You searched for:"Anibal Faúndes"
We found (22) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):437-441
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800002
Purpose:to compare the incidence of preterm labor and birth, premature rupture of membranes (PROM) and low birth-weight newborns (< 2,500 g) between two groups of pregnant women (with or without BV). To verify the adequacy of including a regular prenatal BV investigation. Methods:a total of 217 women between 28 and 32 weeks of pregnancy (35 with BV and 182 without BV) were studied. The diagnosis of BV was established according to Amsel's criteria. The data were analyzed by the chi² test, Fisher's test, Mann-Whitney test and the relative risk. Results:the incidence of preterm labor, preterm birth, PROM and low birth-weight was statistically higher in the group of women with BV than in the control group (29.4% vs. 3.8%; 28.6% vs. 3.3%; 22.9% vs. 10.4%; 20.0% vs. 3.3%; respectively). The means of gestational age and birth-weight were significantly lower in the newborns from mothers with BV (265.8 days vs. 279.9 days; 2,958 g vs. 3,294 g, respectively). Conclusion:all perinatal complications studied were significantly associated with the presence of untreated BV during pregnancy. Therefore, the diagnosis and adequate treatment should be included in the routine prenatal assistance at Brazilian Obstetrics Services. Such measure may be effective in the reduction of these perinatal complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):565-569
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998001000004
Purpose: to estimate the duration of cervical neoplasia from human pappilomavirus (HPV) infection to advanced invasive carcinoma, using as paremeter the mean age of the women at diagnosis. Methods: this cross-sectional study included 1,177 women with HPV infection, 1,561 with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and 773 with invasive carcinoma. Results: the mean ages of CIN 1 and CIN 2 on diagnosis were not statistically different. The mean duration of CIN 2 was 2.2 years. The mean duration of CIN 3 was 10.3 years, with 4.1 years as severe dysplasia and 6.2 years as carcinoma in situ (CIS). The mean duration of high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions was 12.5 years. The duration means of invasive carcinoma stages Ia, Ib and II were 3.0, 2.7 and 3.7 years, respectively. Conclusions: according to the results, CIN 1 and CIN 2 may arise directly from HPV infection and most of these lesions are transient. CIS presented the longest duration and the mean asymptomatic period of cervical neoplasia is 18.2 years. These results were discussed considering the present knowledge of the natural history of cervical carcinoma and other studies on duration of this neoplasia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):227-232
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400008
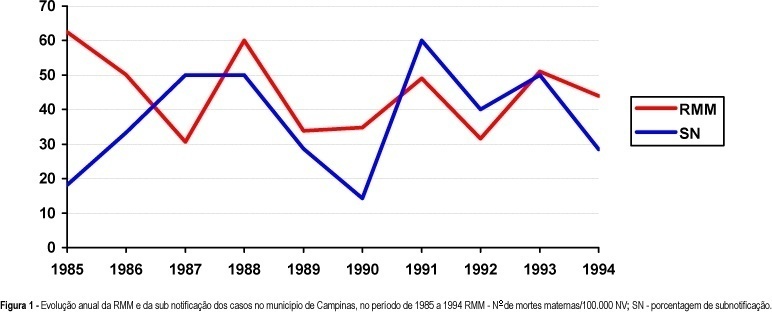
Purpose: to identify and investigate the causes of maternal death that occurred in Campinas from 1992 to 1994. Methods: a total of 204 death certificates (DC) whose causes of death were maternal (declared and/or presumed) were selected among the 1032 DC's of 10 to 49 year-old women. A complementary investigation was performed consulting hospital records, Death Survey Units, and households. Results: a total of 20 maternal deaths were confirmed, corresponding to a maternal mortality ratio of 42.2 deaths per 100,000 live births. The direct obstetrical causes were responsible for 85% of the deaths (17 cases). Abortion complications were the main causes of death (7 cases), followed by hemorrhage (4 cases), preeclampsia (3 cases) and puerperal infection (3 cases). Conclusions: despite the apparent progress concerning the reduction in deaths due to hypertensive syndromes during pregnancy, that were the main causes in earlier periods, there was no improvement in the maternal mortality ratio for this studied period. Unfortunately, this lack of progress was due to abortion complications. A better coverage and efficiency of family planning programs, besides the need for implementation of a real epidemiological surveillance of maternal deaths, as well as a better social protection of the pregnant woman, the mother, and the newborns, could reduce their occurrence and specially those due to abortions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):220-226
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400003
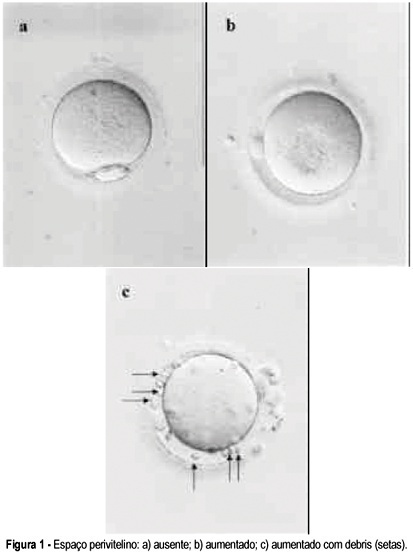
PURPOSE: to verify the possibility of identifying oocytes that would result in a higher fertilization rate. METHODS: retrospective analysis of the fertilization rate after ICSI of 957 oocytes in metaphase II according to three morphology parameters: cytoplasm inclusions, thickness of the perivitelline space, and fragmentation of the first polar body. Oocytes were obtained from 115 cycles performed among 107 women attended at the "Centro de Reprodução Humana de Campinas", from April to December of 2004. For the statistical analysis of differences in the fertilization rate between 'normal' oocytes and those presenting each alteration, the chi2 test was used with confidence levels of 5 and 10%. RESULTS: no significant difference in fertilization rate was observed regarding characteristics of the polar body or thickness of the perivitelline space. Fertilization rate among oocytes with perivitelline space with debris was 14 percentage points lower than among oocytes with absent space (p=0.055) and the rate among oocytes with granular cytoplasm was seven percentage points lower than among oocytes with normal cytoplasm (p<0.10>0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the morphological parameters of oocytes currently being evaluated do not allow us to clearly distinguish those that would lead to a higher fertilization rate and could be used in clinical practice.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):126-135
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200009
Gender-based violence is related to the power imbalance between men and women that is present, to a greater or lesser degree, in all societies. It was recognized as a human rights problem by the UN relatively recently. It includes emotional, physical and sexual violence. Sexual violence is the extreme form of gender violence, usually accompanied by the other types of violence. Its prevalence is difficult to determine, but it most probably affects at least one third of women some time in their life. It has multiple consequences to women's physical and gynecological health, which depends in great part on the quality of the care the woman received immediately after the assault. Unfortunately, most emergency health services, including those in women's hospitals, are rarely prepared to provide the correct care for these women. Care should be multidisciplinary and involves crisis treatment, meticulous clinical examination with complementary auxiliary methods, treatment of physical lesions, prevention of pregnancy and of sexually transmitted infections and AIDS, and follow-up for at least six months after the aggression.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):519-525
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900004
Purpose: to present the perinatal outcomes resulting from the use of a protocol for assistance to diabetic pregnant women used at the Center for Integral Assistance to Women's Health (CAISM), of the University of Campinas. Methods: ninety diabetic pregnant women, who were assisted at the institution with this protocol, were compared with two control grups: the first consisted of 180 pregnant women with equal number of gestations and same age (control A) and the second consisted of 180 randomly selected pregnant women (control B). The study variables were route of delivery, indication for cesarean section, gestational age, Apgar score at first and fifth minute, weight, adequacy of weight for gestational age and perinatal morbidity and mortality. For the statistical analysis Student's t-test and the chi2 test were used. Results: there was a higher incidence of cesarean sections, prematures and large to gestational age (LGA) babies among diabetic women, as well as higher occurrence of neonatal morbidity such as hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyperbilirubinemia, respiratory distress and neonatal depression. The incidence of low Apgar score and perinatal mortality was significantly higher than in the randomly selected group, but the same as in the group matched regarding age and number of pregnancies. Conclusions: although this protocol intends to obtain a perfect metabolic control among diabetic pregnant women, the perinatal outcomes are still unfavorable in comparison to nondiabetic pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(10):579-584
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999001000003
Purpose: to evaluate the accuracy of maternal perception of fetal movements (MPFM) in diabetic pregnant women, using Apgar score at the 1st and 5th min of life, intrapartum fetal distress and neonatal hypoxia as parameters. Methods: two hundred and nine diabetic women evaluated at the High Risk Prenatal Care Clinic of the Women's Hospital (CAISM) were analyzed retrospectively between June 1988 and May 1996. All patients had MPFM records within three days before delivery, fetal heart rate recordings during labor, gestational age greater than 30 weeks and a complete neonatal evaluation. MPFM was classified as normal if seven movements were recorded in 60 min. Results: the sensitivity of the test was 23 and 29% for Apgar score <7 at the 5th min and intrapartum fetal distress, respectively, and close to 50% for neonatal hypoxia (45.5%). Specificity was near 95% for the three standards, and the negative predictive value (NPV) was 80% for fetal distress, increasing to 97 and 98% for Apgar >7 at 5 min and neonatal hypoxia. Conclusions: MPFM is a useful test to identify diabetic women needing fetal evaluation with more complex techniques, given the high NPV, that indicates the capacity to separate the cases where the fetus is in good condition.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(3):153-157
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000300006
Purpose: to evaluate, in a Brazilian population, the possible association between history of sexual violence and some of the more frequent gynecologic complaints related by women. Methods: secondary analysis of data from a cross-sectional study in which 1838 women between 15 and 49 years of age were interviewed in their homes. They were residents of the cities of Campinas and Sumaré, in the state of São Paulo. A structured and pretested questionnaire was used, which allowed to characterize the interviewees' history of sexual violence, the existence of sexual dysfunctions and the presence of gynecologic symptoms in the year previous to the interview. The statistical differences were evaluated by the chi² test. Results: little more than one third (38.1%) of the women did not report history of sexual violence; 54.8% related that at least once they had had sexual intercourse against their will, without being forced to, although 23% mentioned some kind of coercion; 7.1% reported having been forced to have sex. Statistical association was found between history of sexual violence and the reference to gynecologic complaints and sexual dysfunctions. Conclusions: it was observed that even less aggressive forms of imposition of the man's will in the couple's sexual life were associated with a higher prevalence of the most frequent gynecologic complaints. The gynecologist must, therefore, have in mind this etiological factor which is rarely being considered at the present time.