Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 08-01-2015;37(8):366-373
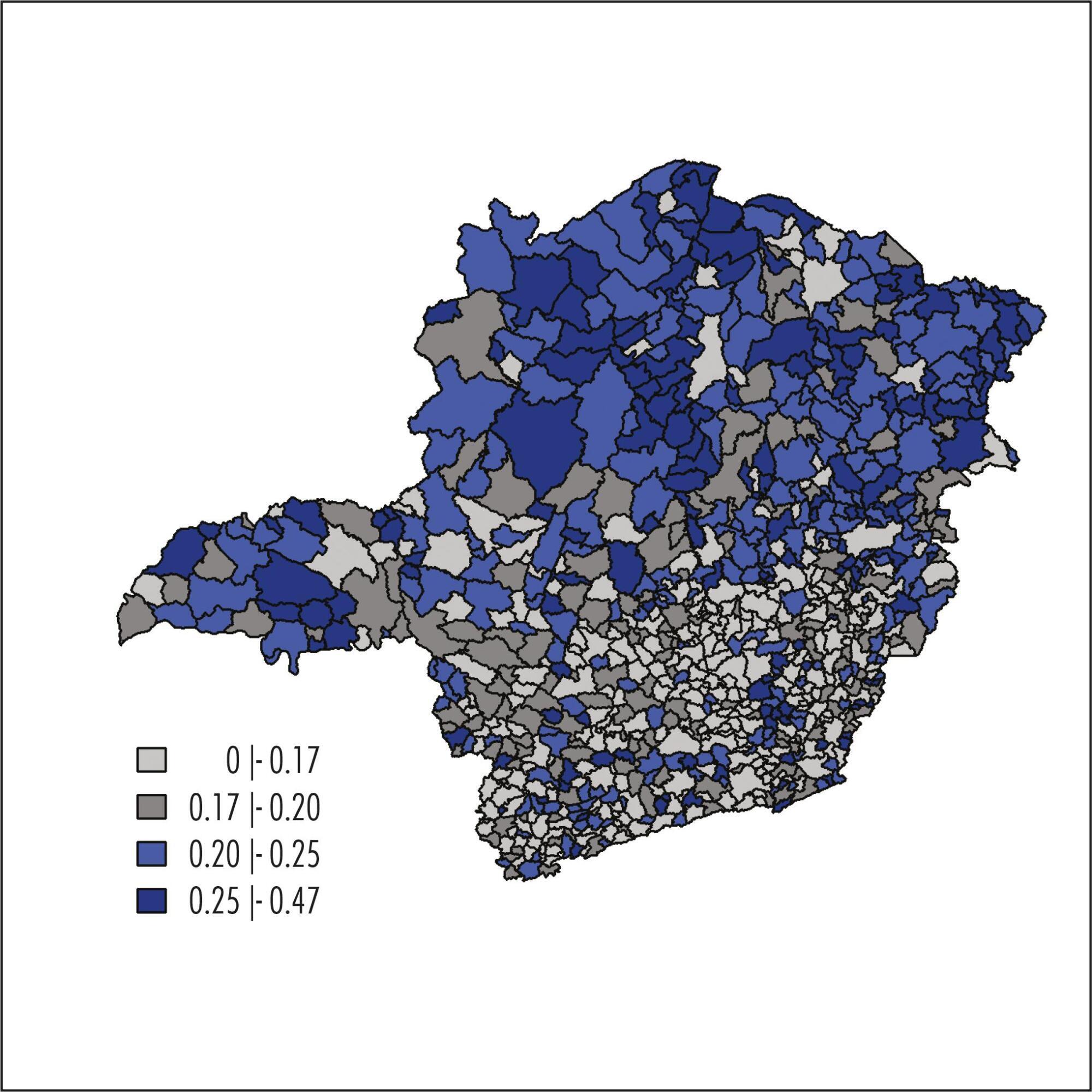
To describe associations between pregnancy rates in adolescence and socioeconomic and social responsibility indicators in the municipalities of the State of Minas Gerais, Southeast of Brazil, in the year of 2010.
Ecological study using data from the Brazilian Live Birth Information System (SINASC). The percentage of live births to adolescent mothers (LBAM) for each municipality was calculated based on the quotient between number of born alive infants of mothers aged 10-19 years old and total number of live births in the year of 2010. Fully Bayesian models were used to obtain the percentages of LBAM adjusted for spatial effects and to assess possible associations with socioeconomic and social responsibility indicators.
The crude percentage of LBAM for the total number of live births in the municipalities of Minas Gerais in 2010 ranged from 0 to 46.4%, with median percentage being 19.6% and the first and third quartiles being 15.6 and 23.1%, respectively. This study has demonstrated a close relationship between adolescent pregnancy and socioeconomic indicators. LBAM percentages were found to be higher in municipalities with low population density, low human development index and other low development indicators.
The strong relationship between LBAM percentages and socioeconomic indicators suggests that adolescent pregnancy is more a social than a biological problem. Therefore, programs and actions should go beyond sexual education and information on preventive health methods.
Search
Search in:


Comments