Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(1):9-14
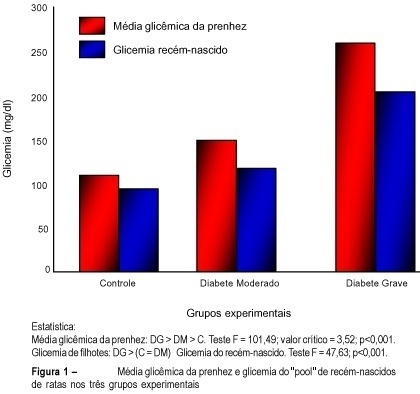
Purpose: to evaluate the effects of maternal diabetes on the fetal lung phospholipid profiles of rats with moderate and severe diabetes measuring lecithin (L), sphingomyelin (S), phosphatidyl-glycerol (PG), phosphatidyl-inositol (PI), and the relationships between L/S and PG/PI. Methods: fifty-four mature Wistar rats were submitted to experimental diabetes and pregnancy¹. Diabetes was induced by alloxan (42 mg/kg of weight, iv) and three groups were formed: control; moderate diabetes (MD), with glycemia levels between 120 and 200 mg/dl, and severe diabetes (SD), with glycemia levels higher than 200 mg/dl. On the 21st day, cesarian section was performed, and the fetal lungs were macerated and pooled. The phospholipids were measured by unidirectional thin-layer chromatography. Results: 1) the fetal lungs of the rats with moderate diabetes showed higher weight (0.159 g) and lower concentration of PG (3.0 µg/ml) and PI (3.4 µg/ml) than the controls, and the same relationship between L/S (2.2) and PG/PI (2.0). The fetal lungs of the rats with severe diabetes showed lower weight (0.145 g), the same values of L/S (1.9) and PG/PI (2.1), and lower PI (5.1 µg/ml) value than the controls. Conclusions: 1) the pulmonary maturity retardation in the pups of rats with moderate diabetes is explained by the higher pulmonary weight associated with lower concentration of PG and PI; 2) the pulmonary maturity acceleration in the pups of rats with severe diabetes is explained by the lower pulmonary weight associated with the same concentration of PG and PI.
Search
Search in:


Comments