Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 09-01-2017;39(9):480-487
To evaluate the coverage of the Papanicolaou test in Brazil and the associated factors.
Cross-sectional study based on data from the Brazilian Health Survey 2013 comprising the proportion of 25- to 64-year-old women who had undergone a Papanicolaou test within the previous 3 years, categorized by sociodemographic variables and access to healthcare services.
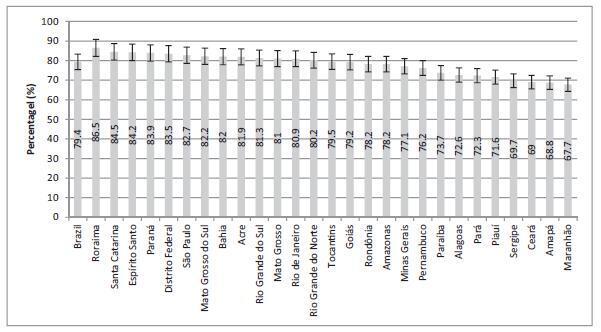
The screening coverage in Brazil was of 79.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 78.4-80.3), showing significant differences between the different states of the country, with the highest rate in the state of Roraima (86.5; 95%CI: 83.5-89.4), and the lowestone in the state ofMaranhão (67.7; 95%CI: 61.3-74.0).Undergoing the test was significantlymore frequent amongmarriedwomen (83.6%; 95%CI: 82.4-84.8), those with higher educational levels (88.7%; 95%CI: 87.0-90.5), of white ethnicity (82.6%; 95%CI: 81.3-83.9) and who reside in urban areas (80.1%; 95%CI: 79.1-81.2). Those who had undergone the test more than three years prior to the survey and the ones who had never undergone it were associated with a lower level of education, being of black or brown ethnicity, single or divorced, and rural dwellers.
The coverage of cervical cancer screening in Brazil is below the recommended rate and presents regional and sociodemographic disparities.
Search
Search in:


Comments