Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(10):725-730
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003001000005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the perinatal outcome of fetuses with congenital anomalies of the urinary tract. METHODS: we reviewed the perinatal outcome of 35 fetuses with congenital anomalies of the urinary tract. The following characteristics related to the uropathy were analyzed: type (hydronephrosis, dysplasia and renal agenesis), side of lesion (bilateral or unilateral), and level of the obstruction (high or low, in hydronephrosis). The perinatal outcome was evaluated according to these characteristics. The data were analyzed by the c² test and by the exact Fisher test. The level of significance was 0.05. RESULTS: the incidence of hydronephrosis was 68.6%. Half of the fetuses had unilateral hydronephrosis. Renal dysplasia occurred in 17.1% of the cases; 83.3% of these were bilateral and 16.7%, unilateral. The incidence of renal agenesis was 14.3%, all bilateral. The fetuses with dysplasia/agenesis had a 91% incidence of oligohydramnios, preterm birth, low birth weight, and death. In the group with bilateral disease the presence of oligohydramnios, preterm birth, low birth weight, death, urinary tract infections, and the need of hospitalization for a period greater than 7 days was significant when compared to the group with unilateral disease. The need of hospitalization for a period greater than 7 days in patients with low obstruction was significantly higher when compared to the patients with high obstruction. CONCLUSIONS: hydronephrosis, bilateral disease, and lower obstruction were the most frequent uropathies. The dysplasia/agenesis group had a worse prognosis when compared with the hydronephrosis group. Bilateral disease had a worse prognosis when compared with the unilateral disease group. In the low obstruction group, the need for a period of hospitalization greater than seven days was higher than in the high obstruction group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(6):419-423
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the perinatal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by oligohydramnios, not due to premature rupture of membranes (PRM), diagnosed until the 26th week of gestation. PATIENTS AND METHODS: we analyzed retrospectively the cases of oligohydramnios that occurred from January 1994 to December 2000, and were diagnosed until the 26th week of gestation. Oligohydramnios was present when the amniotic fluid index was less or equal to 5.0 cm. After diagnosis the patients were followed-up with serial ultrasound evaluation, with emphasis on the maintenance of the oligohydramnios state. When remission of the oligohydramnios occurred, patients remained in the study. Cases due to PRM, fetal death detected on the first examination and the women who gave birth in another institution were excluded from the study. Concerning the patients, the presence of clinical and obstetric diseases was investigated. As regards the newborns, we evaluated birth weight, time of admission/death, occurrence of death or malformations. RESULTS: twenty-seven cases of oligohydramnios were analyzed. Thirteen fetuses had congenital anomalies, and among them, eight had anomalies of the urinary tract, four of the nervous system and one had cystic hygroma. Fourteen patients had a clinical or an obstetric disease, mainly hypertension (10 cases). In addition, we found three cases of placenta previa and one case of thyropathy. There were thirteen fetal deaths and fourteen neonatal deaths. CONCLUSION: oligohydramnios not due to PRM, occurring in the second trimester of gestation, independent of the etiology or the presence of congenital anomalies, was associated with a fatal perinatal result.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):207-210
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300010
Bronchopulmonary sequestration is a mass of anomalous lung tissue, which in general does not communicate with the tracheobronchial tree and receives systemic arterial blood supply more often originating from the aorta. This is such a rare malformation, that is not always thought of as a diagnostic possibility. We present a case of bronchopulmonary sequestration and emphasize the significant role of color Doppler in its diagnosis, as it identifies the artery originating from the descending aorta irrigating the sequestration. We also present its three-dimensional ultrasound features.
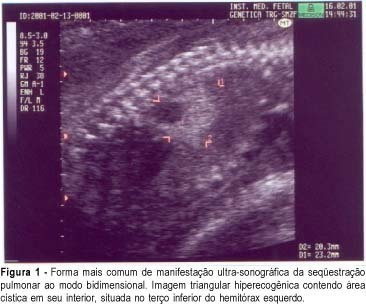
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):511-517
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800007
Purpose: to demonstrate the types of fetal malformations in multiple pregnancy and their relation to chorionicity. Methods: one hundred and sixty-nine multiple pregnancies were evaluated. In all cases prenatal ultrasound examination was performed during antenatal care. Chorionicity was defined by: first trimester ultrasound evaluation (absence of lambda sign); presence of two separate placentas; different fetal sex; pathological placental examination. Results: twenty-four (14.2%) fetal malformations were observed, 22 in twin and 2 in triplet pregnancy. In the group with fetal malformations 13 were monochorionic, 4 dichorionic and in 5 the chorionicity was unknown. Some malformations were unique to twins (conjoined twins n = 5, acardiac twin n = 3) and others were nonunique to twins. The gestational age at delivery was lower in the group with fetal malformations compared to the group without fetal malformations. Conclusion: the majority of malformations occurred in the monochorionic pregnancies. In multiple pregnancies early determination of chorionicity is helpful to establish the prognosis and to plan the management of pregnancy.
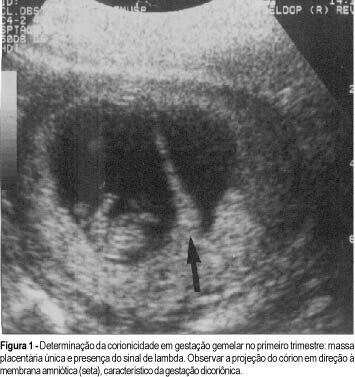
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(9):575-580
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000900005
Purpose: to check alcohol consumption during pregnancy regarding type of drink, amount ingested, awareness of alcohol consumption risk, and tracking its consumption during prenatal care. Methods: interview of 445 women who had just given birth in a maternity hospital from January to May, 1999. The data analysis was performed using Student's t test and Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test. Results: of the women interviewed, 66.3% did not consume alcohol, 17.8% consumed it throughout pregnancy and 15.9% consumed it until pregnancy was confirmed, which occurred when they were 9.6 weeks pregnant on average; 98.7% of the women consumed it on weekends or at parties, and 1.3% daily. The mean ingestion was 14.74 grams/occasion for those who consumed alcohol throughout pregnancy and 25.83% grams/occasion for those who consumed it until pregnancy was confirmed. There were statistical differences between the mean rates in both groups. The mean intake per occasion was classified as moderate. The most ingested alcoholic beverage was beer (64.0%). Regarding awareness of the risk of alcohol intake, 71.5% believe that it is not good for the fetus health, 15.5% believe that it is not good for their own health. Alcohol consumption tracking was referred to by 48.8% of the women. Conclusion: a great number of women consumed alcoholic drinks at some time during pregnancy, despite being aware of the risks to their fetus. Prenatal care is not used as a favorable occasion for alcohol consumption tracking as well as for discontinuing its intake.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(9):561-566
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000900003
Purpose: to evaluate fetuses with facial cleft as to type of lesion, associated malformations and aneuploidies. Method: the following parameters were evaluated: maternal age and previous history, gestational age at diagnosis, lesion side, type of lesion, presence of associated malformations and aneuploidies, mortality rate and postnatal follow-up. Results: forty fetuses had facial cleft, 18 (45%) cases had cleft lip, 19 (47.5%) had cleft lip and palate, and 3 (7.5%) cases presented with cleft palate. Isolated facial cleft was observed in 10 fetuses (25%), all of them unilaterally located. Aneuploidies were identified in 10/30 (33.33%) of the patients with associated malformations. Cleft lip and palate was more often seen in this group (18/30 - 60%), followed by bilateral lesion (8/30 - 26.7%) and median cleft (10/30 - 33.3%). Conclusion: facial clefts are considered excellent signs for the presence of associated malformations and fetal aneuploidies. Fetuses with facial cleft must be referred to specialized centers in order to have specialized ultrasound and genetic analysis which can provide the best prenatal counseling for these cases. Isolated facial cleft was associated with very good prognosis.
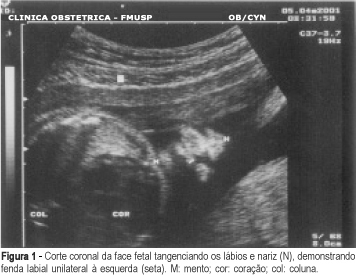
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(8):521-526
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000800004
Purpose: to assess the evolution of epileptic seizures during pregnancy and the occurrence of malformations in neonates born to epileptic mothers who used anticonvulsant drugs during pregnancy, as well as the perinatal characteristics of the newborns. Methods: a total of 126 medical records of epileptic patients seen at the high-risk pregnancy outpatient clinic were analyzed retrospectively in terms of the following variables: age, parity, diagnosis of the type of epileptic seizure, anticonvulsant drug used during the prenatal period, evolution of epileptic seizures during the prenatal period, type of delivery, gestational age at resolution, and perinatal characteristics of the newborns. Results: the incidence of pregnant women with epilepsy was 0.2% in relation to prenatal patients, with simple partial epilepsy being the most frequent type (40% of cases). Monotherapy was applied to 75% of the patients and carbamazepine was the most frequently used drug. Among the 111 patients evaluated in terms of course of the disease during pregnancy, 53% showed no change, 31% became worse and 16% improved. Normal delivery was performed in 62.5% of cases, with a satisfactory perinatal result in terms of Apgar score, and with a rate of low birth weight neonates above the values for low-risk populations. No fetal malformations were observed. Conclusion: epilepsy showed a favorable course during pregnancy and was not aggravated by the latter, with cases of worsening of signs and symptoms being associated with epilepsy of difficult control before pregnancy. Evaluation of the perinatal characteristics of the neonates showed satisfactory Apgar scores and evolution, indicating that epilepsy and anticonvulsant drugs do not cause severe impairment of intrapartum vitality. No cases of malformations or hemorrhagic complications were detected in the present study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(6):383-387
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000600005
Purpose: to evaluate the effectiveness of diagnostic amnioinfusion in severe oligohydramnios. Methods: twelve patients with severe oligohydramnios in the second and third trimester of pregnancy were submitted to amnioinfusion. The procedure was done using a warm physiological saline at a rate of 20 mL/min followed by the instillation of 5 mL of dye. The amniotic fluid index (AFI) was measured before the procedure and 30 min afterwards and in case of fetal anomalies, it was documented. The gestational age ranged from 18 to 34 weeks (average 25 ± 4 weeks). The average of the initial ILA was 10.3cm and after the procedure was 16.4 cm. The volume of saline solution infused ranged from 300 to 1000 mL (605.4 ± 224.1 mL). Results: in nine patients (75%) the procedure led to an etiologic diagnosis: four cases of premature rupture of membranes and major malformations in five fetuses. In two patients the oligohydramnios was considered idiopathic and in one patient the pathological examination revealed a placental infarct. Nine pregnancies (75%) were interrupted after the diagnosis and in three cases it was maintained for 8.8 weeks after the amnioinfusion. All fetuses died, seven of them had neonatal death and the remaining had intrauterine death. Conclusion: amnioinfusion is an effective method with high precision, enabling the etiologic diagnosis of severe oligohydramnios in 75% of the cases.