Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(9):573-577
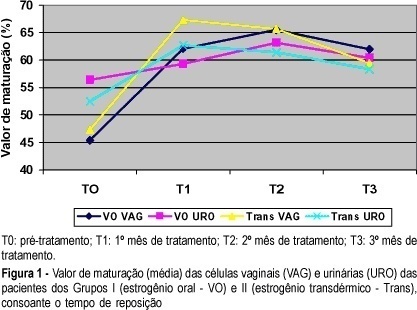
Objective: to study the effects of oral or transdermal estrogen replacement on the lower urinary tract and vagina in postmenopausal women. Methods: we studied 25 postmenopausal women evaluating the oral or transdermic estrogen replacement effects on the vaginal cells and urinary sediment during 3 months. The patients were randomly distributed into 2 groups: Group I, n = 14, treated orally with 0.625 mg equine conjugated estrogen plus 5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate, daily for 3 months; Group II, n = 11, treated transdermally with 50 mug 17-ß-estradiol, once a week, plus 5 mg medroxyprogesterone. Daily, for 3 months, urinary samples were collected from the first miction in the morning after urogenital antisepsis into sterile tubes. The sample was centrifuged and the sediment was smeared. Vaginal and urinary smears were then fixed in absoluted alcohol and stained by the method of Shorr. Results: the patients who used the oral route presented maturation of the vaginal cells (from 45.4 to 65.5% after 2 months of treatment, maintaing 62% afterwards) but this did not occur with urinary cells (56.4 before treatment versus 60.4% at the end of the period). The transdermal route promoted maturation of vaginal and urinary cells. Conclusion: we have concluded that transdermal estrogens have satisfactory effects both on vaginal and urethral sites. However, with the oral route we did not find the expected results in the urinary tract in all cases.
Search
Search in:


Comments