Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(1):27-32
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000100006
PURPOSE: To compare and analyze socioeconomic aspects and the emotional experience of women with spontaneous or induced abortion and in women living in the outskirts of São Paulo. METHODS: A prospective case-control study carried out from July 2008 to March 2010, involving semi-structured interviews with women who presented a previous diagnosis of abortion and who had been admitted to two public hospitals in the outskirts of São Paulo. The study included 100 women with diagnosis of abortion and were hospitalized for curettage. Eleven women who reported induced abortion (11%) represented the case group. The control group (n=22) was selected at a 2:1 ratio according to the following procedure: for every case of induced abortion, the next two cases of spontaneous abortion at the same hospital. A semistructured interview was conducted with questions regarding emotional aspects and family, social and economic context. RESULTS: The women with induced abortion compared to the group with spontaneous abortion had lower educational level, with more frequent elementary level (82 versus 36%, p=0.04), lower income (median, R$ 1,000.00 versus R$ 1,400.00, p=0.04), lower personal income (median, R$ 200.00 versus R$ 333.00, p=0.04), higher frequency of negative feelings upon suspicion (82 versus 22%, p=0.004) and confirmation (72 versus 22%, p=0.03) of pregnancy. CONCLUSION: Among women looking for health care in hospitals in the outskirts of São Paulo, induced abortion is related to unfavorable socioeconomic conditions, which affects the emotional experiences of suspicion and confirmation of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(1):16-21
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000100004
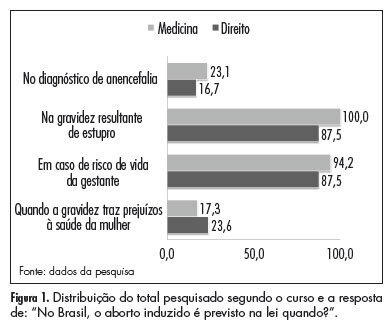
PURPOSE: To analyze and compare the knowledge and opinions of Law and Medical students regarding the issue of abortion in Brazil. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study involving 125 graduate students from the class of 2010. Of these, 52 were medical students (MED group) and 73 law students (LAW group). A questionnaire was applied based on published research about the topic. Dependent variables were: monitoring the abortion debate, knowledge concerning situations where abortion is permitted under Brazilian law, opinion about situations that agree with extending legal permission to terminate pregnancy and prior knowledge of someone who has undergone induced abortion. Independent variables were: sex, age, household income and graduation course. Statistical analysis: χ² and Fisher's exact tests, with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: Most interviewees reported monitoring the debate on abortion in Brazil (67.3% of the MED group and 70.2% of the LAW group, p>0.05). When assessing knowledge on the subject, medical students had a significantly higher percentage of correct answers than law students (100.0 and 87.5%, respectively; p=0.005) regarding the legality of abortion for pregnancies resulting from rape. Elevated percentages of correct responses were also recorded for both groups in relation to pregnancies that threaten the life of the mother (94.2 and 87.5% for MED and LAW groups, respectively), but without statistical significance. A significant percentage of respondents declared they were in favor of extending legal abortion to other situations, primarily in cases of anencephaly (68%), pregnancy severely harming the mother's physical health (42.1%) or that of the fetus in cases of severe congenital malformation (33.7%). CONCLUSION: Results showed a satisfactory knowledge on the part of law and medical school graduate students regarding the legality of abortion in Brazil, combined with a favorable trend towards extending legal permission to other situations not covered by the law. It is important to underscore the inclusion of this topic in the undergraduate curriculum and the development of inter-professional teaching strategies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(3):105-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000300002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion reported by a sample of Brazilian women interviewed in the National Demographic Health Survey of 1996. METHODS: this was a secondary analysis of the Brazilian DHS-96 database, with information from interviews with a representative sample of 12,612 women about their reproductive life, focusing on the prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion in the last five years and the associated factors for the various regions of the country and for Brazil as a whole. The sampling method was implemented with a strategy selection in two stages, one for the households and the other for women. The prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion was estimated for Brazil and regions, and the socio-demographic characteristics of the women were analyzed as a function of the abortion's experience. A multinomial regression model analysis was used for the identification of factors independently associated with both types of abortion; their OR and respective 95% CI are reported. RESULTS: the prevalence of reported spontaneous abortion was 14% and the prevalence of induced abortion was 2.4% for the country as a whole. The state with the highest prevalence of induced abortion was Rio de Janeiro with 6.5%, followed by the Northeast region with 3.1%. The places with the lowest prevalence were the state of São Paulo and the South region. Both spontaneous and induced abortion showed higher prevalences with increasing age of the women studied. Being from the urban area (OR=1.5; 95%CI=1.0-2.3), having had more than one live child (OR=2.2; 95%CI=1.5-3.2) and being non-white (OR=1.4; 95%CI=1.0-1.8) were the main risk factors for induced abortion. CONCLUSIONS: the non-modifiable risk factors for induced abortion identified in this study indicate the need for improvement of educational and contraceptive actions, with priority for these specific demographic groups.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(1):19-35
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000100004
PURPOSE: failed attempted abortions with the use of misoprostol (Cytotec®) without medical indication have been associated with the occurrence of congenital malformations. The objective of the present study was to identify, in newborns with malformations and in normal controls, the frequency of exposure to misoprostol and the spectrum of associated malformations. METHODS: this was a case-control study involving a daily survey at four public maternities in Fortaleza (CE) for the identification of newborns with malformations and paired controls (1:1) during the period from July to November 2005. The sample comprised 252 parturients interviewed by a trained team by means of a structured questionnaire based on the Latin American Collaborative Study of Congenital Malformations (Estudo Colaborativo Latino-Americano de Malformações Congênitas, ECLAMC). The questionnaire was used to obtain sociodemographic data and a family history of malformations, as well as to identify diverse forms of exposure during pregnancy, including misoprostol. Bivariate analysis and the chi-square test were used to compare cases and controls regarding their characteristics and factors associated with malformation, and the Odds Ratio was calculated to determine the chance of the Case Group to present malformations as compared to the Control Group after exposure to misoprostol. RESULTS: there were no significant differences between groups regarding most of the risk factors for malformations investigated. Attempted abortion was reported by 6.8% of the mothers, with a higher exposure to misoprostol during pregnancy resulting in a greater proportion of malformed newborns, Odds Ratio (OR)=3.65 (95%CI=0.74-17.91). The spectrum of congenital defects encountered with exposure to misoprostol included defects of the central nervous, musculoskeletal, urogenital and cardiovascular systems, in agreement with literature data. CONCLUSION: the findings of this study suggest that fetuses exposed to misoprostol tend to be at higher risk of developing congenital malformations in comparison to non-exposed fetuses. Other studies should be encouraged for a better identification of the damage caused by the improper use of misoprostol, especially in countries where the control of medication is inadequate.