Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):397-402
To analyze the perioperative results and safety of performing gynecological surgeries using robot-assisted laparoscopy during implementation of the technique in a community hospital over a 6-year period.
This was a retrospective observational study in which the medical records of 274 patients who underwent robotic surgery from September 2008 to December 2014 were analyzed. We evaluated age, body mass index (BMI), diagnosis, procedures performed, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification, the presence of a proctor (experienced surgeon with at least 20 robotic cases), operative time, transfusion rate, perioperative complications, conversion rate, length of stay, referral to the intensive care unit (ICU), and mortality. We compared transfusion rate, perioperative complications and conversion rate between procedures performed by experienced and beginner robotic surgeons assisted by an experienced proctor.
During the observed period, 3 experienced robotic surgeons performed 187 surgeries,while 87 surgeries were performedby 20 less experienced teams, always with the assistance of a proctor. The median patient age was 38 years, and the median BMI was 23.3 kg/m2. The most frequent diagnosis was endometriosis (57%) and the great majority of the patients were classified as ASA I or ASA II (99.6%). The median operative time was 225 minutes, and the median length of stay was 2 days. We observed a 5.8% transfusion rate, 0.8% rate of perioperative complications, 1.1% conversion rate to laparoscopy or laparotomy, no patients referred to ICU, and no deaths. There were no differences in transfusion, complications and conversion rates between experienced robotic surgeons and beginner robotic surgeons assisted by an experienced proctor.
In our casuistic, robot-assisted laparoscopy demonstrated to be a safe technique for gynecological surgeries, and the presence of an experienced proctor was considered a highlight in the safety model adopted for the introduction of the robotic gynecological surgery in a high-volume hospital and, mainly, for its extension among several surgical teams, assuring patient safety.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(2):87-93
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004650
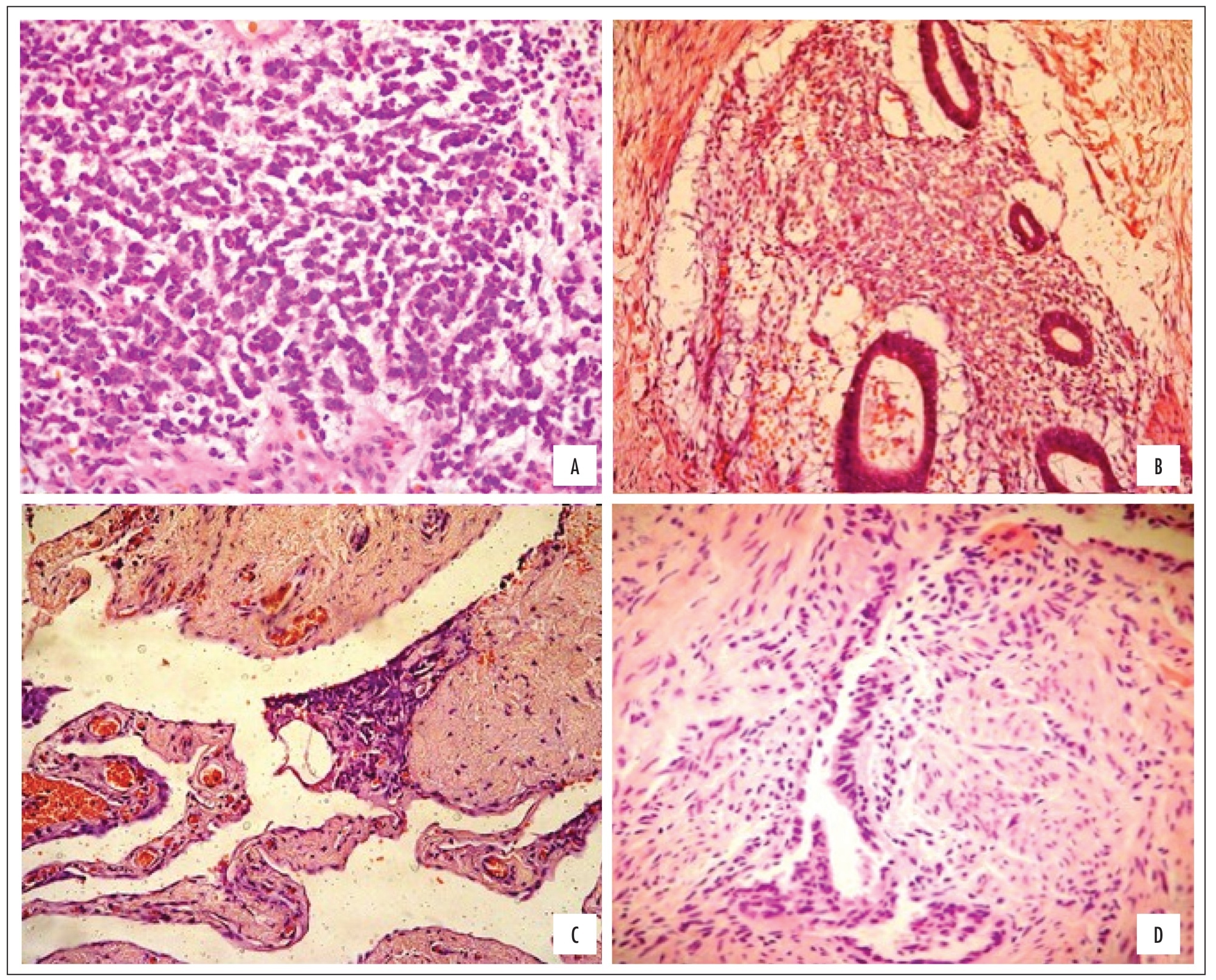
To assess the relationship between the histological classification and the quality of life of patients operated for endometriosis. METHODS: A cross-sectional observational study, with assessment of 32 biopsies of the intestine, peritoneum and uterosacral ligament from 40 women with deep endometriosis. The quality of life (QOL) was determined by applying the SF-36 questionnaire pre-operatively and at 6 and 12 months postoperatively. Biopsies were histologically classified into pure stromal (EP), glandular differentiated (GD), glandular undifferentiated (GI) and mixed (GM), remaining in the sample only GI and GM, which are related to eight domains of the SF-36.
According to the histologic type, the following distribution was observed: peritoneum 63% GI and 35% GM; intestine 19% GI and 24% GM; uterosacral ligament with 41% GI and 35% GM. Regarding the QOL and the histological classification, in the intestine only GM was associated with improvement of social and emotional aspects from 0 to 6 months; the domains general health status (p=0.01) and social aspect (p=0.04) were significantly related to improvement of the QOL from 0 to 6 months, and the general health status tended to improve from 0 to 12 months. Regarding pain (p=0.06) and the emotional aspect (p=0.05), the QOL tended to improve from 0 to 6 months and the vital capacity (p=0.1) improved from 0 to 6 months and from 0 to 12 months. Regarding the emotional aspect, evolution of the two histological types was not favorable for improvement in MG from 0 to 6 months. No significant relationships between histologic type and QOL were evident in the uterosacral ligament samples.
Improvement in the QOL of women undergoing laparoscopic surgery for deep endometriosis is associated with the histologic grade. The peritoneal biopsy of GI revealed improved QOL after surgery.