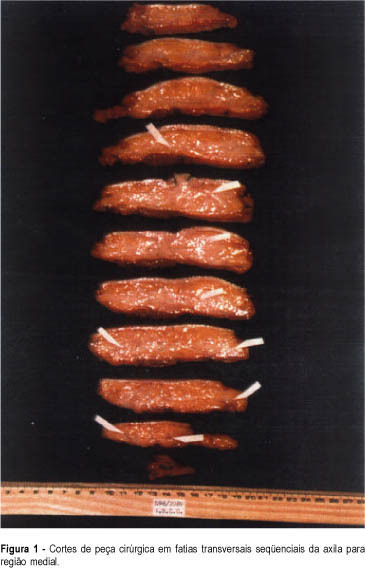
Purpose: analysis of histopathologic alterations caused by neoadjuvant chemotherapy (fluorouracil, epirubicine, cyclophosphamide; FEC – 4 cycles) at the tumor site, adjacent mammary tissue and homolateral lymph nodes, as observed in sections of patients with primary breast carcinomas. Method: histological studies performed on 30 surgical sections obtained from radical mastectomy (Patey) of patients with primary breast carcinomas, who underwent prior neoadjuvant systemic therapy. Results: all sections showed tumor regression with variable intensity. This regression occurred irregularly, several refractory tumor cells remaining at the primary tumor site. Resistant tumor cells, independent of the primary tumor, were found in mammary tissue. Other histopathological findings, resulting from chemotherapy in tumoral and mammary tissues, such as calcifications and fibrosis, and in axillary homolateral lymph nodes were obtained. Conclusion: the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy is not uniform, refratory tumor cells remaining not only at primary tumor site, but also in distant regions. Furthermore, we found no correlation between the regression of the tumor and the axillary metastatic lymph nodes. Thus, a conservative surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (FEC) should be avoided.
Search
Search in:


Comments