Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(6):477-482
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000600009
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the neonatal morbidity and mortality related to mothers at the age of 35 or older than that. METHODS: in 2377 births in a year, 316 newborns (13.26%) from mothers at the age of 35 or more were selected for the study. These women were compared to pregnant controls aged 20 to 29, randomly selected among the 1170 women in the same age group (49,2%). For the inclusion criteria, pregnancies should have been over 22 weeks and the newborns should have weighted 500g or more at birth. Fourteen twin cases were excluded. To evaluate mortality and morbidity the following variables were considered: Apgar Index, birth weight, newborn health conditions, fetal malformations and neonatal mortality until hospital discharge. RESULTS: when analyzed as a whole, nulliparous and multiparous women showed significantly less favorable perinatal results for the selected group of women at 35 or more years old as compared with pregnant controls, what was not sustained when the nulliparous were excluded. Multiparous at the age of 35 or over presented a higher rate of low Apgar index in the 1st minute: 21.3 and 13.1%: (p<0,0033); small NB for the gestational age: 15.2% and 6.7% (p<0,02); big NB for the gestational age: 5.7 and 0.0% (p<0,02); low weight at birth: 23.8 and 14,5% (p<0,01), and prematurity, 16,7 and 6,7%, (p<0,005). Significant differences were not found for the Apgar index in the 5th minute, fetal malformations, newborn health conditions at hospital discharge and neonatal mortality. CONCLUSIONS: Neonatal morbidity increased among pregnant women at the age of 35 and older, but not the neonatal mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(6):483-488
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000600010
OBJECTIVE: to determine whether the clinical presentation of hydatidiform mole has changed in the recent years (1992-1998) when compared with historic controls (1960-1981). METHODS: medical records of 80 patients with hydatidiform mole attended in the 1960-1981 period (Group I) were reviewed and compared to data from 801 patients followed in the 1992-1998 period (Group II). The clinical signals and symptoms analyzed were: age distribution, number of pregnancies, vaginal bleeding, hyperemesis, edema, hypertension, large uterus for gestation date and theca lutein cysts of the ovaries. Statistical analyses employed chi-square tests and odds ratio (OR) estimate with the confidence interval (CI) of 95%. RESULTS: concerning age, the disease occurred more frequently in group II than in group I, in patients under 15 and over 40 years old. As to the number of pregnancies, there was no statistical difference only in those patients who were in their third or fourth pregnancies. Arterial hypertension was the only symptom that occurred with similar frequency in both groups. Enlarged uterus was more frequent in group II (41.4 X 31.2% - p <0.05; OR: 1.5; IC: 1.0-2.3). Bleeding remained the most common symptom, occurring in 76.9% of patients (Group II), although it has occurred in 98.7% of the historic controls (p<0.05; OR: 0.04; IC: 0.03 0.04). The following symptoms were also less frequent in group II as compared to group I: hyperemesis (36.5% X 45% - p<0.05; OR: 0.7; IC: 0.4 0.9), edema (12.7% X 20% - p<0.05, OR: 0.5, IC: 0.3 0.8), enlarged uterus for gestational age (41.4% x 31.2% - p<0.05; OR: 1.5; IC: 1.0 2.3) and theca lutein cysts (16.4% X 41.2% - p<0.05; OR: 0.3; IC: 0.2 0.4). Ultrasound has become the commonest method of diagnosis (89.2% - p<0.05), allowing early detection of hydatidiform moles. CONCLUSION: there was a decrease of the traditional symptoms in current patients with hydatidiform mole as compared to historic controls, due to early diagnosis through ultrasonography.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(6):489-494
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000600011
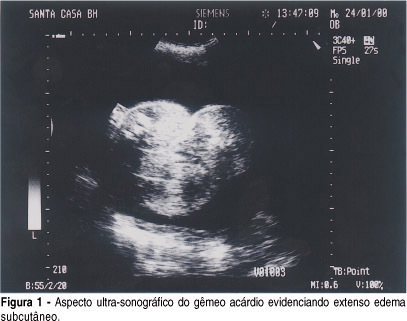
Twin pregnancy with an acardiac twin is a rare event characterized by the presence of a placentary arterial anastomosis between the pump twin, morfologically normal, and the acardiac twin, causing a reverse circulation in one of the twins. The major complications are associated with cardiac failure in the normal twin, which is due to circulatory overload and prematurity. Many therapeutic options have been proposed, but there is no consensus about which one is the best therapy. However, intrafetal ablation of the umbilical artery of the acardiac fetus proved to be an inexpensive method that is easy to perform and highly efficient in controlling circulatory overload. We presented two cases of intra-fetal ablation and good evolution. A triplet pregnancy in which the intra-fetal ablation was done in a 29-week-old fetus that evolved to premature delivery of a healthy baby, and a twin pregnancy in which intra-fetal ablation was done in a 31-week-old fetus that evolved to premature rupture of membranes and the premature delivery of a healthy baby.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(6):495-495
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(6):495-496
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(6):496-496
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(6):497-498
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(6):497-497