Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(11):489-496
To evaluate the predictive clinical factors for the development of endometrial polyps in postmenopausal women.
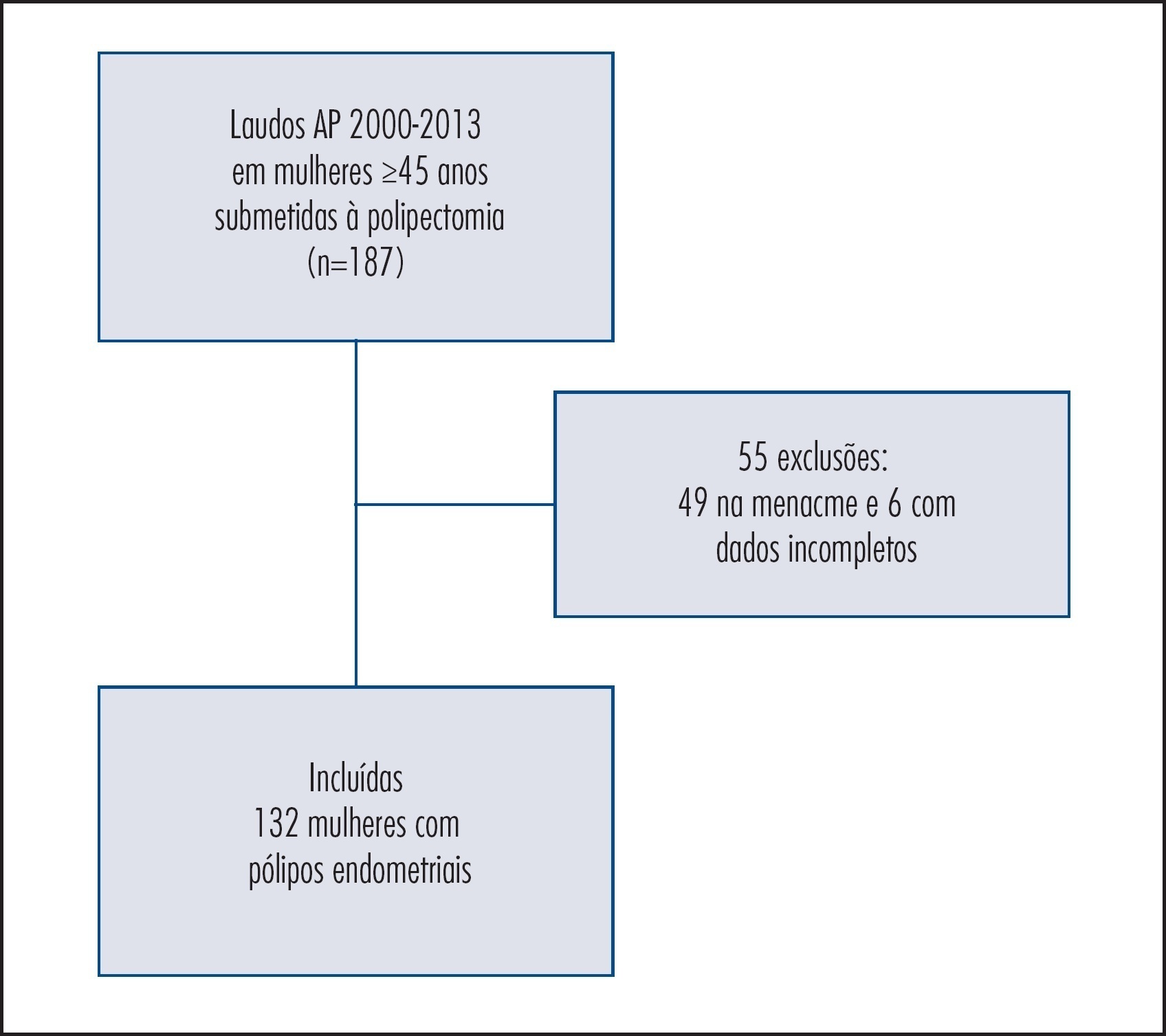
Observational cohort study with postmenopausal women who had been at a public university hospital. Clinical, anthropometrical, laboratorial, and ultrasonographic data of 132 patients with a histopathological diagnosis of endometrial polyps and 264 women without endometrial alterations (control) were compared in order to evaluate the predictive factors of endometrial polyps. Women with amenorrhea ≥12 months and ≥45 years of age were included in the study at a proportion of 1 case for 2 controls. The Student’s t, χ2, and logistic regression tests were used for statistical analysis – odds ratio (OR).
Patients with endometrial polyps were older and had been in menopause for a longer time compared to control (p<0.0001). The percentage of obese women with polyps (72.0%) was higher compared to the Control Group (39%; p<0.0001). The measurement of waist circumference was superior among patients with polyps (p=0.0001). We observed a higher incidence of diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia in patients with endometrial polyps (p<0.0001). According to the US National Cholesterol Education Program/Adult Treatment Panel III (NCEP/ATP III) criteria, 48.5% of women with polyps and 33.3% of the Control Group were classified as having metabolic syndrome (p=0.004). Analysis of risk for endometrial polyps formation showed higher chances of occurrence of the disorder in patients with: BMI≥25 kg/m2 (OR=4.6; 95%CI 2.1–10.0); glucose ≥100 mg/dL (OR=2.8; 95%CI 1.3–5.9); dyslipidemia (OR=7.0; 95%CI 3.7–13.3); diabetes (OR=2.5; 95%CI 1.0–6.3), and metabolic syndrome (OR=2.7; 95%CI 1.1–6.4) compared to the Control Group.
In postmenopausal women, obesity, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia and presence of metabolic syndrome were predictive factors for the development of endometrial polyps.
Search
Search in:


Comments