Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):280-286
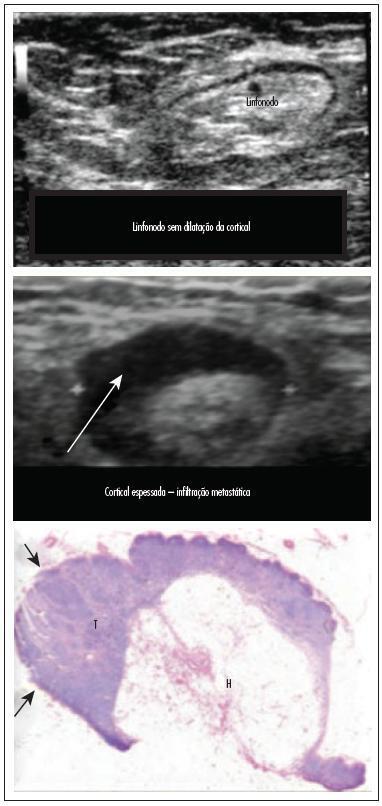
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is the standard treatment for locally advanced breast cancer. However, some tumors will not respond to this treatment due to histological and molecular features. The protein EZH2 (enhancer of zest homolog 2) is a histone methyltransferase that is correlated with poorly differentiated breast carcinomas and aggressive tumor behavior.
The present study evaluated the association between EZH2 expression and response to NAC, and its correlation with HER2 overexpression, estrogen and progesterone receptors (ER, PR) and Ki-67 proliferation index.
A total of 60 patients with locally advanced breast cancer treated with NAC were selected for this study. Twenty-three paraffin blocks had not enough material for tissue resection, and were not evaluated. A tissue microarray based in immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis of EZH2 was performed for the remaining 37 specimens. Patients were divided into two groups based on response to NAC.
EZH2 expression was significantly associated with markers of poor prognosis such as ER negativity (p = 0.001), PR negativity (p = 0.042) and high Ki-67 proliferation index (p = 0.002). High EZH2 expression was not correlated with the response to NAC.
Our data suggested that EZH2 protein expression may not correlate with the clinical response to NAC. Other studies with more patients are needed to confirm this observation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):473-479
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005354
To validate the instrument Body Image Relationship Scale (BIRS) for Brazilian women with breast cancer
The instrument was administered by trained interviewers to 139 women who used the Brazilian Unified Health System (SUS). All of them had been submitted to cancer treatments between 2006 and 2010. The instrument was validated considering internal consistency and reliability. In order to compare the techniques, the same factorial analysis as used in the original paper was carried out
The Spearman-Brown correlation value was 0.8, indicating high internal reliability. The Cronbach's alpha found was 0.9, indicating a high level of internal consistency. Factorial analysis showed that four items had low factorial load and no discriminatory power, and another five items were relocated to other factors. When the instrument was applied, it showed variability to that of the original instrument
The Brazilian version of the Body Image Relationship Scale (BIRS), namedEscala de Relacionamento e Imagem Corporal (ERIC), showed evidence of adequate reliability and internal consistency, making this instrument suitable to be recommended for application to Brazilian women with breast cancer, despite some limitations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):233-240
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005333
To assess the effect of tibolone on mammary tissue of castrated rats over 3
different periods of time.
Sixty virgin female Wistar rats were submitted to oophorectomy. Twenty-one days
after surgery, with hypoestrogenism confirmed, the experimental rats were randomly
assigned to six groups: Tibolone 1 (n=10) received tibolone 1 mg/day for 23 days,
tibolone 2 (n=10) for 59 days and tibolone 3 (n=10) for 118 days. The groups
control 1 (n=8), control 2 (n=7) and control 2 (n=10) received distilled water for
23, 59 and 118 days, respectively. After treatment, all six pairs of mammary
glands were removed and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) for histological
analysis after euthanasia. The histological parameters evaluated were: epithelial
cell proliferation and secretory activity. The variables were analyzed
statistically, with the level of significance set at 0.05.
Histological changes were observed in 20/55 rats, mild epithelial hyperplasia in
7/55, moderate epithelial hyperplasia in 5/55, alveolar-nodular hyperplasia in
7/55, atypia without epithelial proliferation in 1/55, and no cases of severe
epithelial hyperplasia were found. Secretory activity was observed in 31/55 rats.
The secretory activity was significantly higher in the tibolone groups compared to
control at all the time points assessed (p=0,001). The histological changes were
did not show significance when the control and tibolone groups were compared. The
time of exposure to tibolone did not show significance when the three different
periods of evaluation were compared.
No relation between histological modification and tibolone treatment was verified
after short-, medium- and long-term treatment.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):119-126
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005247
To assess fatigue and quality of life in disease-free breast cancer survivors in relation to a sample of age-matched women with no cancer history and to explore the relationship between fatigue and quality of life.
A cross-sectional study was conducted in a sample of 202 consecutive disease-free Brazilian breast cancer survivors, all of whom had completed treatment, treated at 2 large hospitals. The patients were compared to age-matched women with no cancer history attending a primary health care center. The Piper Fatigue Scale-Revised and the World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument (WHOQOL-BREF) were used to measure the fatigue and quality of life, respectively. Socio-demographic and clinical variables were also obtained. The χ2 test, generalized linear model, and Spearman correlation coefficient were used for statistical purposes. The adopted level of significance was 5%.
Breast cancer survivors experienced significantly greater total and subscale fatigue scores than comparison group (all p-values<0.05). In addition, survivors reported a poorer quality of life in physical (p=0.002), psychological (p=0.03), and social relationships (p=0.03) domains than comparison group. No difference was found for the environmental domain (p=0.08) for both groups. For survivors of breast cancer and for comparison group, the total and subscale fatigue scores were related to lower quality of life (all p-values<0.01).
The findings of this study highlight the importance of assessing fatigue and quality of life in breast cancer survivors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(12):575-580
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005158
To compare the distributions of patients with clinical-pathological subtypes of luminal B-like breast cancer according to the 2011 and 2013 St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference Expert Panel.
We studied 142 women with breast cancer who were positive to estrogen receptor and had been treated in São Paulo state, southeast Brazil. The expression of the following receptors was assessed by immunohistochemistry: estrogen, progesterone (PR) and Ki-67. The expression of HER-2 was measured by fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis in tissue microarray.
There were 29 cases of luminal A breast cancers according to the 2011 St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference Expert Panel that were classified as luminal B-like in the 2013 version. Among the 65 luminal B-like breast cancer cases, 29 (45%) were previous luminal A tumors, 15 cases (20%) had a Ki-67 >14% and were at least 20% PR positive and 21 cases (35%) had Ki-67 >14% and more than 20% were PR positive.
The 2013 St. Gallen consensus updated the definition of intrinsic molecular subtypes and increased the number of patients classified as having luminal B-like breast cancer in our series, for whom the use of cytotoxic drugs will probably be proposed with additional treatment cost.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(8):340-346
DOI 10.1509/SO100-720320140005034
To examine the expression of AKT and PTEN in a series of HER2-positive primary invasive breast tumors using immunohistochemistry, and to associate these expression profiles with classic pathologic features such as tumor grade, hormone receptor expression, lymphatic vascular invasion, and proliferation.
A total of 104 HER2-positive breast carcinoma specimens were prepared in tissue microarrays blocks for immunohistochemical detection of PTEN and phosphorylated AKT (pAKT). Original histologic sections were reviewed to assess pathological features, including HER2 status and Ki-67 index values. The associations between categorical and numeric variables were identified using Pearson's chi-square test and the Mann-Whitney, respectively.
Co-expression of pAKT and PTEN was presented in 59 (56.7%) cases. Reduced levels of PTEN expression were detected in 20 (19.2%) cases, and these 20 tumors had a lower Ki-67 index value. In contrast, tumors positive for pAKT expression [71 (68.3%)] were associated with a higher Ki-67 index value.
A role for AKT in the proliferation of HER2-positive breast cancers was confirmed. However, immunohistochemical detection of PTEN expression did not correlate with an inhibition of cellular proliferation or control of AKT phosphorylation, suggesting other pathways in these mechanisms of control.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):157-162
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140050.0002
It was to assess the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in breast cancer survivors (BCS).
This cross-sectional study analyzed 67 BCS, aged 45 -65 years, who underwent complete oncological treatment, but had not received hormone therapy, tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors during the previous 6 months. Lipid profile and CVD risk were evaluated, the latter using the Framingham and Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) models. The agreement between cardiovascular risk models was analyzed by calculating a kappa coefficient and its 95% confidence interval (CI).
Mean subject age was 53.2±6.0 years, with rates of obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia of 25, 34 and 90%, respectively. The most frequent lipid abnormalities were high total cholesterol (70%), high LDL-C (51%) and high non-HDL-C (48%) concentrations. Based on the Framingham score, 22% of the participants had a high risk for coronary artery disease. According to the SCORE model, 100 and 93% of the participants were at low risk for fatal CVD in populations at low and high risk, respectively, for CVD. The agreement between the Framingham and SCORE risk models was poor (kappa: 0.1; 95%CI 0.01 -0.2) for populations at high risk for CVD.
These findings indicate the need to include lipid profile and CVD risk assessment in the follow-up of BCS, focusing on adequate control of serum lipid concentrations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):118-123
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300005
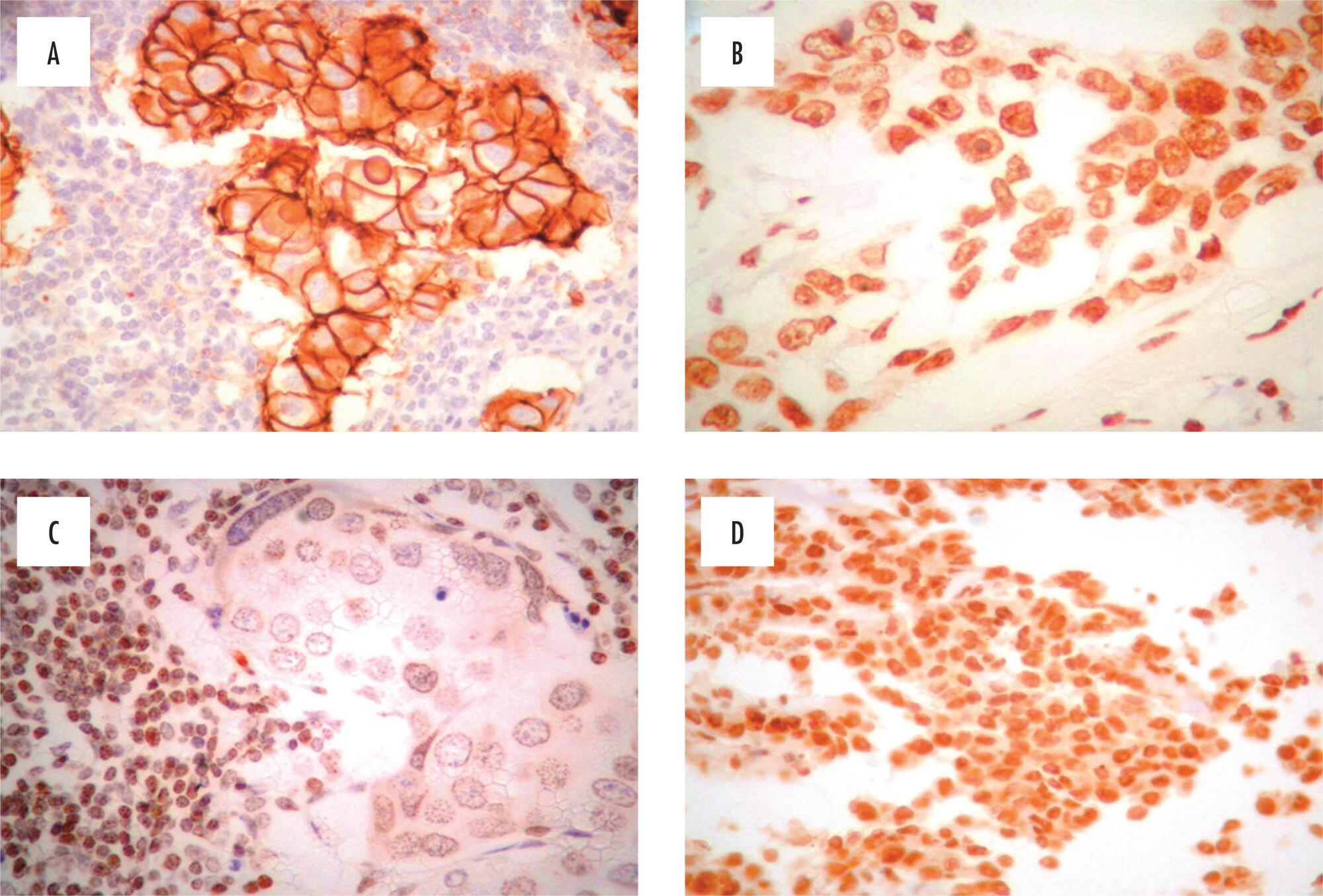
To assess the feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of preoperative ultrasound combined with ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (US-FNA) cytology and clinical examination of axillary lymph node in patients with breast cancer.
In this prospective study, 171 axillae of patients with breast cancer were evaluated by clinical examination and ultrasonography (US) with and without fine needle aspiration (FNA). Lymph nodes with maximum ultrasonographic cortical thickness > 2.3 mm were considered suspicious and submitted to US-FNA.
Logistic regression analysis showed no statistically significant correlation between clinical examination and pathologically positive axillae. However, in axillae considered suspicious by ultrasonography, the risk of positive anatomopathological findings increased 12.6-fold. Cohen's Kappa value was 0.12 for clinical examination, 0.48 for US, and 0.80 for US-FNA. Accuracy was 61.4% for clinical examination, 73.1% for US and 90.1% for US-FA. Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis demonstrated that a cortical thickness of 2.75 mm corresponded to the highest sensitivity and specificity in predicting axillary metastasis (82.7 and 82.2%, respectively).
Ultrasonography combined with fine-needle aspiration is more accurate than clinical examination in assessing preoperative axillary status in women with breast cancer. Those who are US-FNA positive can be directed towards axillary lymph node dissection straight away, and only those who are US-FNA negative should be considered for sentinel lymph node biopsy.