmenopausal women with previous hysterectomy and with bilateral ovarian conservation compared to a group of nonhysterectomized naturally menopausal women. Methods: this is a cross-sectional study of bone densitometry (Lunar DPX) in 30 menopausal women hysterectomized when in the premenopause compared with 102 naturally postmenopausal women. Results: the mean age, body mass index, color of the skin, smoking habits, educational level, menarche, parity and previous tubal ligation were similar in the studied groups. Bone mineral density average and the T-score of the three femural sites analyzed by the Bonferroni test did not show significant differences. The bone mineral density average and the T-score of the lumbar spine were analyzed by the Student t test and did not show statistical differences. Conclusion: these findings suggest that premenopausal hysterectomy with bilateral ovarian conservation does not cause an additional reduction in bone mineral content when evaluated in the postmenopause.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(10):621-626
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001001000002
Purpose: to compare bone mineral density (BMD) of postmenopausal women with and without the antecedent of tubal ligation, as well as to evaluate the associated factors that affect the bone mineral density of femur and lumbar spine of both groups. Methods: 70 postmenopausal women in each group were analyzed at CAISM-UNICAMP, during the year of 1998. All women answered a questionnaire about some clinical and reproductive characteristics and underwent bone densitometry (Lunar DPX) to measure bone mineral density of the femur and lumbar spine. Statistical analyses were performed using Student's t-test, Fisher`s exact test, Pearson c² test, Bonferroni`s test and multiple regression analysis. Results: mean age of patients was 53.2 years and for controls it was 52.6 years. Mean age of 48 years at menopause was similar in both groups. Mean age at tubal ligation surgery was 33.7 years and time since surgery was 18 years. The multiple comparison of the average bone mineral density of femur and lumbar spine did not show statistical differences between the groups. The percentage distribution of the T-score categories of femur and lumbar spine, classified into normal and altered, also did not show statistical differences between both groups. Multiple regression analysis showed that bone mineral density of femur was directly associated with body mass index, but age was indirectly associated. The variables dark skin, parity, age at menopause, educational level and body mass index were directly associated with bone mineral density of lumbar spine, but age at menarche was inversely associated. Conclusion: these findings suggest that tubal ligation does not seem to cause an additional reduction in bone mineral density when evaluated in postmenopause.