-
Artigo Original23/01/2025
A comparison of the efficacy of the effect of online versus face-to-face group counseling based on positive-approach on sexual intimacy of women after benign abdominal hysterectomy: a clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo102
Resumo
Artigo OriginalA comparison of the efficacy of the effect of online versus face-to-face group counseling based on positive-approach on sexual intimacy of women after benign abdominal hysterectomy: a clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo102
Visualizações282Ver maisAbstract
Objective
The study investigates the influence of positive-approach counseling through both online and face-to-face group therapy on the sexual intimacy of women after benign complete abdominal hysterectomy, addressing challenges such as the loss of femininity and other psychosexual complications that disrupt the couple’s relationship post-surgery.
Methods
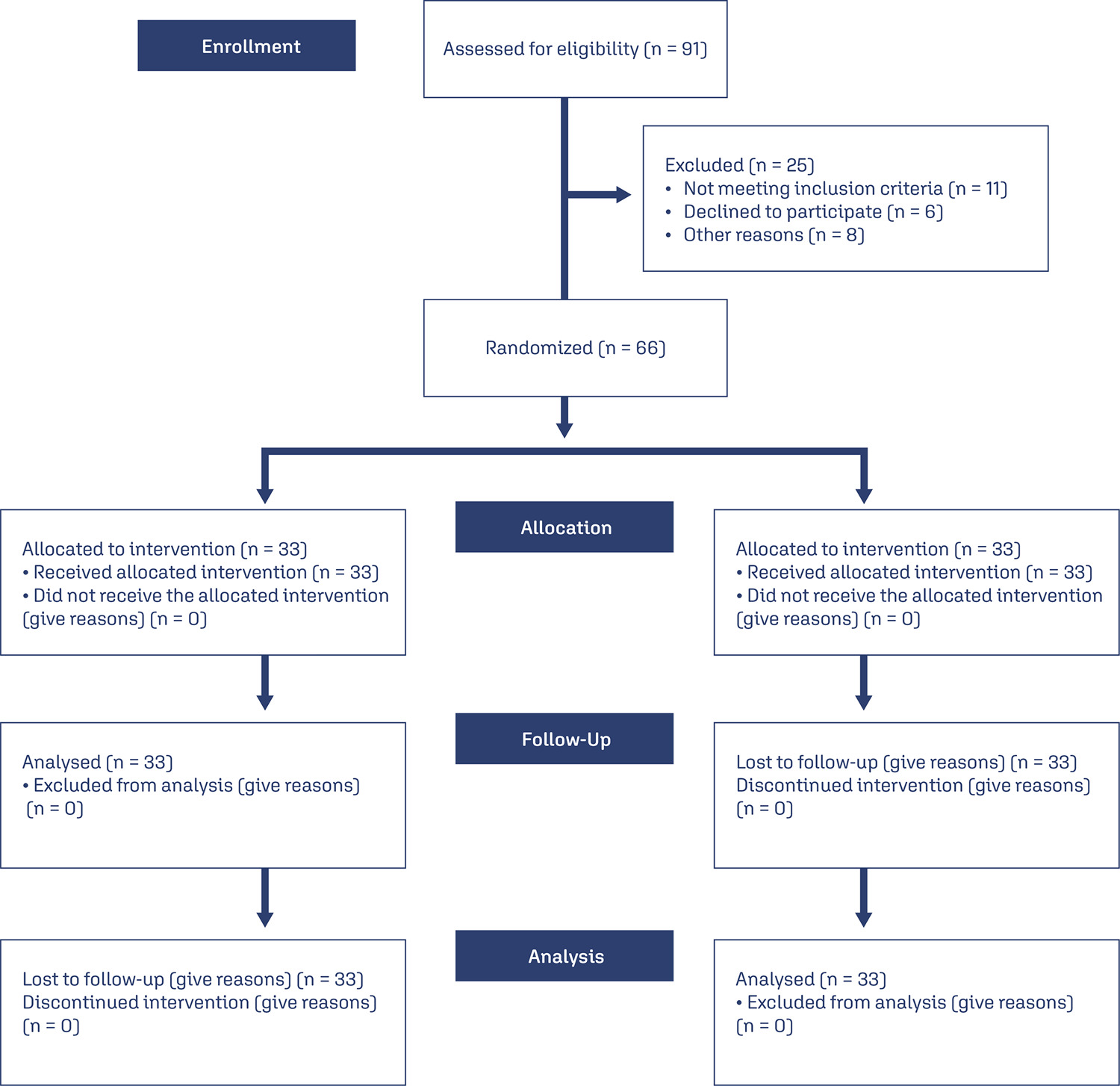
This is a parallel clinical trial, conducted in 2023 in Yazd, Iran; with sixty-six participants post- benign complete abdominal hysterectomy were randomly assigned to online and face-to-face counseling groups. Each group had eight 90-minute sessions, and data were collected using demographic and intimacy scale (IS) questionnaires at baseline, eighth week, and twelfth week follow-up. Statistical analysis used SPSS version 23 (P < 0.05).
Results
In the Online Group, the mean sexual intimacy score significantly increased from 72.42 ± 9.05 to 87.06 ± 7.98 at eight weeks and 90.30 ± 8.23 at twelve weeks (P < 0.001). In the Face-to-Face Group, the mean score increased from 70.21 ± 6.75 to 81.24 ± 5.55 at eight weeks and 85.03 ± 5.40 at twelve weeks (P < 0.001). Online counseling proved more effective than face-to-face counseling in enhancing sexual intimacy (P = 0.043).
Conclusion
Online and face-to-face counseling based on the positive approach improved sexual intimacy in women with a history of benign hysterectomy. Moreover, it seems that online counseling was more effective, so it is recommended that this method be employed in follow-up sessions after hysterectomy. Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials – IRCT20230209057373N1
-
Artigo Original23/01/2025
Therapeutic resources used by physiotherapists for the relief of labor pain: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo99
Resumo
Artigo OriginalTherapeutic resources used by physiotherapists for the relief of labor pain: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo99
Visualizações306Abstract
Objective
The aim of the study was to identify non-pharmacological therapeutic resources used by physiotherapists for pain relief during labor and childbirth.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional study conducted from January to March 2021, followed the STROBE guidelines. It included Brazilian physiotherapists with a minimum of two years in obstetric care experience. Data were collected using a 33-item online questionnaire, which covered sociodemographic details and the utilization of non-pharmacological resources. Descriptive analysis was used to determine participant characteristics. Associations between sociodemographic variables, specialist titles, participation in scientific events, and methods for pain relief methods during childbirth were assessed using chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 23.0, with a significance level set at 5% (p < 0.05).
Results
A total of 114 Brazilian physiotherapists participated in this study. Participants chose to utilize non-pharmacological therapies and resources that are within the scope of physiotherapists’ practice for labor pain. Kinesiotherapy with the use of devices was the most employed technique for pain relief during the birthing process.
Conclusion
The study highlights the prevalent use of non-pharmacological therapeutic resources, particularly kinesiotherapy with devices, among Brazilian physiotherapists for labor pain relief.
Palavras-chave: childbirthlabor painLabor, obstetricNon-pharmacological resourcespain managementParturiationPhysical therapistsPregnancysurveys and questionnairesVer mais -
Artigo Original23/01/2025
Maternal erythrocytosis as a risk factor for small for gestational age at term in high altitude
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
Resumo
Artigo OriginalMaternal erythrocytosis as a risk factor for small for gestational age at term in high altitude
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
Visualizações292Abstract
Objective
To determine if maternal erythrocytosis is a risk factor for small-for-gestational age at term at 3,400-m altitude in pregnant women without intercurrent disease.
Methods
Analytical study of retrospective cohorts at Cusco, a city at 3,400-m altitude. Our participants were 224 and 483 pregnant women with and without exposure to maternal erythrocytosis, respectively. A logistic regression with the goodness of fit to the proposed model was also performed with the Hosmer and Lemeshow test, evaluating the small-for-gestational-age results with or without exposure to hemoglobin >14.5 g/dl.
Results
The incidence of small-for-gestational-age was 6.9% for this entire cohort. The maternal erythrocytosis during gestation without any maternal morbidity at 3,400-m altitude has an ORa=0.691 (p=0.271) for small-for-gestational-age at term. Inadequate prenatal control has an ORa=2.115 (p=0.016) for small-for-gestational-age compared to adequate prenatal control.
Conclusion
Maternal erythrocytosis in pregnant women without any morbidity is not a risk factor for small-for-gestational-age at 3,400 m-altitude.
Palavras-chave: AltitudeFetal growth retardationGestational agehemoglobinHypoxiaMorbidityNeonatal mortalityPolycythemiaPregnancyPregnant womenRisk factorssmall for gestational ageVer mais -
Artigo Original23/01/2025
Comparison of serum ischemia modified albumin levels between preeclamptic and healthy pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo97
Resumo
Artigo OriginalComparison of serum ischemia modified albumin levels between preeclamptic and healthy pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo97
Visualizações371Ver maisAbstract
Objective
Our aims to compare level of serum ischemia modified albümin(IMA) between healthy and preeclamptic pregnancies and to evaluate the relationship of IMA with preeclampsia, preeclampsia severity and perinatal outcomes.
Methods
Our study is a prospective case-control study. A total of 134 pregnant women (66 preeclamptic and 68 healthy pregnant) between 18-45 years of age and between 24- 41 gestational weeks participated. Serum IMA levels were measured by the Albumin Cobalt Binding (ACB) test.
Results
The mean IMA values were found to be significantly higher in the preeclampsia group compared to the control group (p<0,001). Patients were divided into 3 groups; severe preeclampsia(n=29), non-severe preeclampsia(n=37) and healthy pregnant(n=68). Statistically significant difference was not found between severe preeclampsia and non-severe preeclampsia (p=0.505). The performance of IMA values in predicting the development of preeclampsia among all participants was evaluated with Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. According to the ROC analysis, the best cut-off value at which the maximum area under the curve (AUC) was obtained was found when IMA>0.98(AUC: 0.690 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 0.600-0.781 p<0.001). When IMA threshold value of >0.98 was taken to predict preeclampsia; the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated as 65.15%, 64.71%, 64.18%, and 65.67%, respectively.
Conclusion
IMA level may be a useful new marker in recognizing and predicting preeclampsia. However, despite the power of recognizing the disease, serum IMA levels do not give an idea about the severity of the disease. More comprehensive studies are needed in order to use IMA levels in the diagnosis of preeclampsia.
-
Nominata 202431/12/2024
Nominata 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:eRBGO20242024
Resumo
Nominata 2024Nominata 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:eRBGO20242024
DOI 10.61622/rbgo/2024nominata02024
Visualizações218We wish to thank everyone who contributed to the edition of the Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia – RBGO volume 46, year 2024, especially the authors and reviewers whose work and opinions were essential to maintain the scientific and methodological rigor of the published articles.A. Seval Ozgu-Erdinc, University of Health Sciences, Ankara Eğitim ve […]Ver mais -
Carta ao Editor04/12/2024
Comment on: Effect of combined training on body image, body composition and functional capacity in patients with breast cancer: controlled clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo96
Resumo
Carta ao EditorComment on: Effect of combined training on body image, body composition and functional capacity in patients with breast cancer: controlled clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo96
Visualizações210Dear Editor,I am writing to express my appreciation for the recent article titled “Effect of Combined Training on Body Image, Body Composition, and Functional Capacity in Patients with Breast Cancer: Controlled Clinical Trial,” published online on June 20, 2023. The study provides crucial insights into the benefits of combined training for breast cancer patients, highlighting […]Ver mais -
Artigo Original04/12/2024
Prognosis and cardiotoxicity associated to adjuvant trastuzumab for breast cancer: real world study in a public health system
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo93
Resumo
Artigo OriginalPrognosis and cardiotoxicity associated to adjuvant trastuzumab for breast cancer: real world study in a public health system
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo93
Visualizações250Abstract
Objective:
To analyze the prognosis of patients with breast cancer who developed trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity and to analyze factors associated with and resulting from cardiotoxicity.
Methods:
This was a retrospective cohort study that included 255 HER2-positive breast cancer patients who received adjuvant trastuzumab therapy. The inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of HER2-positive breast cancer and adjuvant trastuzumab therapy; disease stage I-III; <70 years; and a baseline echocardiogram showing a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥ 55%. The Kaplan-Meier method, the log-rank test, and the Cox proportional hazards model were used.
Results:
In all, 15.3% (39/255) of patients presented with cardiotoxicity. Treatment was suspended in 92.3% (36/39) of patients who presented with cardiotoxicity during trastuzumab treatment. The treatment was suspended in 46 of 255 patients and it was permanently interrupted in 84.8% (33/46) of these patients, with 84.8% (28/33) due to cardiotoxicity. Cardiotoxicity was not associated with disease-free survival (DFS) (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.48; 95% confidence interval (CI = 0.79-2.78) or overall survival (OS) (HR = 1.68; 95%CI= 0.83-3.41). Patients with clinical stage III and whom trastuzumab therapy was suspended (all causes) had worse DFS; (HR = 3.19; 95% CI=1.77-5.74) and (HR = 1.83; 95% CI=1.01-3.32) respectively. Those with clinical stage III and whom trastuzumab therapy was permanently interrupted had worse OS; (HR = 3.80; 95% CI =1.82-7.94), and (HR = 2,26; 95% CI =1.09-4.68 respectively.
Conclusion:
Cardiotoxicity was not associated with DFS or OS. Clinical stage III, Suspension and permanent interruption of treatment regardless of the cause were associated with worse DFS and OS in breast cancer patients.
Palavras-chave: Breast neoplasmsCardiotoxicityChemotherapyDisease-free survivalPrognosisTrastuzumabUnified Health SystemVer mais -
Artigo Original04/12/2024
Clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo91
Resumo
Artigo OriginalClinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo91
Visualizações220Ver maisAbstract
Objective:
The average age of patients with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) has been reported to have declined. Human papilloma virus (HPV)-related lesions have been shown to be associated with the expression of the immunohistochemical (IHC) marker p16. Non-HPV-related tumors have been characterized by p53 abnormal expression and PDL1 expression. We aimed to evaluate the correlation between these markers and vulvar SCC and to relate it to the clinical and pathological characteristics.
Methods:
Histopathologic assessments and IHC analyses of p16, p53, and PDL1 were performed in 41 samples of vulvar SCC collected between 2016 and 2021. The data were correlated with clinical and pathological characteristics of the patients.
Results:
The mean age of the patients was 72.1 years. Positive p16 and PDL1 staining was detected in 24.4% and 17.1% of the samples, respectively. p53 expression was negative in 19.5% of the samples, whereas it was overexpressed in 24.4%. p16-positive tumors showed a smaller depth of invasion (DOI) (p = 0.014), while tumors with p53 abnormal expression showed greater DOI (p = 0.041). PDL1 expression was correlated with increased number of inflammatory cells (p = 0.055). In addition, lesions with lymphovascular space invasion were p16-negative.
Conclusion:
In our sample, regarding to the SCC incidence the patients’ mean age did not change. The expression of p16 was inversely correlated with p53 results. Tumors with p53 abnormal expression and absence of p16 showed a greater DOI. Our data suggest an association between PDL1 expression and increased inflammatory infiltrates in vulvar SCC.
Busca
Pesquisar em:
Nuvem de Tags
Gravidez (167)Fatores de risco (89)Menopausa (79)Pré-eclâmpsia (66)Endometriose (65)Mama (59)Infertilidade (58)Obesidade (57)Complicações na gravidez (56)Diagnóstico pré-natal (54)Gestação (54)Qualidade de vida (53)Saúde da mulher (51)Cesárea (50)Complicações da gravidez (50)Neoplasias da mama (49)Fertilização in vitro (48)Cuidado pré-natal (47)Mortalidade materna (43)Ultra-sonografia (43)


