Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):647-652
To determine cervical biometry in pregnant women between 18 and 24 weeks of gestation and the ideal mode of measurement of cervical length in cases of curved and straight cervical morphology.
The uterine cervices of 752 low-risk pregnant women were assessed using transvaginal ultrasound in a prospective cross-sectional study. In women with straight uterine cervices, cervical biometry was performed in a continuous manner. In women with curved uterine cervices, the biometry was performed using both the continuous and segmented techniques (in segments joining the cervical os). Polynomial regression models were created to assess the correlation between the cervical length and gestational age. The paired Student t-test was used to comparemeasuring techniques.
The cervical biometry results did not vary significantly with the gestational age and were best represented by linear regression (R2 = 0.0075 with the continuous technique, and R2 = 0.0017 with the segmented technique). Up to the 21st week of gestation, there was a predominance of curved uterine cervix morphology (58.9%), whereas the straight morphology predominated after this gestational age (54.2%). There was a significant difference between the continuous and the segmented measuring methods in all the assessed gestational ages (p < 0.001).
Cervical biometry in pregnant women between 18 and 24 weeks was represented by a linear regression, independently of the measuring mode. The ideal measuring technique was the transvaginal ultrasound performed at a gestational age 21 weeks.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(11):547-551
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009001100004
PURPOSE: to study the effect of acoustic stimulation in the fetal cardiac response, according to parameters from computerized cardiotocography in low risk pregnancies. METHODS: twenty low risk pregnant women were included in the study, according to the following criteria: age over 18; single gestation, living fetus; gestational age between 36 and 40 weeks; amniotic liquid index over 8.0 cm and absence of fetal malformation. Cases with post-natal diagnosis of fetal anomaly were excluded. Computerized cardiotocography was performed for 20 minutes, before and after fetal acoustic stimulation. Results were analyzed by the t test for dependent samples, with significance level at p<0.05. RESULTS: acoustic stimulation was successfully performed in all cases analyzed. By the analysis of the cardiotocographic parameters, there was no significant difference when the pre and post-stimulation parameters were compared: average number of fetal movements per hour (55.6 versus 71.9, p=0.1); mean basal fetal heart rate (FHR) (135.2 versus 137.5 bpm, p=0.3); mean FHR increases>10 bpm (6.5 versus 6.8, p=0.7); mean FHR increases>15 bpm (3.8 versus 4.3, p=0.5); mean duration of high FHR variation episodes (11.4 versus 10.9 min, p=0.7); mean duration of low FHR variation episodes (2.5 versus 1.1 min, p=0.2), and mean short-term variation (10.6 versus 10.9 ms, p=0.6). CONCLUSIONS: in low risk gestations at term, computerized cardiotocography has not evidenced differences in the FHR parameters after the fetal sonic stimulation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(9):453-460
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000900006
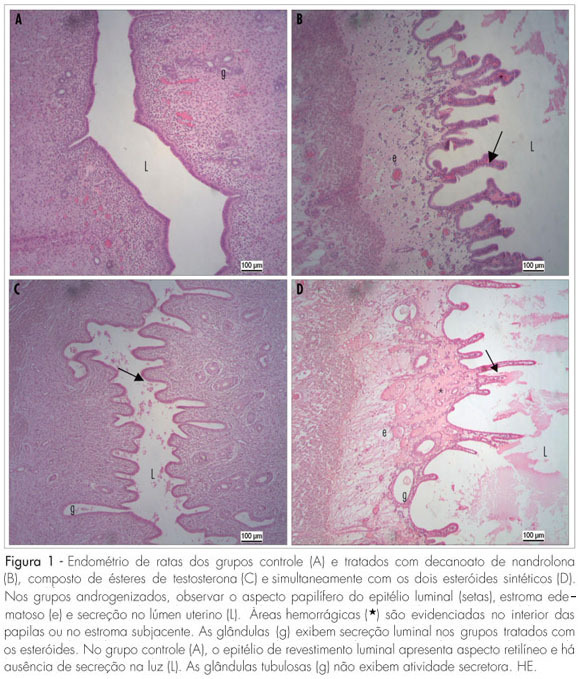
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of the administration of two synthetic steroids in the uterus morphology and in the reproductive parameters of adult female rats. METHODS: divided into four experimental groups: control (C; physiological solution); treated with nandrolone decanoate (DN; 7.5 mg/kg of body weight); with a testosterone esters compound (T; 7.5 mg/kg); and simultaneously with DN and T (7.5 mg/kg of each steroid), in a single intraperitoneal weekly dose, for eight weeks. Five females of each group were sacrificed and the uterine horns were collected, weighted and prepared for histological and morphometrical evaluation. The remaining rats were mated with normal male rats for reproductive parameters evaluation, composing the groups treated during the pre-gestational period. Another group of 20 female rats were treated during the gestational period (7th-14th days). For data analysis, the Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric variance analysis was used, followed by the test of Dunn or of Student-Newman-Keus (5% significance level). RESULTS: there was a significant body weight increase in the androgenized females (ND: 305±50; T: 280±35; ND+T: 275±30 versus C: 255±22 g; p<0.05). Uterine weight was not affected by the steroidal treatment (ND: 0.6±0.2; T: 0.4±0.04; ND+T: 0.7±0.1 versus C: 0.4±0.09 g). All the androgenized females presented estral acyclicity and endometrium characterized by papilliferous luminal lining, oedematous stroma with hemorrhagic areas and secretory activity. There were changes in the morphometrical thickness parameters of the luminal epithelium, myometrium and perimetrium in the androgenized groups. None of the female rats got pregnant when treated with steroids in the pre-gestational period and the treatment during organogenesis affected negatively the reproductive parameters. CONCLUSIONS: steroidal agents alter the uterine structure and impair fertility and gestational outcome in female rats.