Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):77-81
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200004
Purpose: to evaluate the frequency of urinary disorders and variation of the urodynamic parameters according to the time of post-menopause. Method: two hundred forty-two post-menopausal women with urinary complaints were studied at the Division of Gynecology, Escola Paulista de Medicina, UNIFESP. They were grouped according to the time of post-menopause: group A - up to 4 years; group B - 5 to 9 years and group C - more than 10 years. They were submitted to anamnesis, gynecological examination and urodynamic study. The frequency of urinary alterations and the variation of the urodynamic parameters were analyzed, such as voiding volume; flow time; maximum flow rate, average flow rate; residual urine; vesical capacity at the first desire to void; maximum bladder capacity; maximum urethral closure pressure and functional profile length, with full and empty bladder. The data were statistically analyzed. Results: the most common clinical diagnosis was stress urinary incontinence in the three groups, but the longer the time of post-menopause, the more frequently urinary urgency was observed. Regarding urodynamic diagnosis, 93.6%, 84.6% and 90.7% of the patients of the groups A, B and C, respectively, presented stress urinary incontinence, while 4.8%, 13.5% and 6.2% revealed detrusor instability. There was a decrease in the following urodynamic parameters, according to the time of post-menopause: flow time, maximum flow rate and vesical capacity at the first desire to void, and an increase of the residual urine. Conclusion: in spite of the high incidence of urinary symptoms such as urgency incontinence, stress urinary incontinence was the main urinary problem we have found in post-menopause.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(1):47-54
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000100008
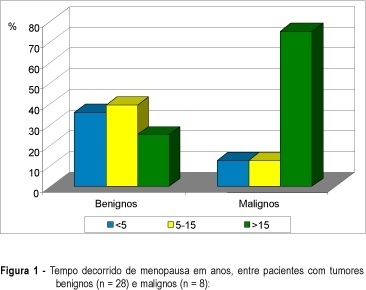
Purpose: to evaluate clinical and ultrasonic findings in patients with pelvic tumors at postmenopause and to correlate them with the final diagnosis. Patients and Methods: thirty-six postmenopausal women with pelvic tumor diagnosis were prospectively evaluated through clinical examination and endovaginal ultrasonography. Clinical follow-up with no surgical procedures was indicated for anechoic cystic tumors with or without thin unique septation and volume under 50 cm³. Needle aspiration was indicated for tumors with the same aspect, and volume of 50 to 100 cm³, whereas exploratory laparotomy was performed in the remaining patients. Diagnosis defined two groups of patients: benign (28) and malignant (8) pathologies. Results: anechoic cystic tumor with or without a thin septum indicates benignity (p = 0.0091). Tumors with solid areas indicate malignancy (p = 0.0024). Ascites correlates with malignancy (p = 0.0278). Heterogeneity, thick capsule, thick septa, and papillary projections predominated in malignancies but without no statistical significance (p > 0,05). Tumor volume indicates malignancy, with a median of 85.2 cm³ in benign tumors and 452.5 cm³ in malignancies (p = 0.0048), with a cutoff at 295 cm³ (sensitivity = 83.3% and specificity = 85.2%). Following this protocol, all malignancies were submitted to surgery and 11 benign tumor patients were treated with a conservative protocol (39.3% of all benign patients). Conclusion: conservative management is an adequate protocol for women with anechoic pelvic tumors with low volume, with or without single thin septum and without ascites. Differentiation between benign and malignant of complex and/or high volume tumors requires complementary investigation.
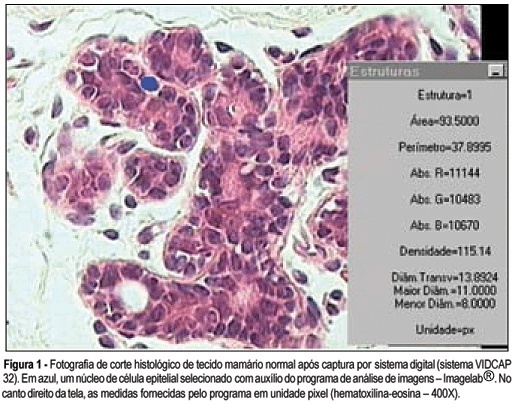
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):658-663
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100005
PURPOSE: to analyze breast tissue of postmenopausal women before and after six months of continuous combined estrogen-progestin replacement therapy (0.625 mg conjugated equine estrogens associated with 2.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate). METHODS: all patients were evaluated before treatment and considered eligible to receive the drug. The material was obtained from the upper outer left quadrant, through a percutaneous large-core breast biopsy. Epithelial density and nuclear volume on hematoxylin-eosin-stained plates were evaluated for the morphological study. Morphometry was graphically analyzed by optical microscopy (400X) after acquisition of image by a digital image-capturing system (Vidcap 32) and image analysis system (Imagelab 2000 Software®). RESULTS: after six months of estrogen-progestin replacement therapy, there was a significant increase in nuclear volume in late postmenopausal women (103.6 to 138.1 µm³). There was no difference in epithelial density with the treatment (before 0.08 and later 0.10). CONCLUSIONS: estrogen-progestin combined replacement therapy for six months induced an enhacement in nuclear volume of breast epithelial cells, suggesting an increase in their metabolic activity. However, it is important to emphasize that this finding was observed only in late postmenopausal women. The increased nuclear volume could precede other events that confirm the stimulation of cellular proliferation by these hormones.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):292-297
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500005
PURPOSE: to verify if there is a relationship between the clinical periodontal parameters and estrogen levels and bone mineral density (BMD). METHODS: forty-six post-menopausal women aged 44 to 68 years (52.2±4.8) and 15 women aged 35 to 54 years (44.7±7.5) were evaluated. Periodontal parameters like probing depth (PD), clinical attachment loss (CAL), and missing teeth (MT) were compared with estrogen levels (sufficient and insufficient) and BMD (normal, osteopenic and osteoporotic). Data of the mean difference between the groups were compared by the Aspin-Welch test. RESULTS: the means of PD, CAL and MT, when associated with the normal (2.1±0.5; 2.9±1.4 and 10.6±5.0), osteopenic (2.3±0.7; 3.0±1.1 and 12.8±5.1) and osteoporotic BMD (2.4±0.6; 2.7±0.9 and 14.3±5.7), did not show statistical difference (p>0.05). A significant difference was found between the control group and postmenopausal women for CAL and MT. When compared with the estrogen levels the results did not show a difference regarding the periodontal parameters. CONCLUSION: although some studies showed a positive correlation with osteoporosis and estrogen level, in this population of menopausal women these findings were not confirmed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(1):18-23
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000100004
PURPOSE: to characterize postmenopausal endometrial polyps and to determine risk for concomitant premalignant and malignant pathology. METHODS: a retrospective study including 82 postmenopausal women with a histological diagnosis of endometrial polyps who underwent hysteroscopic polypectomy, after a diagnosis of endometrial thickening made by transvaginal ultrasound, was performed. Medical reports provided clinical and gynecological history, data related to the operative hysteroscopy and definitive histological findings. RESULTS: among the 82 patients who underwent hysteroscopic polypectomy, 10.9% were receiving some type of hormonal therapy. Twenty-eight women (34.1%) reported abnormal vaginal bleeding. Single polyp was encountered in 56 women (68.3%), two polyps were found in 19 cases (23.2%) and in 7 cases (3.6%), three or more polyps were found. The definitive histopathologic analysis revealed 63 (76.8%) benign polyps, 17 (20.8%) hyperplastic polyps (10 cases 12.2% - of simple endometrial hyperplasia without cytologic atypia and 7 cases 8.6% - of complex endometrial hyperplasia without cytologic atypia). Two polyps (2.4%) were diagnosed as harboring neoplasia. For the statistical analysis we employed chi2 test improved by Yates. The authors correlated the polyps' histology with the occurrence of abnormal vaginal bleeding (p=0.0056), number of endometrial polyps (p=0.921) and time after menopause (p=0.720). CONCLUSIONS: endometrial polyps are commonly found entities in postmenopausal women, related with low frequency to endometrial hyperplasia or carcinomas and only histological evaluation seems to allow the exclusion of premalignant and malignant pathology.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):118-124
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of the association of estrogen and androgen on the quality of life and sexuality of women during climacterium. METHODS: ninety-six postmenopausal women with vasomotor symptoms and sexual dysfunction were included. The participants were randomly divided into three treatment groups with 32 pacients each: placebo, conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) (0.625 mg per day) and CEE (0.625 mg per day) associated with methyltestosterone (2.5 mg per day). The length of the treatment period was three months. The Women Health Questionnaire (WHQ) and the Modified Sexuality Questionnaire were applied to evaluate the quality of life and sexuality before and after the treatment. Some parameters of cardiovascular risk, endometrial echo and hepatic toxicity were evaluated. ANOVA was used for data analysis followed by the Fisher test and the Shapiro-Wilk post hoc test. RESULTS: the improvement in WHQ parameters was significant in the hormonal treatment groups (CEE and CEE + methyltestosterone) compared to the placebo group. However, there were no differences in somatic symptoms among the three groups. The association of estrogen with androgen significantly improved sexual function (score (mean): 64 vs 67, p<0.05) and depressive humor (score (mean): 75 vs 80, p<0.05) compared to estrogen alone. This therapy also presented a large number of WHQ questions with a high score (p<0.05). The use of CEE associated with methyltestosterone decreased the total cholesterol (212±42 and 194±43, before and after the treatment, respectively) and HDL colesterol (56±16 and 48±14, before and after the treatment, respectively), and slightly increased the endometrial echo (4.7±2.3 and 5.5±2.3, before and after the treatment, respectively). No signifcant changes in liver enzymes during the treatment period was detected. CONCLUSIONS: estrogen associated with methyltestosterone resulted in significant improvement in the quality of life and sexuality of postmenopausal women. This effect was superior to estrogen alone and placebo. The effect of treatment with the estrogen-androgen association was evident regarding depressive humor and sexual function questions of the WHQ.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):479-484
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800008
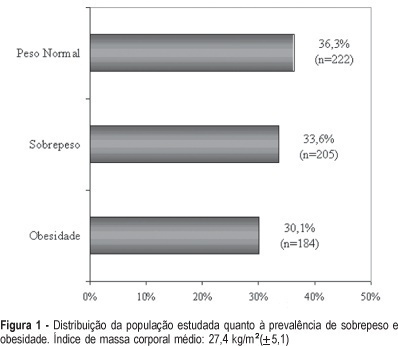
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of overweight and obesity among climacteric women. METHODS: this cross-sectional study included 611 women aged between 45 and 60 years attended at a climacteric clinic from January to June 2003. The prevalence of overweight and obesity was evaluated through the body mass index (BMI). Overweight or obesity was considered when there was a BMI equal or higher than 25 kg/m². Sociodemographic and reproductive variables as well as life style were also evaluated. The chi2 test followed by logistic regression was performed for statistical analysis. RESULTS: the average age of the studied women was 51.4 (±4.4) years, whereas 52.9% of them were postmenopausal. About 63.7% of them had a BMI equal or higher than 25 kg/m². The prevalence of overweight and obesity was 33.6 and 30.1%, respectively. The prevalence of overweight and obesity was higher among older women (OR=1.2; 95%IC: 1.1-1.4) or non hormonal therapy users (OR=1.8; 95%IC: 1.2-2.8). The opposite was observed among the women without a professional occupation (OR=0.6; 95%IC: 0.5-0.9) or a steady partner (OR=0.7; 95%IC: 0,4-0,9). CONCLUSIONS: in this study, the prevalence of overweight and obesity was influenced by age, but not by the menopausal status. The association between the marital status and occupation and the BMI strengthens the hypothesis that the health of the climacteric women may be influenced by biological factors as well as by psychosocial factors and life style. The lowest prevalence of overweight and obesity among the users of hormonal therapy may be explained by possible restrictions in relation to its prescription for women with previous overweight or obesity. Further studies are necessary to get more conclusive results, in particular with longitudinal studies.
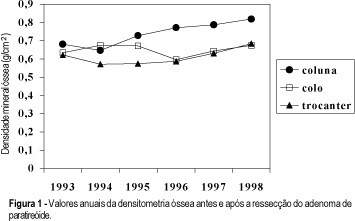
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):239-241
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000400009
Osteoporosis is an important disease which can affect millions of patients all over the world, leading to complications, often even to death. Prevention and the early diagnosis may help in the success of treatment but there are diseases which can occur at the same time. Primary hyperparathyroidism is a diagnosis which must be remembered in women after the menopause.