Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):519-523
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700009
PURPOSE: to analyze the accuracy of sonohysterography for the evaluation of the uterine cavity in patients with an implantation failure, at the first attempt of an in vitro fertilization cycle. METHODS: in a prospective double blind study, the authors analyzed patients previously submitted to at least one embryo transfer, who presented implantation failures. The patients were submitted to a sonohysterographic examination followed by a diagnostic hysteroscopic examination, carried out by different professionals each of whom was not aware of the results of the other. The results were recorded and only interpreted after the end of the trial. Sonohysterography was performed by the introduction of a urethral catheter 8 into the uterine cervix followed by infusion of physiological saline. The anechoic interface shown by the physiological saline can reveal abnormalities, like uterine polyps or submucosal myomas. Hysteroscopy was performed with a Karl Storz equipment, 4 mm 30º rigid telescope, and infusion of physiological saline for uterine cavity distention. RESULTS: twenty-eight of the 33 originally selected patients for this study were analyzed. Sonohysterography detected abnormalities in 8 patients, five with endometrial polyps (62.5%), two with endocervical polyps (25.0%), and one with submucosal myoma (12.5%). Hysteroscopy (gold standard) detected abnormalities in 7 patients, two with endometrial polyps (28.6%), two with cervical polyps (28.6%) and one with submucosal myoma (14.2%). Sonohysterography, when compared with diagnostic hysteroscopy, presented 71.4% sensibility, 85.7% specificity, 62.5% positive predictive value, and 90% negative predictive value of. CONCLUSION: due to its low positive predictive value, the authors suggest confirmation of the sonohysterography result by diagnostic hysteroscopy. Because sonohysterography presents a good level of specificity and a favorable low negative predictive value, the authors suggest that after a normal sonohysterography diagnostic hysteroscopy to evaluate the uterine cavity before in vitro fertlization is not necessary. This study leads to the conclusion that sonohysterography is a good screening method for the detection of polypoid lesions of the uterine cavity, which could be responsible for implantation failures in in vitro fertilization cycles.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):525-528
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700010
PURPOSE: to evaluate the results of the use of bovine pericardium in the pubovaginal sling procedure for treatment of stress urinary incontinence. METHODS: a prospective analysis of five patients who underwent pubovaginal sling with the use of bovine pericardium strip for stress urinary incontinence in the "Hospital das Clínicas of UFMG" from October/2001 to December/2001. The mean age was 48.2±11.5 years (33 to 69 years). RESULTS: the mean surgical time was 45±35.3 min and the mean hospital stay was 36±12.4 h (24 to 48 h). Complications in the periperative or immediate postoperative period did not occur. All patients initially presented satisfactory results with normal voiding and without stress incontinence. Postoperative complications occurred in the 5 patients (100%), with dehiscence of the vaginal wound and total expulsion of the strip in 2 patients (40%) and partial expulsion in 3 patients (60%). All patients presented stress urinary incontinence and were submitted to a new sling procedure using the rectus fascia. The patients then progressed without complications and with improvement of urinary continence in 4 patients (80%). CONCLUSIONS: pubovaginal sling with the use of bovine pericardium was associated with high rates of complications. Therefore, its use is not recommended in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):529-532
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700011
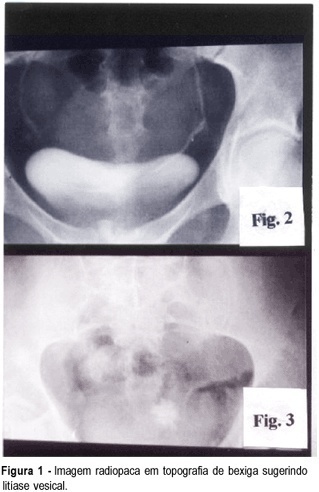
The fistulas caused by mechanical trauma are rare, mainly the intrinsic type caused by vesical lithiasis. The treatment of these fistulas is controversial, concerning the ideal surgical technique. Several techniques have been developed, including the transvaginal and the transabdominal surgical approaches. The authors report the case of a patient with urinary loss for six months. Physical and radiological examination showed the occurrence of a vesicovaginal fistula caused by vesical lithiasis. The treatment was in two stages: first the extraction of the vesical stone by transabdominal approach and second, the correction of the fistula by transvaginal approach.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):533-533
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700012
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):533-533
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700013
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):534-534
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700015
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):534-534
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700014
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):535-535
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700017