Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):259-263
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004812
To analyze the factors related to route of delivery in patients with pre-eclampsia.
A retrospective analytical study was conducted from January 2009 to January 2011, during which 250 medical records of patients diagnosed with pre-eclampsia who gave birth to live fetuses with a gestational age of 28 weeks or more were selected. The variables evaluated were: maternal age (19 years, 20−34 years and over 35 full years), gestational age at delivery (28−37 weeks and more than 37 weeks), parity (primiparous or multiparous), previous cesarean section, history of pre-eclampsia or chronic hypertension, current diagnosis of mild or severe pre-eclampsia, and birth weight of the newborn. The information was transcribed to a questionnaire based on the variables being investigated. The chi-square test was applied to identify the relationship between the variables, with the level of significance set at p<0.05, and the Odds Ratio (OR) was calculated only for the variables showing a statistically significant difference in order to determine the odds for the patient to be submitted to a cesarean section.
In this study, we observed a 78.4% rate of cesarean delivery, with 54.1% of the patients submitted to the procedure having a gestational age of 28 to 37 weeks (OR=3.1; p<0.01). Patients with a history of pre-eclampsia were 2.5 times more likely to have cesarean delivery (OR=2.5; p<0.02). All patients who had had a previous cesarean were submitted to cesarean delivery in the current pregnancy (p<0.01). Pregnant women with severe pre-eclampsia were 3.3 times more likely to progress to cesarean delivery than those with mild pre-eclampsia (OR=3.3; p<0.01).
After individual analysis, only gestational age and a diagnosis of severe pre-eclampsia showed significant differences, representing risk factors for this type of delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):65-71
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200004
To analyze the relationships among gestational risk, type of delivery and
immediate maternal and neonatal repercussions.
A retrospective cohort study based on secondary data was conducted in a
university maternity hospital. A total of 1606 births were analyzed over a 9-month
period. Epidemiological, clinical, obstetric and neonatal characteristics were
compared according to the route of delivery and the gestational risk characterized
on the basis of the eligibility criteria for high clinical risk. The occurrence of
maternal and neonatal complications during hospitalization was analyzed according
to gestational risk and cesarean section delivery using univariate and
multivariate logistic analysis.
The overall rate of cesarean sections was 38.3%. High gestational risk was
present in 50.2% of births, mainly represented by hypertensive disorders and fetal
malformations. The total incidence of cesarean section, planned cesarean section
or emergency cesarean section was more frequent in pregnant women at gestational
high risk (p<0.001). Cesarean section alone did not influence maternal outcome,
but was associated with poor neonatal outcome (OR 3.4; 95%CI 2.7-4.4). Gestational
high risk was associated with poor maternal and neonatal outcome (OR 3.8; 95%CI
1.3-8.7 and OR 17.5; 95%CI 11.6-26.3, respectively). In multivariate analysis, the
ratios were maintained, although the effect of gestational risk has determined a
reduction in the OR of the type of delivery alone from 3.4 (95%CI 2.7-4.4) to 1.99
(95%CI 1.5-2.6) for adverse neonatal outcome.
Gestational risk was the main factor associated with poor maternal and neonatal
outcome. Cesarean delivery was not directly associated with poor maternal outcome
but increased the chances of unfavorable neonatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):516-522
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100007
PURPOSE: To analyze the impact of vaginal delivery after a previous cesarean section on perinatal outcomes. METHODS: Case-control study with selection of incident cases and consecutive controls. Maternal and perinatal variables were analyzed. We compared secundiparas who had a vaginal delivery after a previous cesarean delivery (VBAC) (n=375) with secundiparas who had a second cesarean section (CS) (n=375). Inclusion criteria were: secundiparas who underwent a cesarean section in the previous pregnancy; singleton and term pregnancy; fetus in vertex presentation, with no congenital malformation; absence of placenta previa or any kind of bleeding in the third quarter of pregnancy. RESULTS: The rate of vaginal delivery was 45.6%, and 20 (5.3%) women had forceps deliveries. We found a significant association between VBAC and mothers younger than 19 years (p<0.01), Caucasian ethnicity (p<0.05), mean number of prenatal care visits (p<0.001), time of premature rupture of membranes (p<0.01), labor duration shorter than 12 hours (p<0.04), Apgar score lower than seven at 5th minute (p<0.05), fetal birth trauma (p<0.01), and anoxia (p<0.006). In the group of newborns delivered by cesarean section, we found a higher frequency of transient tachypnea (p<0.014), respiratory disorders (p<0.048), and longer time of stay in the neonatal intensive care unit (p<0.016). There was only one case of uterine rupture in the VBAC group. The rate of neonatal mortality was similar in both groups. CONCLUSIONS: Vaginal delivery in secundiparas who had previous cesarean sections was associated with a significant increase in neonatal morbidity. Further studies are needed to develop strategies aimed at improving perinatal results and professional guidelines, so that health care professionals will be able to provide their patients with better counseling regarding the choice of the most appropriate route of delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):281-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000600008
PURPOSE: It was to describe and compare the preference of nulliparous and primiparous women for a particular mode of delivery and to determine whether the previous experience of childbirth influences the delivery process. METHODS: We conducted a prospective cross-sectional study. One-hundred interviews were held with 56 nulliparous and 44 primiparous women using previously prepared questionnaires. The quantitative and categorical data were evaluated by the chi-square or Fisher's Exact Test. RESULTS: 60.7% of nulliparous women and 70.5% of primiparous women reported to prefer vaginal delivery. When analyzing the answers about receiving sufficient information about the type of delivery, the presence or absence of influence on the choice of route of delivery and the preferred route of delivery by the partner, there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups. The level of significance used for the tests was 0.05. CONCLUSIONS: This study permitted us to conclude that the previous experience of delivery does not influence the expectation of the delivery process or the choice for a specific mode of delivery. When choosing the route of delivery, women seek to ensure the health of mother and neonate, as well as to avoid the process of pain and suffering.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):233-237
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500008
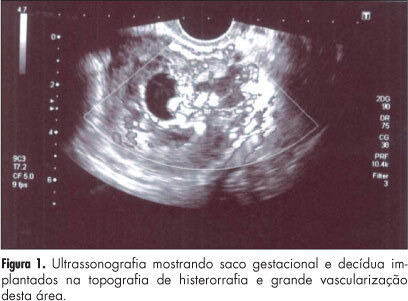
Implantation of a pregnancy within a cesarean delivery scar is considered to be the rarest form of ectopic pregnancy, with a high morbidity and mortality. Pregnancy in a cesarean delivery scar may cause catastrophic complications which may result in hysterectomy and compromise the reproductive future of a woman. We report an ectopic pregnancy in cesarean scar case in a 28-year old pregnant woman that was treated with success with the association between three treatment modalities (methotrexate, uterine artery embolization and curettage) and preserve her fertility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(4):148-152
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000400003
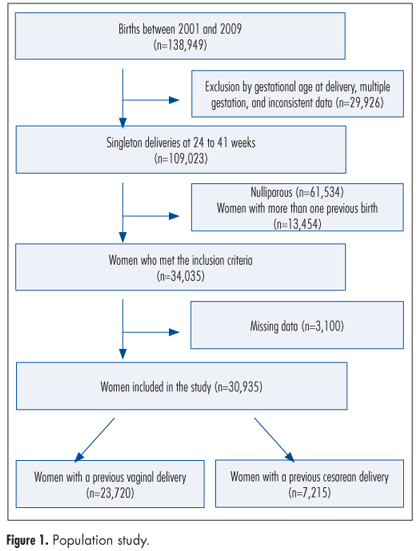
PURPOSE: To examine obstetric outcomes in the second birth of women who had undergone a previous cesarean delivery. METHODS: This was a large hospital-based retrospective cohort study. We included pregnant women who had a previous delivery (vaginal or cesarean) attending their second birth from 2001 to 2009. Main inclusion criteria were singleton pregnancies and delivery between a gestation of 24 and 41 weeks. Two cohorts were selected, being women with a previous cesarean delivery (n=7,215) and those with a vaginal one (n=23,720). Both groups were compared and logistic regression was performed to adjust for confounding variables. The obstetric outcomes included uterine rupture, placenta previa, and placental-related complications such as placental abruption, preeclampsia, and spontaneous preterm delivery. RESULTS: Women with previous cesarean delivery were more likely to have adverse outcomes such as uterine rupture (OR=12.4, 95%CI 6.8-22.3), placental abruption (OR=1.4, 95%CI 1.1-2.1), preeclampsia (OR=1.4, 95%CI 1.2-1.6), and spontaneous preterm delivery (OR=1.4, 95%CI 1.1-1.7). CONCLUSIONS: Individuals with previous cesarean section have adverse obstetric outcomes in the subsequent pregnancy, including uterine rupture, and placental-related disorders such as preeclampsia, spontaneous preterm delivery, and placental abruption.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(3):117-122
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000300005
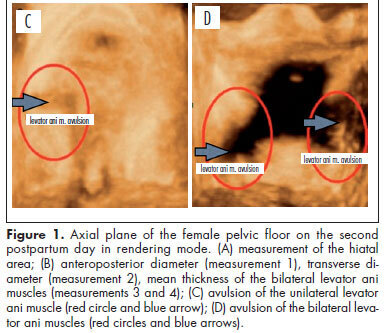
PURPOSE: To evaluate changes to the pelvic floor of primiparous women with different delivery modes, using three-dimensional ultrasound. METHODS: A prospective cross-sectional study on 35 primiparae divided into groups according to the delivery mode: elective cesarean delivery (n=10), vaginal delivery (n=16), and forceps delivery (n=9). Three-dimensional ultrasound on the pelvic floor was performed on the second postpartum day with the patient in a resting position. A convex volumetric transducer (RAB4-8L) was used, in contact with the large labia, with the patient in the gynecological position. Biometric measurements of the urogenital hiatus were taken in the axial plane on images in the rendering mode, in order to assess the area, anteroposterior and transverse diameters, average thickness, and avulsion of the levator ani muscle. Differences between groups were evaluated by determining the mean differences and their respective 95% confidence intervals. The proportions of levator ani muscle avulsion were compared between elective cesarean section and vaginal birth using Fisher's exact test. RESULTS: The mean areas of the urogenital hiatus in the cases of vaginal and forceps deliveries were 17.0 and 20.1 cm², respectively, versus 12.4 cm² in the Control Group (elective cesarean). Avulsion of the levator ani muscle was observed in women who underwent vaginal delivery (3/25), however there was no statistically significant difference between cesarean section and vaginal delivery groups (p=0.5). CONCLUSION: Transperineal three-dimensional ultrasound was useful for assessing the pelvic floor of primiparous women, by allowing pelvic morphological changes to be differentiated according to the delivery mode.
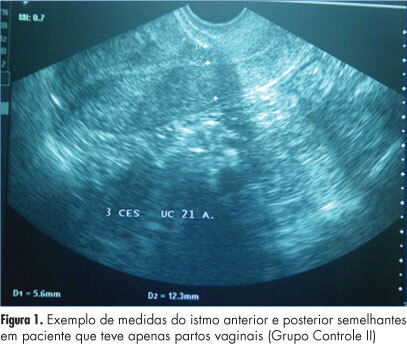
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(5):221-227
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000500006
PURPOSE: To evaluate the thickness of the lower uterine segment by transvaginal ultrasound in a group of non-pregnant women and to describe the morphologic findings in the scar of those submitted to cesarean section. METHODS: A retrospective study of 155 transvaginal ultrasound images obtained from premenopausal and non-pregnant women, conducted between January 2008 and November 2011. the subjects were divided into three groups: women who were never pregnant (Control Group I), women with previous vaginal deliveries (Control Group II) and women with previous cesarean section (Observation Group). We excluded women with a retroverted uterus, intrauterine device users, pregnant women and those with less than one year of tsince the last obstetrical event. The data were analyzed statistically with Statistica®, version 8.0 software. ANOVA and LSD were used to compare the groups regarding quantitative variables and the Student's t-test was used to compare the thickness of the anterior and posterior isthmus. The Spearman correlation coefficient was calculated to estimate the association between quantitative variables. P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. RESULTS: There was significant difference between the thickness of the anterior and posterior isthmus only in the group of women with previous cesarean section. Comparing the groups two by two, no significant differences between the thickness of the anterior and posterior isthmus were observed in the Control Groups, but this difference was significant when we compared the Observation Group with each Control Group. In the Observation Group, no correlation was found between the thickness of the isthmus and the number of previous cesarean deliveries or the time elapsed since the last birth. A niche was found in the cesarean scar in 30.6% of the women in the Observation Group, 93% of whom complained of post-menstrual bleeding. CONCLUSION: The relationship between the thickness of the anterior and posterior wall of the lower uterine segment by transvaginal ultrasound is a suitable method for the evaluation of the uterine lower segment in women with previous cesarean sections.