-
Artigo Original30/04/2025
An assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Resumo
Artigo OriginalAn assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Visualizações224Abstract
Objective:
In vitro, fertilization is the primary treatment method for infertility. Follicular fluid analysis is an approach used to optimize the results of assisted reproductive techniques. Oxidative stress represents the imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and their detoxification. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative Stress Index levels are the main oxidative stress markers. This study investigated the effects of oxidative stress markers on infertility etiology, embryo quality, and success of In vitro fertilization.
Methods:
Before enrolling in the ICSI-ET cycle, participants had their FSH and LH levels assessed on the second day of the cycle. The ovarian degrees of the participants were evaluated by transvaginal ultrasonography. Participants underwent controlled ovarian stimulation using the GnRH antagonist protocol. TV-USG and serial E2 measurements were performed at appropriate intervals to follow follicular development. Follicle sizes, quantity, and endometrial thickness were recorded. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative analyses were conducted using Rel Assay Diagnostics Assay Kits.
Results:
The average number of total oocytes in the participants was 10.25±6.66, and the average of mature M2 stage oocytes was 6.71±3.72. The average number of fertilized oocytes was 4.65±2.81. Fertilization rates were calculated as approximately 54.75±25.58%. A statistically significant positive correlation was found between embryo quality and serum Total Antioxidant Status levels (p=0.004). Similarly, a significant positive correlation was observed between embryo quality and follicular Total Antioxidant Status values (r = 0.42, p = 0.01).
Conclusion:
This study concluded that oxidative stress markers affect certain stages of the IVF treatment process.
Palavras-chave: AntioxidantsFertilization in vitroFollicular fluidInfertilityOocytesOxidantsOxidative stressVer mais
-
Artigo de Revisão30/04/2025
Letrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in women with PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo21
Resumo
Artigo de RevisãoLetrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in women with PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo21
Visualizações253Abstract
Objective:
We aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of letrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Data Sources:
We systematically searched EMBASE, PubMed, and Cochrane databases on October 31, 2024.
Study selection:
We included studies of women with PCOS treated with a combination of clomiphene and letrozole or letrozole alone to induce ovulation that reported any of the outcomes of interest, namely rate of mature follicles and ovulation, ovulation, pregnancy, miscarriages, endometrial thickness, and number of mature follicles.
Data collection:
We pooled odds ratios (OR) and mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) using a random effects model using R statistical software, version 4.2.1. Heterogeneity was assessed with I statistics, and a random effects model was used.
Data Synthesis:
Four RCTs and two observational studies comprising 592 patients were included. Combined therapy was associated with a higher rate of a mature follicle (OR 2.74; 95% CI 1.72-4.37; p< 0.001; I=0%) and ovulation (OR 2.55; 95% CI 1.57-4.12; p< 0.001; I=35.9%). The number of mature follicles, number of pregnancies, thickness of endometrial lining, and the incidence of adverse events, including headache, abdominal bloating, fatigue, back pain, breast discomfort, and night sweats, were similar between groups.
Conclusion:
In women with anovulatory infertility secondary to PCOS, letrozole and clomiphene citrate combined therapy was associated with improved mature follicle and ovulation rates, with a similar safety profile compared to letrozole alone. However, no significant impact was observed on pregnancy rates.
Palavras-chave: ClomipheneInfertility, femaleLetrozoleOvulationOvulation InductionPolycystic ovary syndromeVer mais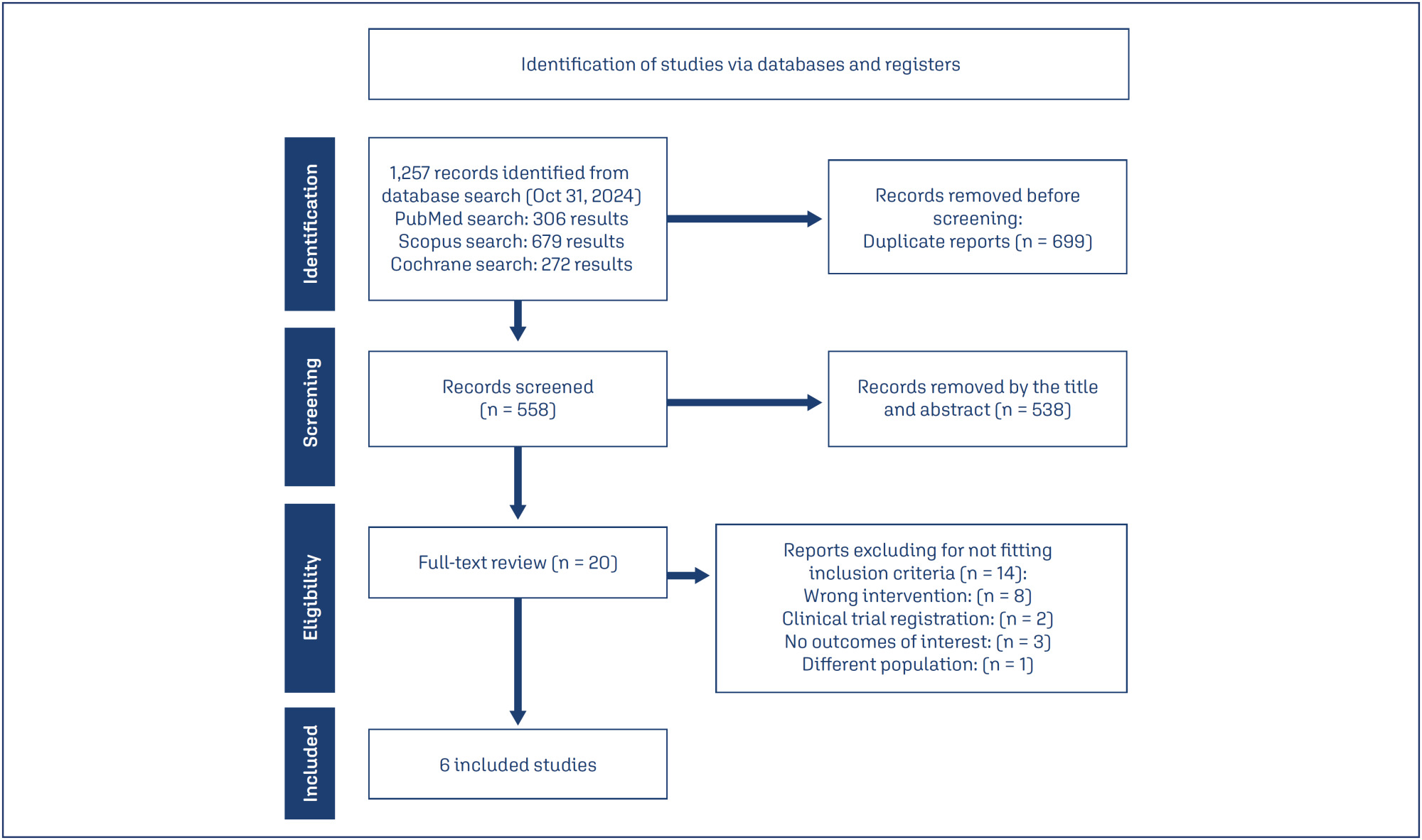
-
Artigo Original30/04/2025
Incidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
Resumo
Artigo OriginalIncidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
Visualizações189Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to assess the incidence of small for gestational age (SGA) newborns in pregnant women infected with COVID-19 and examine the associated neonatal outcomes.
Methods:
This study involved a secondary analysis of the REBRACO Network, a prospective cohort study conducted in 15 maternity hospitals in Brazil before the introduction of COVID-19 vaccination (February 2020 to February 2021). Demographic data of pregnant women tested for COVID-19 were analyzed, and fetal outcomes were compared between women with positive and negative COVID-19 results who had SGA fetuses.
Results:
A total of 729 symptomatic pregnant women with COVID-19 were included in the study. However, there were 248 participants with missing information regarding childbirth or loss of follow-up, and 107 participants without confirmatory tests for COVID-19. Among the remaining participants, 198 had confirmed COVID-19 and 176 tested negative. The incidence of SGA among women with COVID-19 was 22.4%, whereas the incidence among women who tested negative for COVID-19 was 14.8%. SGA newborns born to COVID-19 positive pregnant women were 1.6 times more likely to experience adverse outcomes (such as prematurity, stillbirth, neonatal death, and admission to a neonatal ICU) compared to non-SGA newborns [OR = 1.655 (1.145 – 2.394); P=0.017]. In SGA newborns of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection, mechanical ventilation use was found to be associated with the infection [OR = 0.692 (0.562 – 0.853); P=0.002].
Conclusion:
The higher incidence of SGA newborns and its stronger association with prematurity in pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection suggest that COVID-19 infection is a significant factor contributing to neonatal morbidity and mortality.
Palavras-chave: coronavirus infectionsCOVID-19Infant, newbornInfant, small for gestational agematernal healthPregnancy complicationsVer mais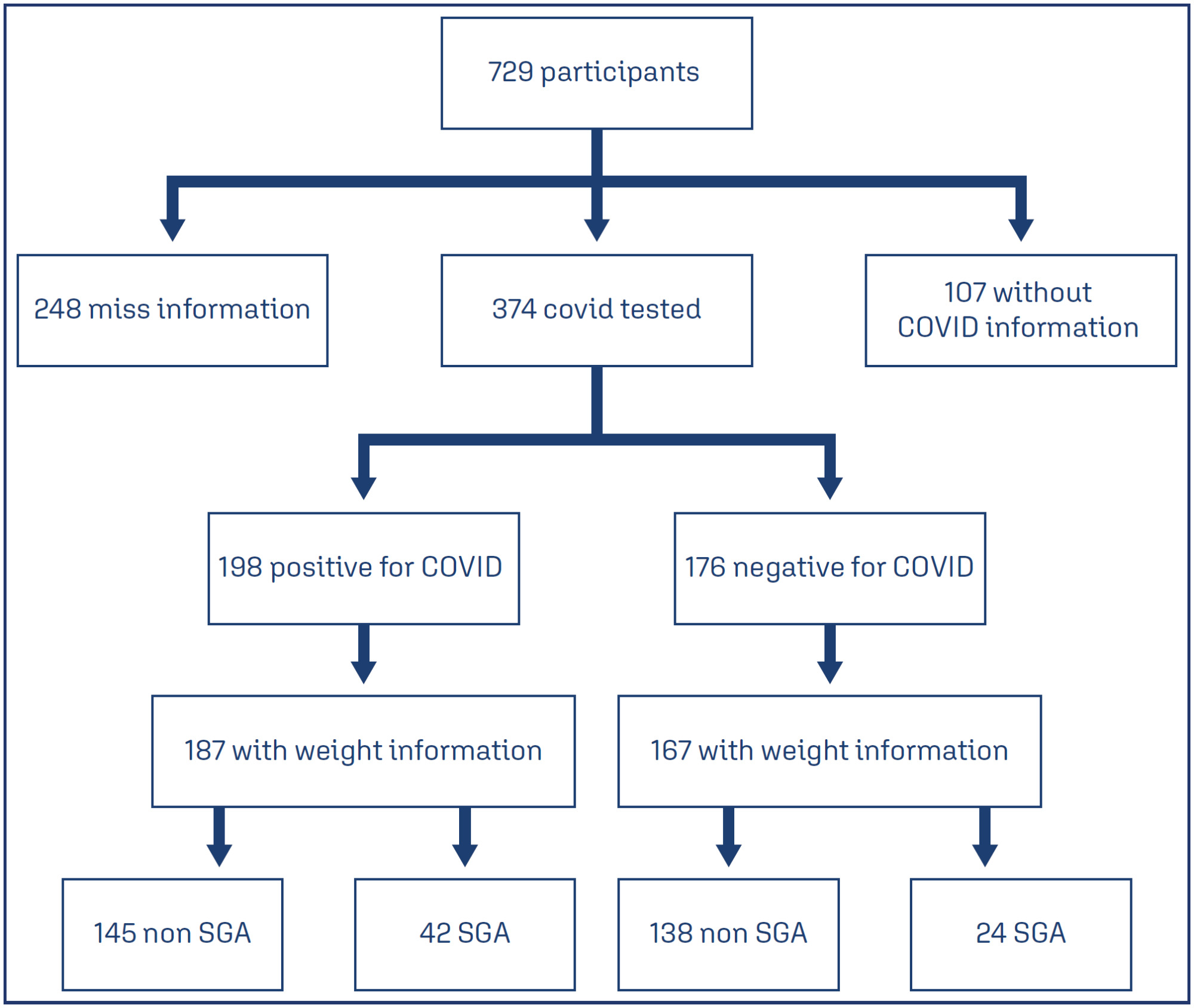
-
Artigo de Revisão30/04/2025
Efficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
Resumo
Artigo de RevisãoEfficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
Visualizações201Abstract
Objective:
This umbrella review aimed to synthesize evidence from systematic reviews of clinical trials on the efficacy of tranexamic acid in gynecology and obstetrics procedures.
Methods:
We searched Medline, Embase, SciELO and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews on March 11, 2024, using the term “tranexamic acid”. Four reviewers independently select studies and extract data. We assessed the quality of systematic review and the quality of evidence, using AMSTAR 2 and GRADE tools, respectively.
Results:
Of 651 systematic reviews identified, 16 reviews with 96663 patients were included. The surgical procedures were cesarean section, myomectomy, hysterectomy, and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia surgery. All reviews showed a statistically significant and clinically relevant reduction in intraoperative and post-procedure blood loss, associated with intravenous or topical use of tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid resulted in a significant reduction in the need for blood transfusions and a less pronounced drop in postoperative hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in cesarean section. Several reviews addressed the same question, but the number of included trials varied substantially, which might indicate flaws in search and selection of studies of these reviews. The quality of systematic reviews was low or critically low, and the quality of evidence was moderate.
Conclusions:
This umbrella review shows that tranexamic acid can reduce blood loss and hemorrhage in gynecology and obstetrics procedures. High quality systematic reviews are still needed.
Palavras-chave: Blood transfusionCesarean sectionEfficacyGynecologic surgical procedureshematocritHemorrhageHysterectomyObstetric surgical proceduresTranexamic acidUterine cervical dysplasiauterine myomectomyVer mais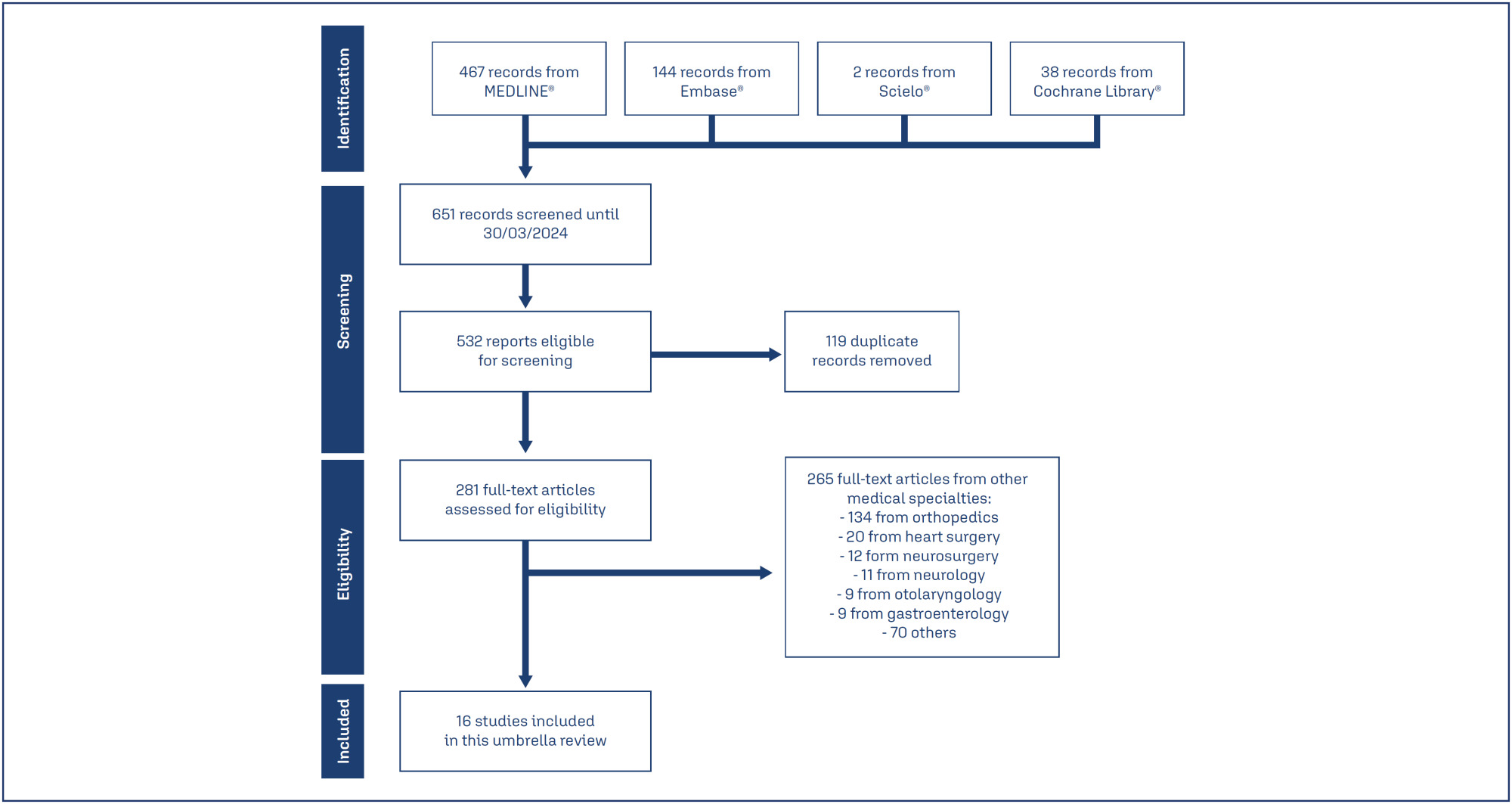
-
Artigo Original30/04/2025
Assessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
Resumo
Artigo OriginalAssessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
Visualizações187Abstract
Objective:
This retrospective study aimed to investigate blood-based immune-inflammatory biomarkers (IIBs) in predicting neonatal outcomes in pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus (PGDM).PIV[(neutrophil×platelet×monocyte)/lymphocyte)], SII (neutrophil×platelet/lymphocyte), and NLR neutrophil/lymphocyte) values were evaluated in all three trimesters, and their correlation with neonatal outcomes was examined.
Methods:
We included 82 cases of PGDM pregnancies delivered after 32 weeks. Maternal age, gravidity, parity, types of diabetes, and route of delivery were noted. For neonatal outcomes, we recorded gestational age at birth, birth weight percentile, existence of fetal growth restriction, LGA, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) requirement, Apgar Score <7 at 1, 5, or 10 minutes, need for positive pressure ventilation (PPV), need for mechanical ventilation, hypoglycaemia, hyperbilirubinemia and the need for phototherapy. PIV, SII and NLR values were calculated in each trimester and their association with adverse neonatal outcomes was analyzed.
Results:
We could not detect any consistent and significant correlation between SII and PIV values and adverse neonatal outcomes for each trimester. There was a correlation between 3rd trimester NLR and adverse neonatal outcomes, including APGAR <7, the requirement for PPV and mechanical ventilation (p=0.056, 0.013 and 0.060, respectively).
Conclusion:
While SII and PIV values did not consistently correlate with adverse neonatal outcomes throughout each trimester in PGDM pregnancies, 3rd-trimester NLR showed a notable association with the requirement for PPV with statistical significance and with Apgar Score <7 and the requirement for mechanical ventilation without statistical significance. NLR in the third trimester may hold potential as a predictive marker for specific adverse neonatal outcomes in PGDM pregnancies, warranting further investigation.
Palavras-chave: biomarkersDiabetes mellitusGestational ageHypoglycemiaInfant, newbornIntensive care units, neonatalLymphocytesMaternal ageMonocytesNeuthrophilsPregancyPregnancy in diabetesRespiration, artificialVer mais -
Artigo Original30/04/2025
Effects of domestic violence on menopausal symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo16
Resumo
Artigo OriginalEffects of domestic violence on menopausal symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo16
Visualizações180Abstract
Objective:
To investigate the association between lifetime experience of domestic violence and climacteric symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life in climacteric women in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 700 pre-, peri-, and postmenopausal women, recruited online via an anonymous questionnaire (REDCap platform). Women aged 40 to 65 years, residing in Rio Grande do Sul, and classified by the STRAW+10 criteria were included. Climacteric symptoms and sexual function were assessed using the 10-item Cervantes Scale (CS-10) and the 6-item Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-6). Data were analyzed using SPSS version 18.0; quantitative data as median [IQR], qualitative as frequencies. Group comparisons used Kruskal-Wallis, Chi-Square, and Spearman’s correlation between violence against women (VAW) and/or climacteric groups on CS-10 or FSFI-6. Significance was set at 5%.
Results:
The median [IQR] age of pre- (46 [43 – 50] years), peri- (50 [47 – 52] years), and postmenopausal (55 [51 – 58] years) were different among groups. Prevalence rates of psychological (38.8%), sexual (34.9%), and physical (21.3%) violence were observed. Postmenopausal women showed the poorest outcomes. Premenopausal women experiencing violence had severe anxiety, while postmenopausal women reported feeling worthless. Various sexual dysfunctions were associated with violence, including low desire, lubrication issues, and sexual pain.
Conclusions:
Domestic violence was linked to worse climacteric symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life, particularly in postmenopausal women. These findings underscore the need for improved care and public policies to enhance safety and well-being among women of all ages.
Palavras-chave: AnxietyClimactericDomestic violenceMenopausePostmenopauseQuality of lifeSexualitysurveys and questionnairesViolence against womenVer mais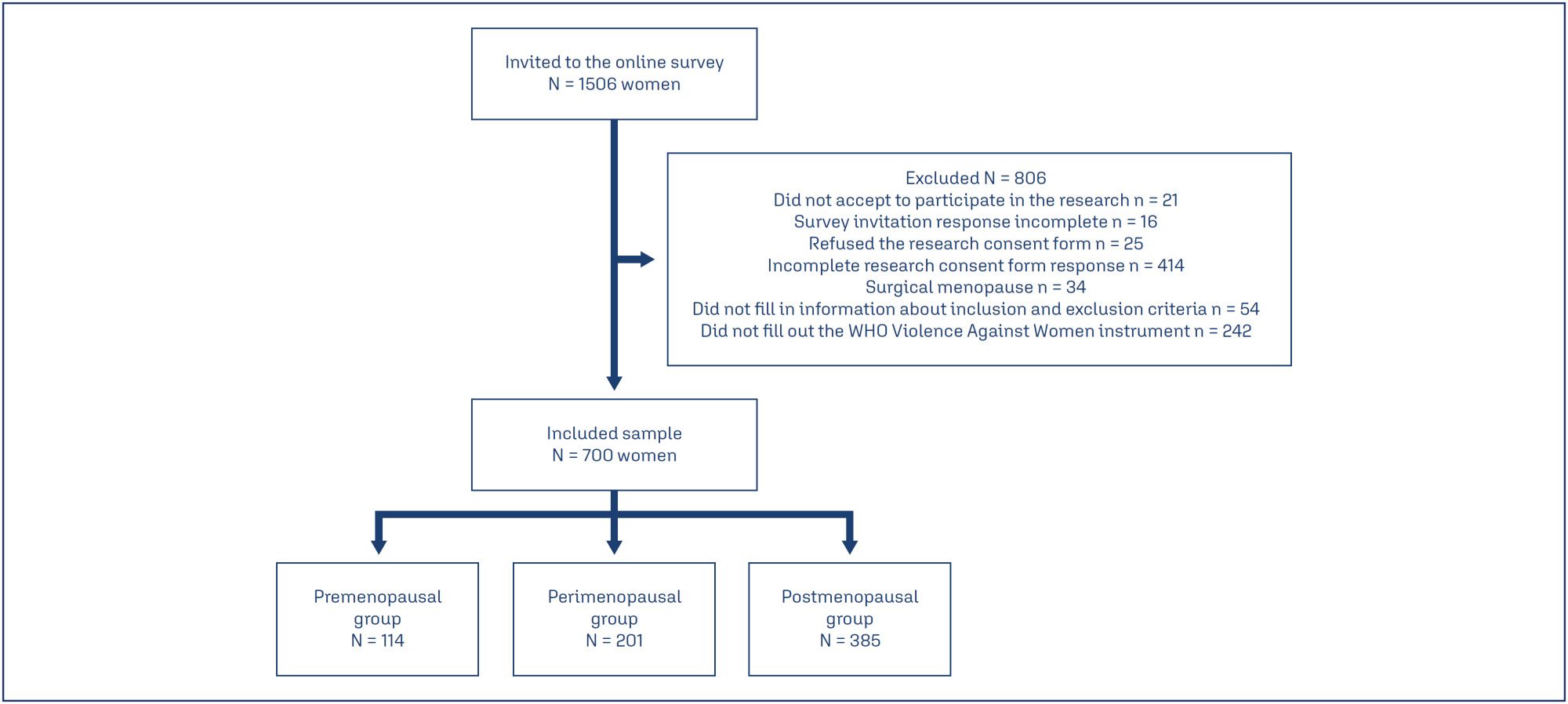
-
Artigo Original30/04/2025
The ımpact of demographic and obstetric factors on perception of traumatic birth and breastfeeding attitudes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo15
Resumo
Artigo OriginalThe ımpact of demographic and obstetric factors on perception of traumatic birth and breastfeeding attitudes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo15
Visualizações148Abstract
Objective:
This study aims to examine the effects of sociodemographic and obstetric factors on traumatic birth perception and breastfeeding attitudes in primiparous mothers who have had a vaginal birth in the early postpartum period.
Methods:
The sample of the research, developed with a cross-sectional and correlational design, consisted of 252 women residing in a province in the Western Black Sea region of Türkiye. The data were obtained by employing a Personal Information Form, Traumatic Childbirth Perception Scale, and Breastfeeding Attitudes of The Evaluation Scale. Data analysis was conducted using the statistical programming language R (R version 4.3.3).
Results:
Women who were not employed, had a planned pregnancy, and did not experience health problems during pregnancy had higher mean breastfeeding attitude scores, and this difference was statistically significant. It was determined that a one-unit increase in gestational week led to an average increase of 1.926 units in breastfeeding attitude score, and a one-unit increase in Traumatic Childbirth Perception Scale score led to an average decrease of 0.110 units in breastfeeding attitude score. The mean traumatic childbirth perception scores of women living in urban areas were found to be lower than those living in villages or towns, and the difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion:
The research findings indicate that gestational age, perception of traumatic childbirth, and certain sociodemographic factors significantly affect breastfeeding attitudes. Additionally, mothers living in urban areas have a lower perception of traumatic childbirth. Therefore, individualized approaches to childbirth and breastfeeding support are crucial.
Palavras-chave: Breast feedingDelivery, obstetricParturitionperceptionPostpartum periodSociodemographic factorsStress disorders, post-traumaticVer mais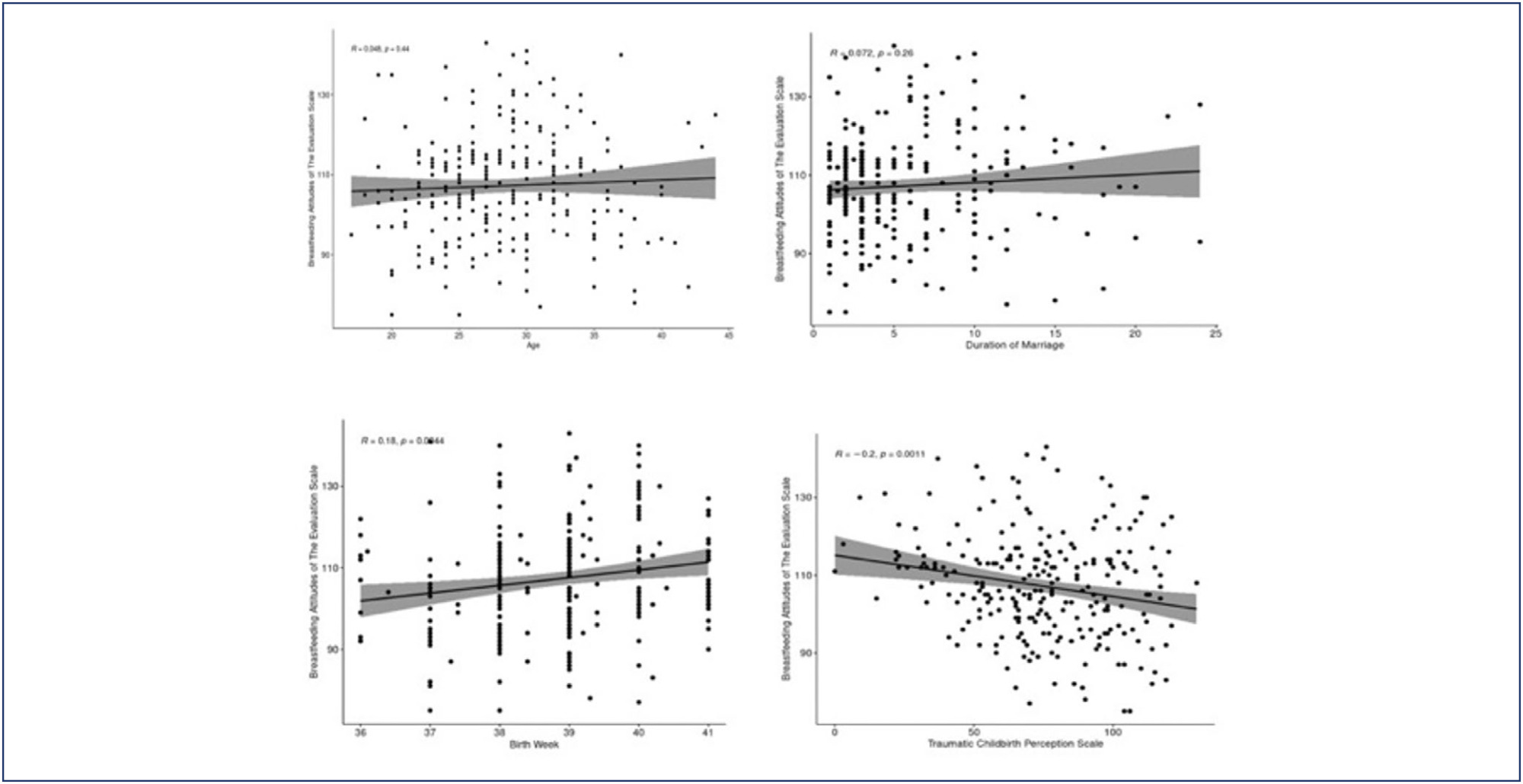
-
Artigo Original30/04/2025
Clinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant and postpartum women affected by COVID-19 who required respiratory support
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo14
Resumo
Artigo OriginalClinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant and postpartum women affected by COVID-19 who required respiratory support
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo14
Visualizações156Abstract
Objective:
This study described the clinical and epidemiological profile and the management provided to pregnant and postpartum women with COVID-19 who required respiratory support.
Methods:
A descriptive study was conducted with pregnant and postpartum women with confirmed COVID-19 who received care between April 2020 and December 2021 in eight referral centers in northeastern Brazil. Statistical analysis was conducted using Epi-Info 7.2.5 and Medcalc, version 20.112.
Results:
Of the 720 patients admitted, 208 (32.7%) required respiratory support. Mean age of the participants was 28.9±7.1 years. Most (52.8%) were brown-skinned; 31.3% had little formal schooling; 41.1% had a personal income and 23.1% were married. Around half were referred from another hospital. Overall, 36.8% were obese and 36.9% were hypertensive. Criteria for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) were present in 80.7% of cases. Overall, 151 patients (74.7%) required corticoids, and 150 (76.1%) were admitted to an intensive care unit. Non-invasive ventilation was needed in 89.4% of cases, with nasal catheters being the most common type (55.3% of cases). Invasive mechanical ventilation was necessary in 35.5% of cases and 91.6% had a cesarean section. Maternal near miss and death occurred in 24% and 12.9% of cases, respectively.
Conclusion:
Pregnant and postpartum women with COVID-19 who required respiratory support were predominantly brown-skinned, in the third trimester of pregnancy and had been referred from another hospital. The cesarean section rate was high; the presence of criteria for SARS was common and the rates of COVID-19-related maternal near miss and death were high.
Clinical Trials registry:
NCT04462367
Palavras-chave: Cesarian sectionCOVID-19Intensive care unitsNear miss, healthcareNoninvasive ventilationObesityPostpartum periodPregnancyPregnancy trimester, thirdRespiration, artificialSARS-CoV-2severe acute respiratory syndromeVer mais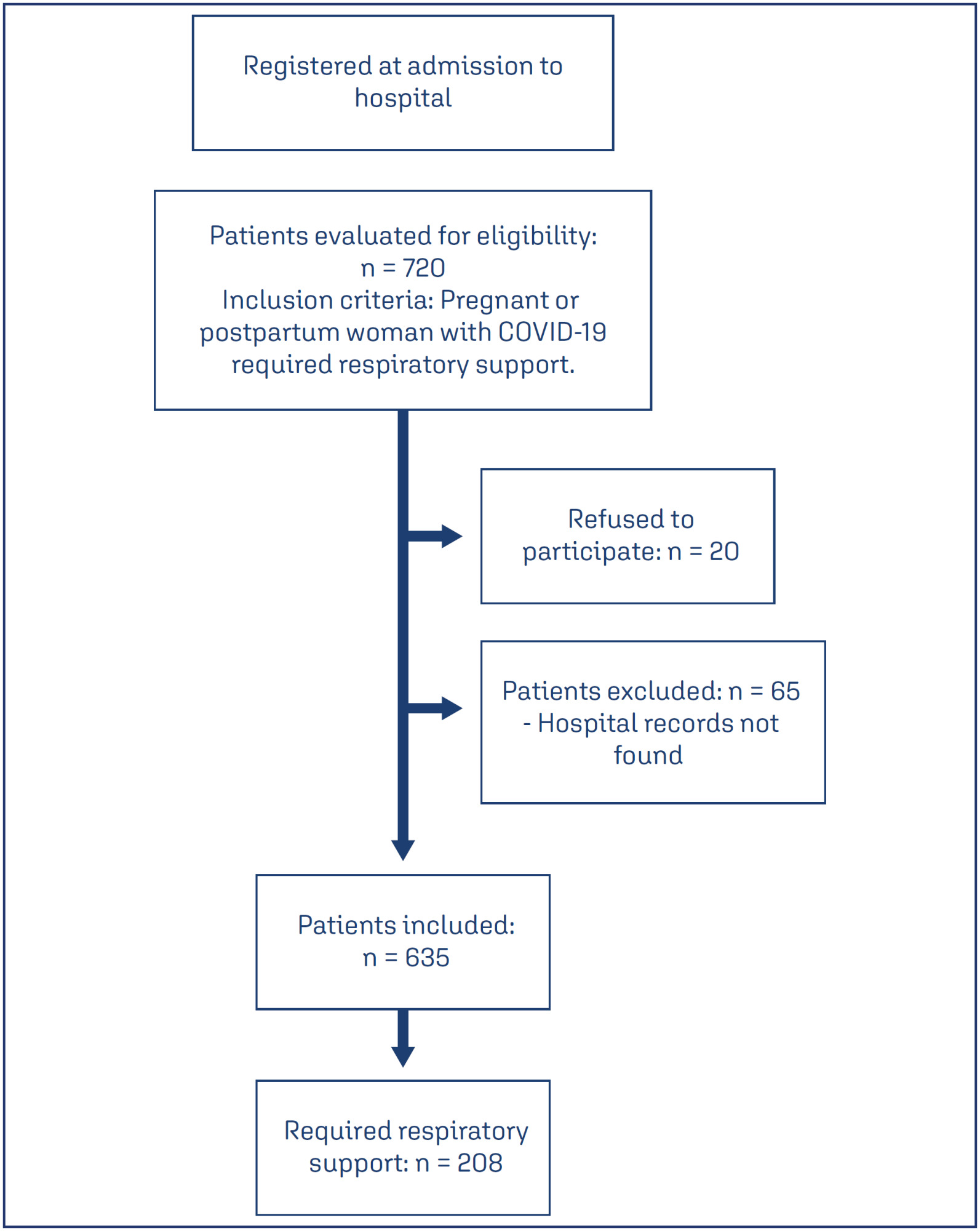
-
Artigo Original20/07/2004
Pesquisa da prevalência do papilomavírus humano em amostras de tecido endometrial normal e com carcinoma pela técnica de PCR
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):277-287
Resumo
Artigo OriginalPesquisa da prevalência do papilomavírus humano em amostras de tecido endometrial normal e com carcinoma pela técnica de PCR
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):277-287
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400003
Visualizações12869Ver maisOBJETIVO: comparar a prevalência da presença do DNA do papilomavírus humano (HPV) pela técnica de PCR em amostras de tecido endometrial normal e com carcinoma endometrial de mulheres submetidas a tratamento cirúrgico (histerectomia) ou carcinoma endometrial e doença benigna. MÉTODOS: trata-se de um estudo observacional do tipo caso-controle onde foram avaliadas 100 mulheres (50 com endométrio normal e 50 com carcinoma endometrial) quanto a presença do DNA do HPV em amostra tecidual conservada em blocos de parafina, pelo método de PCR. Foram excluídos os casos de carcinoma endometrial cujo sítio primário da lesão era duvidoso ou com história prévia ou atual de lesões pré-neoplásicas ou carcinoma do trato genital inferior. Variáveis como idade, tabagismo, trofismo endometrial, diferenciação escamosa e grau de diferenciação tumoral foram também avaliadas. RESULTADOS: o risco relativo estimado da presença do HPV foi o mesmo nas mulheres com e sem carcinoma endometrial. O HPV foi detectado em 8% dos casos de carcinoma e 10% no endométrio normal. Apesar de o HPV ter sido detectado 3,5 vezes mais em mulheres fumantes no grupo sem carcinoma, não houve diferença estatística. A presença do HPV também não esteve correlacionada com a idade das mulheres, trofismo endometrial, diferenciação escamosa e grau de diferenciação tumoral. Os HPV 16 e 18 (5 dos casos com o tipo 16 e 4 com o tipo 18) foram os vírus mais freqüentemente encontrados, tanto no tecido endometrial normal, quanto no carcinomatoso. Nenhum vírus de baixo risco oncogênico foi detectado nas amostras. CONCLUSÃO: o HPV está presente no tecido endometrial de mulheres com carcinoma endometrial na mesma proporção que nas com tecido endometrial normal, não se demonstrando a possível associação deste vírus no desenvolvimento do carcinoma endometrial.
-
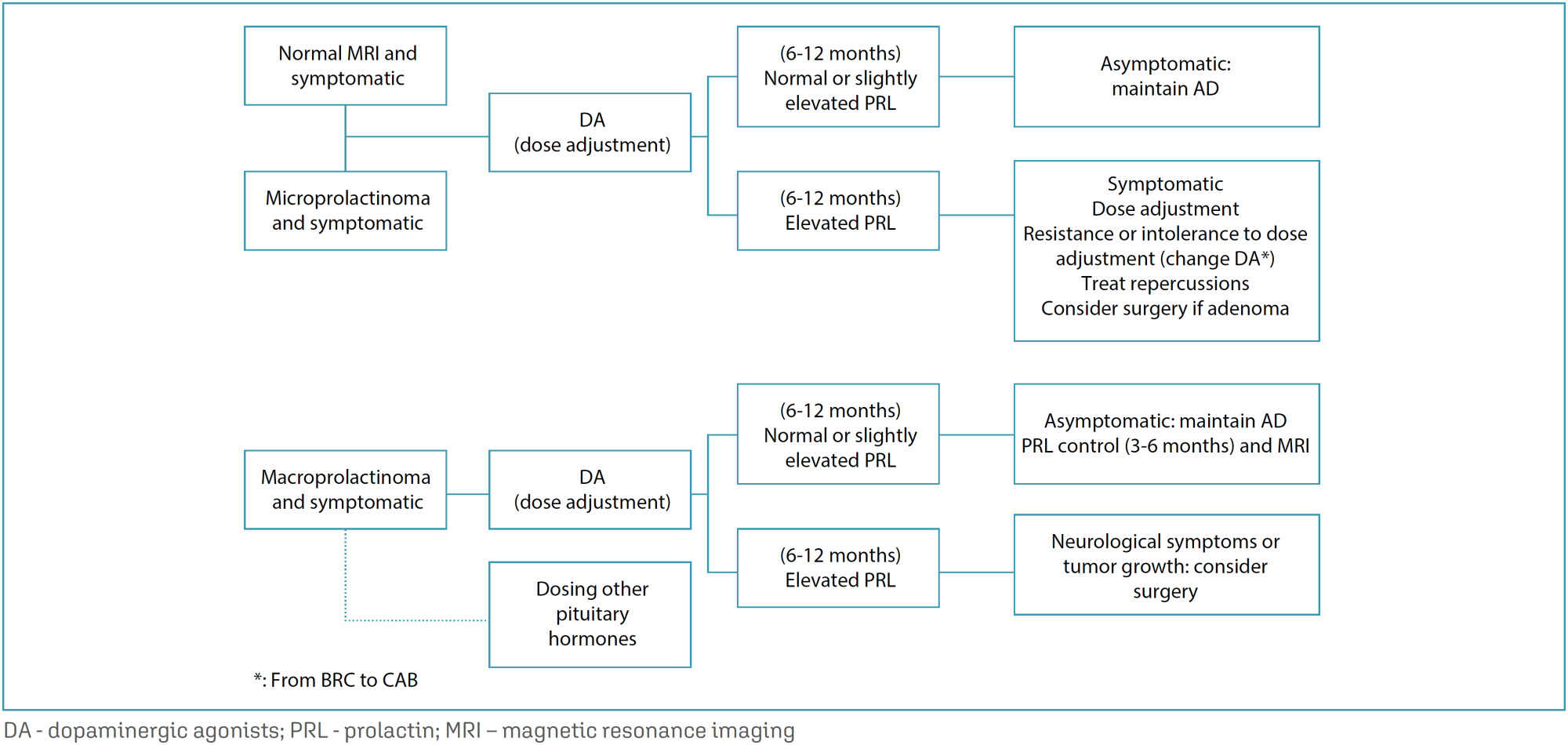
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT25/04/2024
Hyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS05
Resumo
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTHyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS05
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT25/04/2024
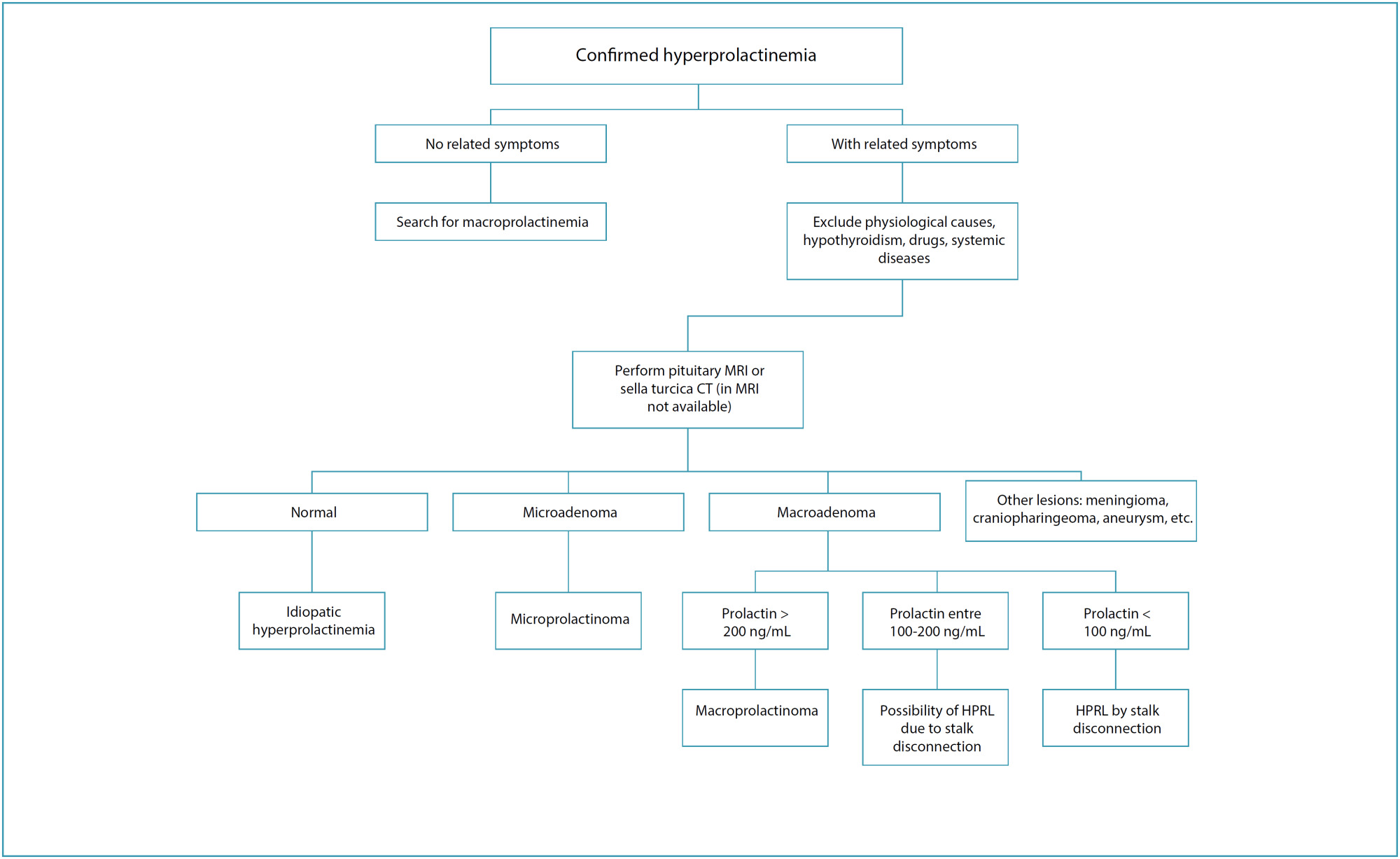
Hyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS04
Resumo
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTHyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS04
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT00/00/2024
Breech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgofps1
Resumo
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTBreech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgofps1
-
Carta ao Editor09/04/2024
Letter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo24
Resumo
Carta ao EditorLetter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo24
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT02/04/2024
Use of hormones and risk of venous thromboembolism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS02
Resumo
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTUse of hormones and risk of venous thromboembolism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS02
Visualizações912Ver maisKey points
•The risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is not increased in women using long-acting reversible contraceptive methods (LARCs) with progestogens.
•Oral contraceptives with levonorgestrel or norgestimate confer half the risk of VTE compared to oral contraceptives containing desogestrel, gestodene or drospirenone.
•Progestogen-only pills do not confer an increased risk of VTE.
•Women using transdermal contraceptive patches and combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are at an approximately eight times greater risk of VTE than non-users of hormonal contraceptives (HCs), corresponding to 9.7 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Vaginal rings increase the risk of VTE by 6.5 times compared to not using HC, corresponding to 7.8 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Several studies have demonstrated an increased risk of VTE in transgender individuals receiving hormone therapy (HT).
•Hormone therapy during menopause increases the risk of VTE by approximately two times, and this risk is increased by obesity, thrombophilia, age over 60 years, surgery and immobilization.
•The route of estrogen administration, the dosage and type of progestogen associated with estrogen may affect the risk of VTE in the climacteric.
•Combined estrogen-progesterone therapy increases the risk of VTE compared to estrogen monotherapy.
•Postmenopausal HT increases the risk of thrombosis at atypical sites.
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT02/04/2024
Vulvovaginitis in pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS03
Resumo
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTVulvovaginitis in pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS03
Visualizações877Ver maisKey points
• The balanced vaginal microbiome is the main factor defending the vaginal environment against infections. Lactobacilli play a key role in this regard, maintaining the vaginal pH within the normal range (3.8 to 4.5).
•Hormonal and immune adaptations resulting from pregnancy influence changes in the vaginal microbiome during pregnancy.
•An altered vaginal microbiome predisposes to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
•Bacterial vaginosis is the main clinical expression of an imbalanced vaginal microbiome.
•Vulvovaginal candidiasis depends more on the host’s conditions than on the etiological agent.
•Trichomonas vaginalis is a protozoan transmitted during sexual intercourse.
•The use of probiotics is not approved for use in pregnant women.
-
Artigo de Revisão01/09/2017
Pré-eclâmpsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Resumo
Artigo de RevisãoPré-eclâmpsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Visualizações216Resumo
Os autores revisam a doença hipertensiva na gestação com uma visão acadêmica e prática, utilizando as melhores evidências disponíveis. A doença clínica mais importante na gestante brasileira pode ter sua incidência diminuída com a prevenção por meio do uso de cálcio e aspirina em gestantes de risco. Antes uma doença que apresentava hipertensão arterial com proteinúria, agora vem sendo classificada com novos parâmetros clínicos além da proteinúria. A morbidade e mortalidade devem ser diminuídas, em um país continental como o Brasil, utilizando-se protocolos para o tratamento precoce de suas complicações mediante o cálculo de desfechos graves em pré-eclâmpsia. O tratamento precoce da hipertensão arterial, o uso do sulfato de magnésio e a internação precoce em casos de pré-eclâmpsia são conceitos para perseguirmos a diminuição da mortalidade de nossas gestantes.
Palavras-chave: Complicações na gravidezGestação de alto riscohipertensão arterial na gestaçãoPré-eclâmpsiaSíndrome HELLPVer mais
-
Artigo Original17/12/2021
A avaliação dos níveis de vitamina D em gestantes não está associada à restrição do crescimento fetal: um estudo transversal
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):743-748
Resumo
Artigo OriginalA avaliação dos níveis de vitamina D em gestantes não está associada à restrição do crescimento fetal: um estudo transversal
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):743-748
Visualizações129Resumo
Objetivo
Avaliar o nível sérico materno de vitamina D em fetos adequados para idade gestacional (AIG), pequenos para idade gestacional (PIG) e com restrição de crescimento (RCF) de acordo com a estimativa de peso fetal (EPF).
Métodos
Realizou-se um estudo transversal envolvendo 87 gestantes entre 26 e 36 semanas, sendo: 38 do grupo AIG, 24 do grupo PIG e 25 do grupo RCF. A dosagem sérica materna de vitamina D foi realizada pelo método de quimiluminescência. Para as comparações entre os grupos, utilizou-se o teste exato de Fisher.
Resultados
A média ± desvio-padrão (DP) da idade materna (anos) e do índice de massa corporal (kg/m2) nos grupos AIG, PIG e RCF foram 25,26 ± 8,40 / 26,57 ± 4,37; 25,04 ± 8,44 / 26,09 ± 3,94; e 25,48 ± 7,52 / 26,24 ± 4,66, respectivamente (p>0,05). A concentração sérica materna de vitamina D (médias ± desvios-padrão) dos grupos AIG, PG e RCF foram 22,47±8,35 ng/ml; 24,80_10,76 ng/ml; e 23,61 ± 9,98 ng/ml, respectivamente, contudo, sem diferenças significativas entre os grupos (p=0,672).
Conclusão
A concentração sérica materna de vitamina D não apresentou diferenças significantes entre gestantes com fetos AIG, PIG ou RCF entre 26 e 36 semanas de acordo com a EPF.
Palavras-chave: concentração sérica maternaGestaçãopequeno para idade gestacionalRestrição de crescimento fetalvitamina DVer mais -
Artigo Original17/12/2021
Melhorando a taxa de implantação no 2° ciclo de ICSI através do estímulo ovariano com FSH e LH no regime com antagonista do GnRH
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):749-758
Resumo
Artigo OriginalMelhorando a taxa de implantação no 2° ciclo de ICSI através do estímulo ovariano com FSH e LH no regime com antagonista do GnRH
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):749-758
Visualizações89Resumo
Objetivo:
Investigar se há algum efeito da suplementação com hormônio luteinizante (LH, na sigla em inglês) no regime com antagonista do hormônio liberador de gonadotropina (GnRH, na sigla em inglês) sobre os resultados dos ciclos consecutivos de injeção intracitoplasmática de espermatozoides (ICSI, na sigla em inglês).
Métodos
Para o presente estudo retrospectivo de caso-controle, foram avaliados 228 ciclos de microinjeção intracitoplasmática de espermatozoides (ICSI, na sigla em inglês) realizados em 114 pacientes entre 2015 e 2018 em um centro privado de fertilização in vitro (FIV) afiliado a uma universidade. O estímulo ovariano controlado (EOC) foi feito com hormônio folículo- estimulante recombinante (rFSH, na sigla em inglês) (Gonal-f, Serono, Genebra, Suíça) no primeiro ciclo de ICSI (grupo rFSH), e com rFSH e rLH (Pergoveris, Merck Serono S.p.A, Bari, Itália) no segundo ciclo (grupo rFSH + rLH). Os desfechos dos ciclos de ICSI foram comparados entre os grupos.
Resultados
Níveis mais elevados de estradiol, de recuperação oocitária, taxa de embriões de alta qualidade no 3° dia e taxa de implantação, e menor taxa de aborto foram observados no grupo rFSH + rLH. Em pacientes < 35 anos, a taxa de implantação foi maior no grupo rFSH + rLH em comparação com o grupo rFSH. Em pacientes com ≥ 35 anos, maiores níveis de estradiol, recuperação oocitária, a taxa de embriões de alta qualidade no 3° dia e a taxa de implantação foram observados no grupo rFSH + rLH. Em pacientes com baixa resposta ao EOC (≤ 4 oócitos recuperados), a recuperação oocitária, a taxa de oócitos maduros, a taxa de velocidade normal de clivagem, a taxa de implantação e a taxa de aborto foram melhoradas no grupo rFSH + rLH. Em pacientes com resposta normal ao EOC (≥ 5 oócitos recuperados), níveis mais elevados de estradiol, recuperação oocitária e taxa de implantação foram observados no grupo rFSH + rLH.
Conclusão
A estimulação ovariana com suplementação de LH resultou em taxas de implantação mais altas, independentemente da idade materna e da resposta ao EOC, em comparação com os ciclos anteriores estimulados apenas com rFSH. Melhorias também foram observadas nos resultados da ICSI e na taxa de aborto quando as pacientes foram estratificadas por idade e número de oócitos recuperados.
Palavras-chave: estímulo ovariano IntroductionHormônio folículo estimulanteHormônio luteinizantemicroinjeção intracitoplasmática de espermatozoidesVer mais -
Artigo de Revisão24/01/2021
Análise do papel dos hormônios femininos durante a infecção por COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):940-948
Resumo
Artigo de RevisãoAnálise do papel dos hormônios femininos durante a infecção por COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):940-948
Visualizações91Ver maisResumo
As mulheres possuem variáveis metabólicas, imunológicas e genéticas que conferem maior proteção à infecção pelo coronavírus. Todavia, a indicação de tratamento para certas patologias e para a contracepção é determinada por hormônios que possuem efeitos adversos e levantam dúvidas quanto ao seu uso durante a pandemia da COVID-19. Desta forma, o presente estudo busca investigar as especificidades da mulher e a relação dos hormônios sexuais femininos com a COVID-19, assim como relatar as principais recomendações neste contexto. Para isso, realizou-se uma revisão da literatura nas principais bases de dados, fontes auxiliares de dados e sites oficiais. Portanto, considerando o estado hipercoagulável da COVID-19, surge o debate quanto à utilização de contraceptivos pelo seu risco relativo de efeitos tromboembólicos. No entanto, as atuais evidências disponíveis, assim como as recomendações dos principais órgãos de saúde do mundo, demonstraram que o uso de contraceptivos hormonais deve ser mantido durante a pandemia.
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT08/04/2022
Perioperative management in gynecological surgery based on the ERAS program
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):202-209
Resumo
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTPerioperative management in gynecological surgery based on the ERAS program
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):202-209
-
Artigo Original28/02/2022
Resultados a curto e médio prazo do onfalocelo e gastrosquisis: uma investigação de um centro terciário
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):10-18
Resumo
Artigo OriginalResultados a curto e médio prazo do onfalocelo e gastrosquisis: uma investigação de um centro terciário
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):10-18
Visualizações112Ver maisResumo
Objetivo
Caracterizar e comparar os desfechos do onfalocelo e gastrosquisis desde o nascimento até aos 2 anos de seguimento numa coorte recente de um centro terciário.
Métodos
Este é um estudo retrospectivo em que foi feita uma revisão dos registos clínicos de todos os pacientes com gastrosquisis e onfalocelo que foram internados na unidade de cuidados intensivos neonatais, entre janeiro de 2009 e dezembro de 2019.
Resultados
Identificamos 38 pacientes, 13 dos quais tinham onfalocelo e 25 dos quais tinham gastrosquisis. Anomalias associadas estavam presentes em 6 pacientes (46.2%) com onfalocelo e 10 (41.7%) com gastrosquisis. Comparativamente com os pacientes com onfalocelo, os pacientes com gastrosquisis tinham mães mais jovens (24.7 versus 29.6 anos; p=0.033), nasceram mais precocemente (36 versus 37 semanas, p=0.006), com menor peso ao nascimento (2,365±430.4 versus 2,944.2±571.9 g; p=0.001), e o internamento teve uma duração mais longa (24 versus 9 dias, p=0.001). A taxa de sobrevivência neonatal foi de 92.3% para o onfalocelo e 91.7% para a gastrosquisis. Trinta e quatro pacientes foram seguidos durante umtempo mediano de seguimento de 24meses: 13 com gastrosquisis (59.1%) e 8 com onfalocelo (66.7%) apresentaram pelo menos um evento adverso, sobretudo hérnia umbilical (27.3% vs 41.7%), obstrução intestinal (31.8% vs 8.3%) ou intervenções cirúrgicas adicionais (27.3% vs 33.3%).
Conclusão
Apesar da alta proporção de prematuridade, de baixo peso e de recuperação lenta, os gastrosquisis, assim como os onfalocelos (sem anomalias cromossómicas), podem ter uma taxa de sobrevivência muito alta; por outro lado, nos primeiros anos de vida, podem surgir complicações não desprezíveis. Assim, aos futuros pais pode ser transmitida uma perspectiva muito positiva em termos de sobrevivência, embora eles também devam ser informados de que pode ocorrermorbidade substancial no médio prazo.
-
Artigo Original08/04/2022
Efeitos protetores do plasma rico em plaquetas para fertilização in vitro de ratos com falência ovariana induzida por ciclofosfamida
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):161-168
Resumo
Artigo OriginalEfeitos protetores do plasma rico em plaquetas para fertilização in vitro de ratos com falência ovariana induzida por ciclofosfamida
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):161-168
Visualizações106Resumo
Objetivo
A insuficiência ovariana prematura (POI) contribui significativamente para a infertilidade feminina. A ciclofosfamida (CYC) tem efeitos adversos na foliculogênese. O plasma rico em plaquetas (PRP) é um produto autólogo rico em muitos fatores de crescimento. Avaliamos o efeito protetor do PRP na fertilização in vitro em ratas com lesão ovariana induzida por CYC.
Métodos
Vinte e oito ratas Sprague-Dawley adultas foram divididas aleatoriamente em quatro grupos. Grupo 1 (controle – cloreto de sódio 0,9%; 1mL/kg, injeção intraperitoneal [IP] em dose única); grupo 2 (CYC), 75mg/kg, injeção IP de dose única e cloreto de sódio 0,9% (1mL/kg, injeção ip de dose única); grupo 3 CYC+PRP, CYC (75mg/kg, dose única e PRP (200 μl, dose única) injeção IP); e grupo 4 (PRP, 200 μl, injeção IP de dose única).
Resultados
Nas comparações em termos de ovócitos M1 e M2, observou-se que o grupo CYC apresentou uma quantidade significativamente menor que os grupos controle, CYC/PRP, e PRP. (Para M1, p=0,000, p=0,029, p=0,025; para M2, p=0,009, p=0,004, p=0,000, respectivamente). O número de oócitos fertilizados e embriões bicelulares de boa qualidade foi considerado estatisticamente significativo entre os grupos CYC e controle, CYC+PRP e grupos PRP (p=0,009, p=0,001, p=0,000 para oócitos, respectivamente. Para embriões, p=0,016, p=0,002, p=0,000).
Conclusão
O PRP pode proteger a função ovariana contra os danos causados pelo CYC e, além disso, proporciona melhora na contagem de oócitos e no desenvolvimento de embriões como resultado da estimulação ovariana durante o procedimento de fertilização in vitro.
Palavras-chave: CiclofosfamidaFertilização in vitroinsuficiência ovariana prematuraOvárioplasma rico em plaquetasVer mais -
Artigo Original28/02/2022
Desempenho da ferramenta de avaliação de risco de fraturas associada à medida de massa muscular e à preensão manual no rastreio de risco de osteoporose em mulheres jovens pós-menopáusicas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):32-39
Resumo
Artigo OriginalDesempenho da ferramenta de avaliação de risco de fraturas associada à medida de massa muscular e à preensão manual no rastreio de risco de osteoporose em mulheres jovens pós-menopáusicas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):32-39
Visualizações109Ver maisResumo
Objetivo
Avaliar a melhora da precisão da Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (Ferramenta de Avaliação do Risco de Fraturas, FRAX, em inglês) no rastreio do risco de desenvolver osteoporose em mulheres jovens pós-menopáusicas com a associação de medidas clínicas de massa muscular e preensão manual.
Métodos
Uma amostra de mulheres pós-menopáusicas foi submetida a ultrassom quantitativo (USQ) de calcâneo, à aplicação do questionário FRAX, e rastreadas quanto ao risco de desenvolver sarcopenia em uma feira de saúde realizada em 2019 em São Bernardo do Campo. Alémdisso, a amostra tambémfoi submetida a antropometria, e a testes de massa muscular, velocidade de marcha, e preensão manual. Um risco de grandes fraturas osteoporóticas (GFOs) ≥ 8,5% no FRAX, classificação de médio risco nas diretrizes clínicas do National Osteoporosis Guideline Group (NOGG), e T-score no USQ ≤ -1,8 dp foram considerados riscos de ter baixa massa óssea, e T-score no QUS ≤ -2,5 sd, risco de ter fraturas.
Resultados
Ao todo, 198 mulheres foram avaliadas, com idade média de 64±7,7 anos, índice de massa corporal (IMC) médio de 27,3±5,3 kg/m2, e T-score médio no USQ de -1,3±1,3 sd. A precisão do FRAX comumrisco de GFO≥ 8,5% para identificar mulheres com T-score ≤ -1,8 dp foi precária, com uma área sob a curva (ASC) de 0,604 (intervalo de confiança de 95% [IC95%]: 0,509-0,694), para mulheres menores de 65 anos de idade, e de 0,642 (IC95%: 0,571-0,709) quando a idade não foi considerada. A inclusão de dados da massa muscular na análise estatística levou a uma melhora significativa no grupo menor de 65 anos de idade, com uma ASC de 0,705 (IC95%: 0,612-0,786). A habilidade da ferramenta NOGG de alto risco para identificar T-scores ≤ -1,8 dp foi limitada.
Conclusão
As medidas clínicas da massa muscular aumentaram a precisão do FRAX no rastreio de osteoporose em mulheres menores de 65 anos de idade.
Busca
Pesquisar em:
Nuvem de Tags
Gravidez (167)Fatores de risco (89)Menopausa (79)Pré-eclâmpsia (66)Endometriose (65)Mama (59)Infertilidade (58)Obesidade (57)Complicações na gravidez (56)Diagnóstico pré-natal (54)Gestação (54)Qualidade de vida (53)Saúde da mulher (51)Cesárea (50)Complicações da gravidez (50)Neoplasias da mama (49)Fertilização in vitro (48)Cuidado pré-natal (47)Mortalidade materna (43)Ultra-sonografia (43)



