Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):416-423
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700007
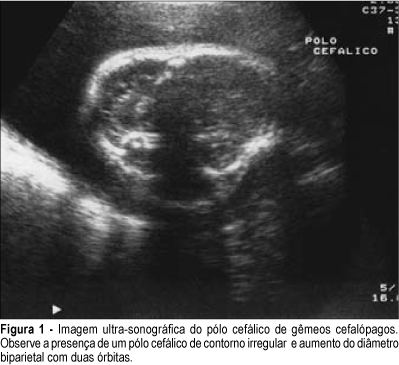
Conjoined twins have a rare prevalence and special curiosity among physicians and the general population. The reported frequency varies from 1:50,000 to 1:200,000 pregnancies. Its early diagnosis becomes very important when we think about pregnancy management, method of delivery and neonatal care. We describe two cases of conjoined twins diagnosed by ultrasound and magnetic resonance during prenatal care with the aim to better studying the fetus anatomy. The first conjoined twins were cephalopagus sharing head, thorax and abdominal wall and with two pelvis and four arms and four legs. The second were thoracopagus, united by thorax and part of abdomen. Magnetic resonance imaging contribution was not important to diagnose conjoined twins. However, it was useful to describe the shared organs, contributing to define fetal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):244-250
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400007
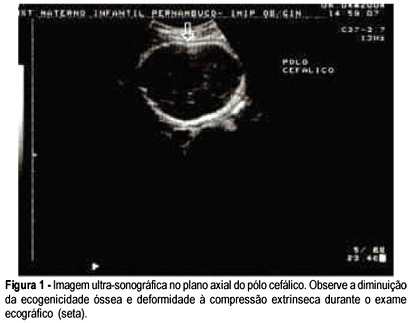
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a connective tissue disorder due to quantitative and qualitative anomalies in type 1 collagen, genetically transmitted by a dominant or recessive autosomal gene, leading to bone fragility. We report a case of a 19-year-old G1 PO patient referred to our institution following a screening ultrasound that demonstrated short limb fetal extremities. A level 3 scan was performed which evidenced an irregular cranial shape and compression of the cephalic pole with moderate transducer pressure. Limb shortening, decreased echoes and fractures of long bones were found on our scan evaluation. A vaginal delivery occurred at 35 weeks of gestation. The male newborn, weighing 1.990 grams had 6 and 8 in Apgar scores. The neonate was clearly abnormal, presenting irregular cranial shape, with poor ossification on X-ray, blue sclera, fractures and limb deformities. Postnatal evaluation was satisfactory and the neonate was discharged in good conditions. Prenatal diagnosis is important for an adequate pregnancy follow-up. Postnatal outcome was not related to vaginal delivery, as there were no recent fractures in the newborn.