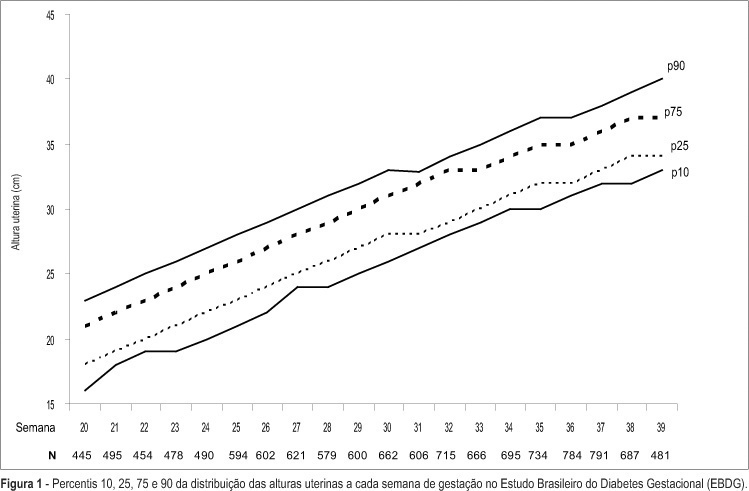
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(9):513-522
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000900003
PURPOSE: to describe, in participants of the Brazilian Study of Gestational Diabetes (EBDG), the percentile distribution of uterine height by gestational age and to validate the use of percentiles of the chart derived by the "Centro Latino-Americano de Perinatologia" (CLAP), used as reference in predicting abnormal fetal growth. METHODS: the EBDG is a cohort study of 5564 pregnant women older than 19 years, followed through and after delivery. Interviews and standardized anthropometry were performed at baseline between 20-28 weeks. Medical records covering prenatal and delivery periods were then reviewed following a standardized approach. Analyses pertain to 3539 women with gestational age confirmed by ultrasound. Diagnostic properties of the 10th and the 90th percentiles of both charts (EBDG and CLAP) as predictors of abnormal neonatal weight were determined. RESULTS: uterine height was higher in EBDG than in the CLAP chart at every gestational week, being 1-4 and 2-6 cm greater, at the 10th and 90th percentiles respectively. The CLAP 10th percentile classified as small the uterine heights of only 0.3 to 1.7% of Brazilian women, while the 90th percentile classified as large the uterine heights of 42 to 57% of the sample. The sensitivity of CLAP percentile 10 in the prediction of small for gestational age varied from 0.8 to 6% and the specificity of CLAP percentile 90 in the prediction of large for gestational age, from 46 to 61%. CONCLUSIONS: the CLAP uterine height reference chart does not reflect the current uterine growth pattern of pregnant Brazilians, limiting its clinical applicability in the detection of abnormal fetal growth, especially intrauterine growth restriction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):310-315
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500008
Maternal mortality rate (MM) is a health quality indicator that is directly influenced by the economic, cultural and technological level of a country. Official data of MM in Brazil, although underestimated, point to the lack of quality in pregnancy, childbirth and puerperium care services. This characteristic is common in developing countries, where poorer pregnant women as well as those facing greater difficulty to quality care access are found. Prenatal care cannot prevent major childbirth complications, which are important causes of MM; however, some interventions during the prenatal period can favor maternal prognosis and prevent MM. In this setting, this study brings a scientifically based update concerning effective interventions for maternal mortality prevention during the prenatal period. The most important strategies consist of a tripod with specific interventions related to maternal health promotion, risk prevention and assurance of nutritional support during gestation, in addition to criteria to investigate gestational risk and inclusion of the pregnant woman in the basic component of the prenatal care model. It ends with the definition of priorities in the prevention of MM related to eclampsia/preeclampsia and reinforces the importance of normalization of reference systems for obstetric emergency cases.
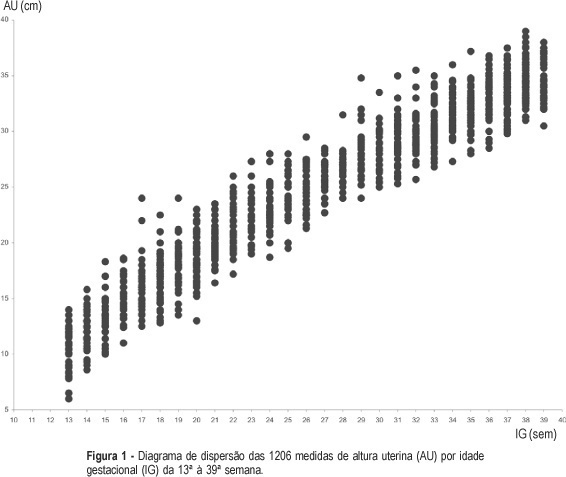
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(1):3-9
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000100002
PURPOSE: to build a curve of fundal height according to gestational age among low-risk pregnant women and to compare it with the official standards used in Brazil. METHODS: a prospective observational study was carried out. A sample of 227 low-risk pregnant women with gestational age from 13 to 39 weeks was followed-up in the prenatal care sector of two public health services from João Pessoa, PB. Women with a known gestational age, a single live fetus, without malformation, with no known maternal-fetal pathological condition that could possibly affect fetal growth, with a normal body weight, and non-smokers were included in the study. Their fundal height was measured in a standard way, after a previous ultrasound done to confirm the gestational age. The same investigator performed 1206 measurements and each woman had a mean of 5.3 measurements. Statistical tests were performed with a significance level of 5%. Tables and graphs of fundal height were built according to the gestational age with the 10th, 50th and 90th percentiles. RESULTS: the values of percentiles 10, 50 and 90 of fundal height in each gestational age allowed the construction of a pattern curve of fundal height by gestational age among low-risk pregnant women. A clear visual difference was observed between this new and the official fundal height curve. Statistical analyses showed significant differences between them from the 19th week on. CONCLUSION: the results suggest different normal fundal height and fetal growth patterns among low-risk pregnant women on prenatal assistance compared to the used standard curve, thus with different performances when used for diagnosing fetal growth deviations. Future studies should validate the current fundal height curve by gestational age in order to possibly use it as a reference pattern.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(12):768-778
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001200010
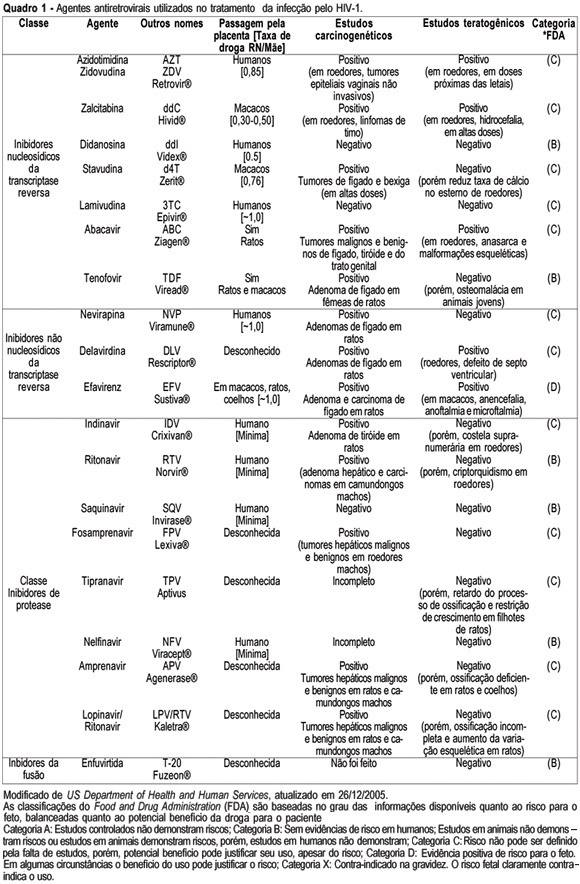
Knowledge about the factors or situations that influence the vertical transmission (VT) of human immunodeficiency type 1 (HIV-1) has led to the implementation of strategies which have promoted a rate decline along the years, from 40% to less than 3% nowadays. One of the major advances in the area has been the prophylactic administration of zidovudine (AZT), in the prenatal phase (oral route), in the predelivery phase (intravenous route) and to the newborn (oral route). This intervention may reduce HIV-1 VT 68%, thus being the most effective isolated strategy used so far. In the chronological sequence of advances, it has been observed that a high viral load is the main risk indicator for this type of transmission. As AZT does not reduce the viral load and does not control the residual rate observed in HIV-1 VT, the use of prophylactic schemes using three antiretroviral drugs has been encouraged. Elective caesarean section completes the range of obstetric strategies with major impact on the reduction of HIV-1 VT. Its effectiveness is linked to the observation of the criteria for its indication: viral load assessed after the 34th week of pregnancy with levels over 1000 copies/mL, gestation over 38 weeks confirmed by ultrasonography, intact chorioamniotic membranes, and performed before labor has started. In cases where normal delivery is indicated, it should be remembered that prolonged chorioamniorrhexis, invasive manipulation of the fetus, delivery with instruments and episiotomy are situations to be avoided. Among the postnatal interventions considered important for the reduction of HIV-1 VT are: pediatric reception (this should be done by trained professionals, avoiding microtraumas in the mucosa during the sucking maneuvers, use of neonatal AZT (for a period of six weeks) and bottle feeding. Special attention should be given to the orientation for the mother, in order to prevent acute infection by HIV-1 in this period, what would markedly increase virus VT rate.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):548-553
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900008
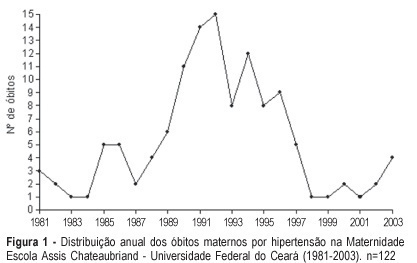
PURPOSE: to study maternal mortality caused by hypertension during pregnancy, determining the mortality rate and the profile of those patients. METHODS: a retrospective study of maternal mortality caused by hypertension at the Maternidade Escola Assis Chateaubriand of the Universidade Federal do Ceará, from 1981 to 2003. General maternal mortality rate (MMR) and specific maternal mortality rate due to hypertension were evaluated, as well as these patients' epidemiological and clinical data. RESULTS: two hundred and ninety six cases of maternal death and 184,672 of live births were recorded, with a MMR of 160.28/100.000 live births. The most frequent cause of death was hypertension (41.2%); with 122 cases and an annual average of 5.3 deaths, and hypertension MMR of 60.10/100,000 live births. The women's age range varied from 13 to 42 years with an average of 26 years. Most of the patients came from the interior of the state. Deaths occurred predominantly in the first 24 hours after admission to the hospital (50.9%). Deaths were predominant in the first pregnancy (40.3%) and in women with 31 to 38 weeks gestational age (48.2%). Eclampsia occurred in 73 patients (64.1%) and was predominant along the gestational period (53.4%). There were 101 deaths in the puerperium. Cesarean section (62.3%) and general anesthesia (45.1%) prevailed. A high percentage of patients (61.4%) had no prenatal care. CONCLUSIONS: General MMR and hypertension MMR were high, the latter being the main cause of death in our maternity hospital.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(7):509-515
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000700002
PURPOSE: to analyze vaginal contents using the fresh wet mount of a cytological exam in the first prenatal visit of women with or without genital complaints and correlate the conclusion with the results from the Pap smears. Microscopy during pregnancy should be valued and recognized as a method capable of providing immediate diagnosis in 90% of bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis and trichomoniasis cases. METHODS: a prospective study was performed in 216 pregnant women selected from the prenatal department of a public hospital, between October 30, 2001 and November 12, 2002. Two samples were collected from the posterior vaginal vault and deposited onto two separate microscope slides. To one slide, a droplet of 0.9% NaCl was applied and to the other, a droplet of 10% KOH. Both slides were covered with a coverslip for immediate microscopic evaluation. Tests were perfomed in one drop of the material to examine pH and whiff. The microscopic examination of the material was carried out at a 100X, 400X and exceptionally 1000X magnification. Pap smears were performed in all pregnant patients. The correlation between the results of the utilized cytological methods was perfomed by the kappa coefficient, which evaluates the concordance for quality variables. RESULTS: the findings of the normal vaginal microflora in the fresh wet mount were 7.8%, representing the most observed cytological aspect, and without correspondence with the 3.70% verified by the Pap smears. In the fresh wet mount, bacterial vaginosis was found in 30.9% and candidiasis in 7.9% of the cases. However, in the Pap smears no similar event occurred, the diagnosis being 0.7 and 24.3%, respectively. The absence of a diagnosis correlation of nonspecific bacterial vaginitis by direct microscopy (17.5%) and Pap smears (51.3%) is probably due to the undervalued diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis by the latter method. The diagnosis of trichomonas vaginalis observed in both cytological methods (3.70 and 2.78%) represents a low prevalence of these parasites in the course of pregnancy. The kappa coefficient between the two cytological procedures in the several microbiological findings showed low correlation of the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis with nonspecific vaginitis, as well as the normal vaginal flora. CONCLUSIONS: although the Pap smear presents the best accuracy of the diagnosis of yeast without pseudomycelium, the fresh wet mount has shown to be a better appraiser of nonepithelial cells the vaginal smears. Because Pap smears allow a better evaluation of vaginal epithelial cells, they represent the most important tool to show the aggressions and reactions of the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(7):517-525
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000700003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the experience of implementation of the Brazilian Prenatal and Birth Humanization Program (PHPN) in 2001 and 2002, through a population descriptive study. METHODS: the study was performed through documental analysis and using data generated by SISPRENATAL, comparatively evaluating the indicators concerning criteria for prenatal follow-up in different states, regions and period. RESULTS: until the end of 2002, 3983 municipalities joined the Program (72% adhesion) and, among them, 71% reported results, constituting a data base of 720,871 women. In 2002 only 28% of the pregnant women were already registered, 25% before 120 days of pregnancy. Nearly 22% of the women had six prenatal visits, 6% had the post-partum visit and the compulsory tests performed, only 4% had also the HIV test and were vaccinated against tetanus, and 12% had two examinations performed for syphilis. There were important regional variations, generally showing better indicators for the Southeast and South regions. CONCLUSIONS: although the indicators of quality of care showed an improvement from 2001 to 2002, the recorded low percentages attest the need for permanent evaluations and new interventions with the aim of improving the quality of this care, especially in the North and Northeast regions.
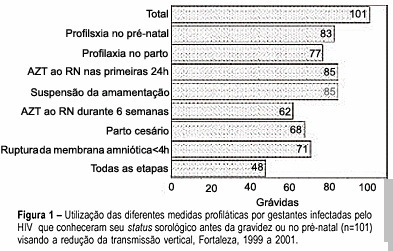
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):131-138
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200008
PURPOSE: to analyze the management for reduction of HIV transmission from mother to infant in infected pregnant women who delivered in public maternity hospitals of the municipality of Fortaleza, Ceará, from 1999 to 2001. METHODS: a descriptive study where data of SINASC, SINAN and LACEN data bank systems were cross-checked looking for HIV-infected pregnant women, followed by an active search for complementary information on the subject through medical records of the maternity hospitals. RESULTS: a hundred and thirty-eight pregnant women infected with HIV were identified. It was observed that 35.5% knew their serum status before pregnancy and 48.6% (67/138) were diagnosed during the prenatal visits. Of those 101 women that knew their serum status before or during pregnancy, only 47.5% followed all steps of prophylaxis, including the management of the newborns. The previous knowledge of the serum status was found to be significantly related to following the correct steps of prophylaxis (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: an increasing number of women who had no access to the different strategies for the reduction of vertical transmission were found in Fortaleza, Ceará, especially among those who became pregnant without knowing their serum status. Continuous awareness and training are very important for all health care providers involved in attending the pregnant women for the application of correct management in order to reduce HIV transmission from mother to infant.