Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):547-553
There are no published studies analyzing the quality of the information for lay women on the Internet regarding uterine fibroids. The accuracy of the provided material is also unknown. Thus, we have performed a cross-sectional study with 381 websites in the English and Brazilian Portuguese languages between May and December 2017.
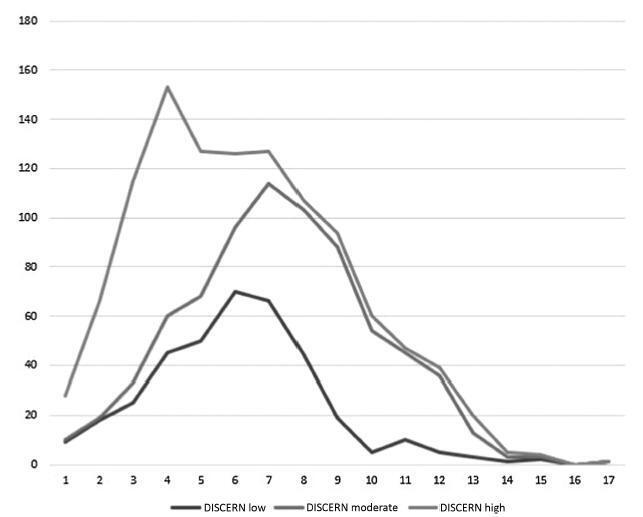
Two investigators performed the analysis, and the Cohen kappa coefficient was calculated to analyze the agreement between them. Search terms (uterine fibroids and derivatives) in the English and Brazilian Portuguese languages were used. The accuracywas analyzed by a 10-itemchecklist created based on the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), National Institutes of Health (NIH) and European Menopause and Andropause Society (EMAS) consensuses about uterine fibroids. The item-test correlation and the intraclass coefficient were performed in the 16 questions from the DISCERN instrument, which was designed to measure the quality of health information on the Internet. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) measurements were performed for the independent variables and the DISCERN/accuracy scores.
Google was the most used search engine, and uterine fibroid was the search term that generatedmost of the analyzed material. The median score for accuracy in all websites was 5 out of 10, and the median score of the DISCERN instrument was 38 out of 80. The top-scoring sites in the English language were derived from scientific organizations and federal governments, and they regarded the DISCERN score (The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists [ACOG], the Food and Drug Administration [FDA]) and the accuracy criteria (NIH, and FDA). On the other hand, in the Brazilian Portuguese language, the highest scores in both instruments were from magazines or physician’s blogs. The Cronbach α test showed a higher correlation (0.77-0.79) between the sites and DISCERN; however, the item-test correlation varied from 0.39 to 0.56.
There is a need to improve the quality of the information regarding uterine fibroids for lay women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):540-546
To determine the frequency of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in asymptomatic women and the association of STIs with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN).
A cross-sectional studywas performed, enrollingwomen examined in a general gynecology clinic and in a colposcopy referral center fromOctober 2014 to October 2015. The colposcopy groupconsisted of 71women, and the general gynecologygroupconsisted of 55 women. Cervical samples were collected for cervical cytology and a multiplex realtime polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was developed to detect human papillomavirus (HPV) and the STIs caused by the following microorganisms: Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. A multivariate analysis was performed by logistic regression, considering the significance level of 0.05.
The general frequency of STIs was: 46.8% (HPV); 27.8% (C. trachomatis); 28.6% (M. genitalium); 0.8% (M. hominis); 4.8% (U. urealyticum); and 4.8% (N. gonorrhoeae). The significant risk factors for CIN were: HPV infection (odds ratio [OR] = 2.53; p = 0.024); C. trachomatis (OR = 3.04; p = 0.009); M. genitalium (OR = 2.37; p = 0.04); and HPV and C. trachomatis coinfection (OR = 3.11; p = 0.023). After the multivariate analysis, a significant associationwas found betweenHPVand CIN(OR = 2.48; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.04-5.92; p = 0.04); and between C. trachomatis and CIN (OR = 2.69; 95%CI: 1.11-6.53; p = 0.028).
The frequency of STIs was high in asymptomatic patients. Infections by HPV and C. trachomatis were independently associated with the presence of CIN. The high frequency of STIs in asymptomatic women suggests the need for routine screening of these infections.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):527-533
Assisted reproduction combines innovative technologies and new forms of procreation through gamete donation; however, it also leads to moral and ethical issues and to the wide application of referential bioethics. The objective of the present study was to understand the bioethical context of shared oocyte donation.
The present qualitative study used the Collective Subject Discourse methodology to interview donors and recipients in Brazil.
Donors suffer from infertility, and in vitro fertilization opens the possibility of having a child; however, the cost is high, and helping the recipient is more important than the financial cost. The recipients regret delaying motherhood; adopting a child is their last option, and they desire to feel the physical stages of pregnancy. The recipients find the rules unfair regarding the lack of an oocyte bank and the fact that the treatment must be performed in shared cycles; however, oocyte donation makes it possible to realize the common dream of motherhood.
The obtained data showed that the patients are suffering and frustrated due to infertility, and they realize that in vitro fertilization may be the treatment they need. These women believe that children are essential in the constitution of the family, and scientific advances bring about innovative technologies and new forms of family constitution, with repercussions in the social, economic, political, and family contexts that lead to bioethical questions in Postmodernity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):79-85
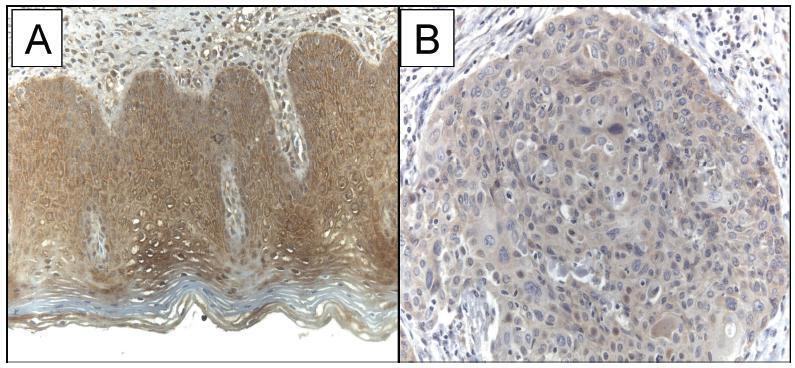
The current study evaluated the expression of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase (WWOX), its association with clinicopathological features and with p53, Ki-67 (cell proliferation) and CD31 (angiogenesis) expression in patients with invasive cervical squamous cell carcinoma (ICSCC). To the best of our knowledge, no other study has evaluated this association.
Women with IB stage-ICSCC (n = 20) and women with uterine leiomyoma (n = 20) were prospectively evaluated. Patients with ICSCC were submitted to type BC1 radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy. Patients in the control group underwent vaginal hysterectomy. Tissue samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological evaluation and protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry studies.
The WWOX expression was significantly lower in the tumor compared with the expression in thebenign cervix (p = 0.019). TheWWOXexpressionwas inversely associated with the CD31 expression in the tumor samples (p = 0.018). There was no association betweentheWWOXexpression with the p53 expression (p = 0.464)or the Ki-67expression (p = 0.360) in the samples of invasive carcinoma of the cervix. There was no association between the WWOX expression and tumor size (p = 0.156), grade of differentiation (p = 0.914), presence of lymphatic vascular invasion (p = 0.155), parametrium involvement (p = 0.421) or pelvic lymph node metastasis (p = 0.310) in ICSCC tissue samples.
The results suggested that WWOX may be involved in ICSCC carcinogenesis, and this marker was associated with tumor angiogenesis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):86-91
To compare the quality of cervicovaginal samples obtained from basic health units (BHUs) of the Unified Health System (SUS) and those obtained fromprivate clinics to screen precursor lesions of cervical cancer.
It was an intervention study whose investigated variables were: adequacy of the samples; presence of epithelia in the samples, and cytopathological results. A total of 940 forms containing the analysis of the biological samples were examined: 470 forms of women attended at BHUs of the SUS and 470 forms of women examined in private clinics in January and February of 2016.
All the unsatisfactory samples were collected at BHUs and corresponded to 4% of the total in this sector (p < 0.0001). There was a higher percentage of samples containing only squamous cells in the SUS (43.9%). There was squamocolumnar junction (SJC) representativeness in 82.1% of the samples from the private clinics (p < 0.0001). Regarding negative results for intraepithelial lesions and/or malignancies, the percentages obtained were 95.9% and 99.1% (p < 0.0049) in the exams collected in the private system and SUS, respectively. Less serious lesions corresponded to 0.89% of the samples from the SUS and 2.56% of the tests from the private sector; more serious lesions were not represented in the samples obtained from BHUs, whereas the percentage was 1.49% in private institutions.
Unsatisfactory cervical samples were observed only in exams performed at the SUS. There is a need for guidance and training of professionals who perform this procedure to achieve higher reliability in the results and more safety for women who undergo this preventive test.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):66-71
To evaluate the impact of sexual function (SF) in the quality of life (QoL) of women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI).
Case-control study in which 80women with POIwere evaluated using estrogen plus progestogen therapy, compared with 80 women matched by age (2 years) and presenting preserved gonadal function. Sexual function was evaluated using the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), and the QoL was evaluated using theWorld Health Organization's (WHO) QoL assessment instrument (WHOQoL-BREF).
The mean age of the women with POI and of the control group was 38.4 ± 7.3 years and 38.1 ± 7.3 years respectively. The QoL, was worse among the POI group, and there were significant differences in the physical (63.4 ± 17.4 and 72.7 ± 15.2 respectively, p = 0.0004) and psychological (63.2 ± 14.6 and 69.3 ± 13.9 respectively, p = 0.0075) domains among this group when compared with the control group. Women with POI presented significantly lower arousal, lubrication, orgasm and satisfaction, more dyspareunia and a worse FSFI scores when compared with the control group. All aspects of SF correlate directly with the worsening of the QoL regarding social relationships.
Women with POI showed worse QoL and SF than the control group. The psychological aspects (desire, excitement, orgasm and sexual satisfaction) of SF had greater influence on the parameters of the QoL, while the physical aspects (pain and lubrication) had a low impact on the QoL. The poor SF in women with POI is directly correlated with a worsening acrossmultiple domains of the QoL; however, the negative impact is particularly important in the social domain. These results suggest that the improvement in sexuality can improve the social interactions of women with POI.