Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(9):557-566
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000900004
Purpose: to study the fetal well-being assessment in pregnancies complicated by diabetes, and to analyze the neonatal results. Methods: we studied 387 pregnant women with diabetes at the Fetal Surveillance Unit. The last examination (cardiotocography, fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index and dopplervelocimetry) was correlated with the neonatal outcome. Results: the studied population included 46 (12%) type I diabetes, 45 (12%) type II and 296 (76%) gestational diabetes. Type I diabetes with abnormal or suspected cardiotocography was related to abnormal 1st minute Apgar (50 and 75%, p<0.05) and to the need for neonatal intensive care unit (50 and 75%, p<0.05). The abnormal biophysical profile in type II diabetic pregnancy was related to the need for neonatal intensive care (67%, p<0.05), and abnormal umbilical artery Doppler study was related to abnormal 1st minute Apgar (67%, p<0.05). Gestational diabetes with abnormal cardiotocography presented 36% abnormal 1st minute Apgar (p<0.05), 18% abnormal 5th minute Apgar (p<0.01) and 18% neonatal death (p<0.01). Abnormal amniotic fluid index was related to abnormal 5th minute Apgar (p<0.05) and need for neonatal intensive care unit (p<0.05). Gestational diabetes with abnormal umbilical artery Doppler was related (p<0.05) to: abnormal 1st and 5th minute Apgar, respectively, 25 and 8%, Need for neonatal intensive care in 17% and neonatal death in 8%. Conclusions: the fetal well-being examinations correlated with adverse perinatal outcome, showing the need for fetal surveillance in diabetic pregnant women.
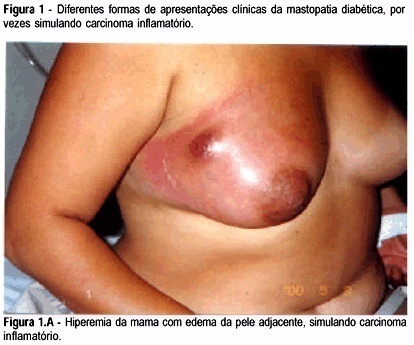
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(8):535-539
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000800006
Purpose: to study the association between long-standing type 1 diabetes with bad glycemic control and breast inflammatory lesions which can simulate inflammatory carcinoma. Patients and Methods: eighteen patients were studied, retrospectively, in a mastology reference center from January 1998 to December 2001, presenting with breast inflammatory lesion with or without palpable mass. They were submitted to serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin determination, as well as image examination and histopathologic analysis, and diabetic mastopathy was diagnosed. Results: the patients' average age was 50.2 years, and all had insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, with average disease time of 14.9 years. All patients, with no exception, had a bad glycemic control; the average blood glucose was 329.6 mg/dL and the glycosilated hemoglobin average was 9.7%. NPH insulin dose being applied per day was 37.2 units. Patients underwent a clinical treatment with antibiotics and control of the glycemic levels with NPH insulin and had resolution of the symptoms in about five weeks. Conclusion: the professionals involved in women health care must be aware of this inflammatory pathology of the breast and its benign characteristics to avoid unnecessary procedures sometimes with patient injury.
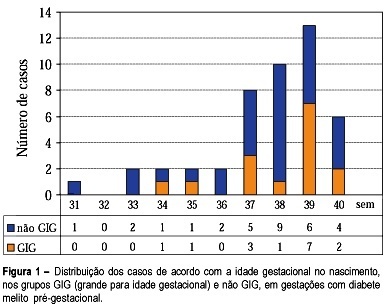
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(2):113-120
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000200007
Purpose: to study fetal surveillance examinations in pregnancies complicated by pregestational diabetes mellitus, and to correlate them with large for gestational age (LGA) newborns. Methods: Between March 1999 and June 2001, 46 singleton pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus without fetal anomalies were followed prospectively. From the 28th gestational week on, the following examinations were performed weekly: fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index (AFI), and dopplervelocimetry of umbilical and middle cerebral arteries. The newborns with birthweight above the 90th percentile according to local standard values were characterized as LGA infants. Fisher's exact test and Student's t test were used for statistical analysis. Results: The mean gestational age at delivery was 37.6 weeks and 15 (32.6%) newborns were LGA. LGA fetuses showed significant increase in the AFI mean performed in the 32nd (16.5 cm, p=0.02), 33rd (16.7 cm, p=0.03), 34th (17.0 cm, p=0.02), 35th (17.9 cm, p=0.000), 36th (15.8 cm, p=0.03) and 37th (17.5 cm, p=0.003) weeks. Non-LGA fetuses presented the following mean AFI values: 13.5cm (32nd week), 13.1cm (33th week), 13.4 (34th week), 12.8 (35th week), 12.5 (36th week) and 12.8cm (37th week). AFI values equal to or above 18.0 cm were associated with the occurrence of LGA infants, when detected at the following gestational ages: 34th (60%, p=0.03), 35th (71.4%, p=0.01), 36th (80%, p=0.02) and 37th (66.7%, p=0.04) week. Non-LGA infants presented the following proportion of AFI values equal to or above 18.0 cm: 40.0% (34th week), 28.6% (35th week), 20.0% (36th week), and 33.3% (37th week). Conclusions: abnormal increase in AFI, mainly with values equal to or above 18.0 cm, is related to LGA infants at delivery. The maternal treatment should be adjusted to achieve the best result for maternal-fetal control, according to the AFI values during pregnancy.