You searched for:"Melânia Maria Ramos de Amorim"
We found (25) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):80-86
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200006
PURPOSE: to describe the clinical and laboratorial profile of HELLP syndrome patients admitted at an Obstetric Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and included in a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of dexamethasone in this clinical setting. METHODS: the present study is a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial design to evaluate the efficacy of dexamethasone in patients with HELLP syndrome. This sample of patients was composed of patients in the puerperium, with the diagnosis of HELLP syndrome (diagnosis made before or after delivery) who were not chronic corticosteroid users and not carriers of any chronic disease which could modify HELLP syndrome's laboratorial parameters. Patients who were too critical or whose condition did not allow them to consent to participate were not included. Data were extracted from the records used in the randomized clinical trial. Age, parity, gestational age at admission and delivery, time of diagnosis (before or after delivery), HELLP syndrome classification (partial or complete), arterial blood pressure, and diuresis at admission were considered for analysis. Among laboratorial findings, hemoglobin, platelet count, liver enzymes, LDH, and serum bilirubin were analyzed. Complications presented by the patients were also analyzed as well as need of blood transfusions and duration of hospitalization. Analysis was made by the Epi-Info 3.3.2 program. RESULTS: one hundred and five patients were analyzed. Age varied from 14 to 49 years (means of 26.7). Regarding parity, 56 patients (53.8%) were primiparas. Analyzing the timing of the diagnosis, 47 patients (45.2%) had the diagnosis before delivery. The mean gestational age in these patients was 32.4 weeks. Hemorrhagic manifestations were observed in 36 patients (34.3%), oliguria was present in 49 patients (46.7%) and criteria for acute renal failure were seen in 21 (20%) of the cases. Hemotransfusions were necessary in 35 (33.3%) patients. Seven patients (6.7%) had pulmonary edema and four patients died, corresponding to 3.8% of the cases. The mean time from diagnosis of HELLP syndrome to discharge or death was 10.3 days, varying from 1 to 33 days. CONCLUSIONS: HELLP syndrome is an ominous diagnosis, which implicates in elevated maternal morbimortality. Among complications, oliguria and hemorrhagic manifestations were the most common findings and hemotransfusions were frequently required. Lethality reached 3.8%.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(6):297-302
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000600004
PURPOSE: to identify the main characteristics of the diagnostic and surgical gynecological laparoscopies carried out in patients with reproductive difficulties at a teaching hospital in Recife, from 2000 and 2004. METHODS: a hospital based descriptive case-series study was carried out with 295 patients who had undergone gynecological laparoscopy for either infertility or tube recanalization in the Mother and Child Health Professor Fernando Figueira Institute. Information was obtained from the surgical records of the laparoscopies carried out from January 2000 to December 2004. The inclusion criteria was infertility or pre-recanalization study as a surgical indication. The information was typed twice into a data bank. Tables with central measurements and dispersion tendency were created for the quantitative variables and frequency distribution for the categorical variables. The statistical program, Epi Info 3.3.2., was used to analyze the data. RESULTS: along the study, 462 gynecological laparoscopies were analyzed, 295 (63.8%) of them having as an indication either infertility (41.1%) or the study of possible tube recanalization (18.8%). The patients’ average age in both groups was from 30 to 34 years old. Among the 87 patients with desire of tube recanalization, 55.2% had one or both tubes inadequate for the procedure, and from those, 52.1% was diagnosed with tube amputation (fimbrectomy). In the infertility cases, the most observed findings were adherences (60.6%), tube obstruction (40.9%) and endometriosis (36.1%). Among the procedures carried out, lysis of adherences (34.2%) and biopsies (21%) were the most frequent, followed by endometriosis treatment (10.8%) and salpingostomy (10.8%). CONCLUSION: videolaparoscopy is an important tool in the study and treatment of patients with infertility and before tube recanalization, especially in those hospitals where advanced reproductive techniques are not available.
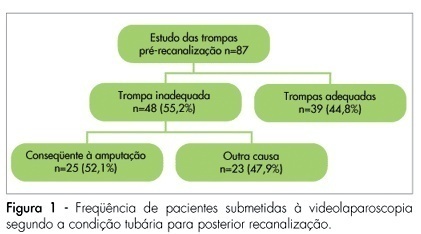
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):253-260
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500004
Objectives: To determine sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of the shake test (Clements) for evaluation of fetal lung maturation in preeclamptic patients. Methods: A prospective study for validation of a diagnostic method was conducted enrolling 163 preeclamptic patients (gestational age between 28-34 weeks) admitted at CAM-IMIP with indication for fetal maturity testing. Preeclampsia diagnosis and classification followed criteria of the National High Blood Pressure Working Group, 1990. Clements' test was performed in three tubes and positive, negative or intermediate results were considered for analysis (related to presence or absence of fetal lung maturity). Accuracy parameters were calculated considering actual incidence of hyaline membrane disease (positive maturity = absent disease) after birth. Hyaline membrane disease was defined by criteria of CLAP, 1978. Statistical analysis was performed using c² test (Epi-Info 6.04b) with a 5% significance level. Results: Intermediate results were considered alternately as positive or negative for analysis. When considered positive, sensitivity was 87.9% and specificity 74.5% with positive and negative predictive values of 8.9.4% and 71.4% respectively - efficiency was 84%. When intermediate results were evaluated as negative, sensitivity decreased to 62% and specificity raised to 89.4% and positive and negative predictive values were 93.5% and 51.2% respectively (efficiency = 70%). False-positive results were rare and usually related to neonatal hypoxia: only 5 (6.5%) of 77 neonates with previous positive Clements had hyaline membrane disease. Nevertheless, false negatives were frequent: almost 40% for negative/intermediate results. Conclusions: Despite its limitations, Clements' test remains a good method for investigation of fetal lung maturation in preeclamptic patients since false positive results are unusual. However sensitivity is low and results have be cautiously analyzed because of elevated rate of false negative results. A good policy is to complement fetal maturity investigation with other tests if a negative result is determined, specially in severe cases when confirmed maturity represents indication for interruption of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):289-292
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500009
Pneumoperitoneum, abdominal pain and paralytic ileus in the postoperative period are usually related to perforation of the gastrointestinal tract. The authors present a case of a patient submitted to cesarean section (abruptio placentae) who had a postoperative course of abdominal distention and abdominal pain. Abdominal X-ray showed important dilatation of the colon and small bowel. Pneumoperitoneum was seen on chest X-ray. An exploratory laparotomy was performed because of suspicion of intestinal perforation. The operation showed a marked dilatation of bowel, pneumoperitoneum, and infected hemoperitoneum and subaponeurotic hematoma (Escherichia coli), without any perforation. Postoperative recovery was good and antibiotics were given for 4 days (ceftriaxone + metronidazole). The patient was diseharged from hospital on the 7th day after laparotomy. After review of the literature the authors concluded that this case of pneumoperitoneum was probably related to infection by a gas-producing bacterium in a patient with clinical findings of paralytic ileus.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(6):353-357
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000600009
Introduction: meconium peritonitis as result of fetal intestinal perforation has a low incidence (1:30,000 deliveries) and high mortality (50% or more). Prenatal ultrasound findings include fetal ascites and intra-abdominal calcifications. Evidence suggests that prenatal diagnosis can improve postnatal prognosis. Case Report: R.C.M.S., 22 years, II pregnancy O para, presented ultrasound (12/02/98) with diagnosis of fetal ascites. Investigation for hydrops fetalis was performed and immune and nonimmune causes were excluded. Severe fetal ascites persisted on subsequent ultrasound examinations, without calcifications. Vaginal delivery occurred at 36 weeks (01/02/99), with polyhydramnios. Female neonate weighing 2,670 g, with signs of respiratory distress, abdominal distension and petechiae. Abdominal distension worsened progressively, with palpation of a petrous tumor in the right upper quadrant and elimination of white mucus at rectal examination. Radiological findings (01/04/99) were disseminated abdominal calcifications, intestinal dilatation and absence of gas at rectal ampulla. Exploratory laparotomy was indicated with diagnosis of meconium peritonitis. A giant meconium cyst and ileal atresia were observed and lysis of adhesions and ileostomy were performed. Initial postoperative evolution was satisfactory but was subsequently complicated by sepsis and neonatal death occurred (01/09/99). Conclusion: meconium peritonitis should be remembered at differential diagnosis of fetal ascites. In the present case, surgical indication could be anticipated if prenatal diagnosis were established, with improvement of neonatal evolution.
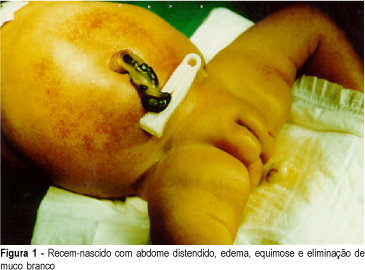
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(10):611-615
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999001000009
Term abdominal pregnancy with live fetus is an obstetrical rarity with high fetal and maternal morbidity and mortality. The authors present a case of abdominal pregnancy in a 43-year-old woman. The diagnosis was made only at term (37 weeks) by clinical findings and echography. Exploratory laparotomy was performed and a living female newborn weighing 2,570 g was extracted. Apgar scores were 3, 6 and 8 at the 1st, 5th and 10th minutes, respectively. Placenta was inserted in the omentum and was removed without complications. Postoperative course was uneventful and both mother and child were discharged healthy.
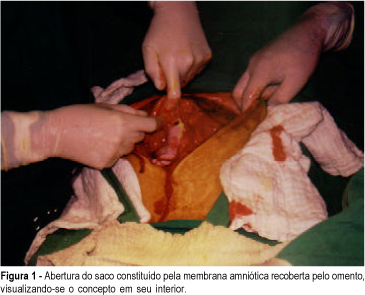
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(3):159-165
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000300007
Purpose: to determine the frequency of recurrence of seizures after anticonvulsant therapy with magnesium sulfate and to evaluate treatment and maternal prognosis. Patients and Methods: a prospective cohort study was conducted, enrolling all cases of eclampsia managed at IMIP between January/1995 and June/1998. Magnesium sulfate and oxygen therapy were administered routinely and interruption of pregnancy was performed after maternal stabilization. The frequency of recurrence of seizures and its association with maternal complications were determined. chi² test for association was used at a 5% level of significance. Results: twelve cases presented recurrence of convulsions after magnesium sulfate (10%) and all received a repeated dose. In four of them convulsions persisted and they received intravenous diazepam. After diazepam, one patient still had seizures, with unsuccessful administration of phenytoin and therefore barbituric coma was induced (thionembutal). This patient had a CT-scan with evidence of intracerebral hemorrhage. Maternal complications were significantly more frequent in the group with recurrence: coma (16.7% versus 0.95), acidosis (50% versus 2.9%), pulmonary edema (16.7% versus 2.9%), cerebral hemorrhage (16.7% versus 0%) and acute renal failure (16.7% versus 1.9%). Three cases of maternal death occurred in patients with recurrence (25%) versus 2 cases in patients without recurrence (1.9%). Conclusions: rate of recurrence after anticonvulsant therapy with magnesium sulfate is low (10%) but it is associated with increased maternal morbidity and mortality. These cases must be managed in an intensive care unit and submitted to routine CT-scan because cerebral hemorrhage can be the cause of recurrence.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):191-199
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000400002
Purpose: to determine the frequency of prenatal diagnosis in newborns with gastroschisis operated at the Instituto Materno-Infantil de Pernambuco (IMIP) and to analyze its repercussions on neonatal prognosis. Patients and Methods: a cross-sectional study was carried out, including 31 cases of gastroschisis submitted to surgical correction in our service from 1995 to 1999. Prevalence risk (PR) of neonatal death and its 95% confidence interval were calculated for the presence of prenatal diagnosis and other perinatal and surgical variables. Multiple logistic regression analysis was carried out to determine the adjusted risk of neonatal death. Results: only 10 of 31 cases of gastroschisis (32.3%) had prenatal diagnosis and all were delivered at IMIP. No newborn with prenatal diagnosis was preterm but 43% of those without prenatal diagnosis were premature (p < 0,05). Birth-to-surgery interval was significantly greater in the absence of prenatal diagnosis (7.7 versus 3.8 hours). The type of surgery, need of mechanical ventilation and frequency of postoperative infection were not different between the groups. Neonatal death was more frequent in the group without prenatal diagnosis (67%) than in the group with prenatal diagnosis (20%). The main factors associated with increased risk of neonatal death were gestational age <37 weeks, absence of prenatal diagnosis, delivery in other hospitals, birth-to-surgery interval > 4 hours, staged silo surgery, need of mechanical ventilation and postoperative infection. Conclusions: prenatal diagnosis was infrequent among infants with gastroschisis and neonatal death was extremely high in its absence. It is necessary to achieve greater rates of prenatal diagnosis and to improve perinatal care in order to reduce this increased mortality.