Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 03-18-2025;47:e-rbgo3
This study aimed to investigate the effect of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on nipple trauma and pain during breastfeeding through a systematic review with a meta-analysis of selected studies.
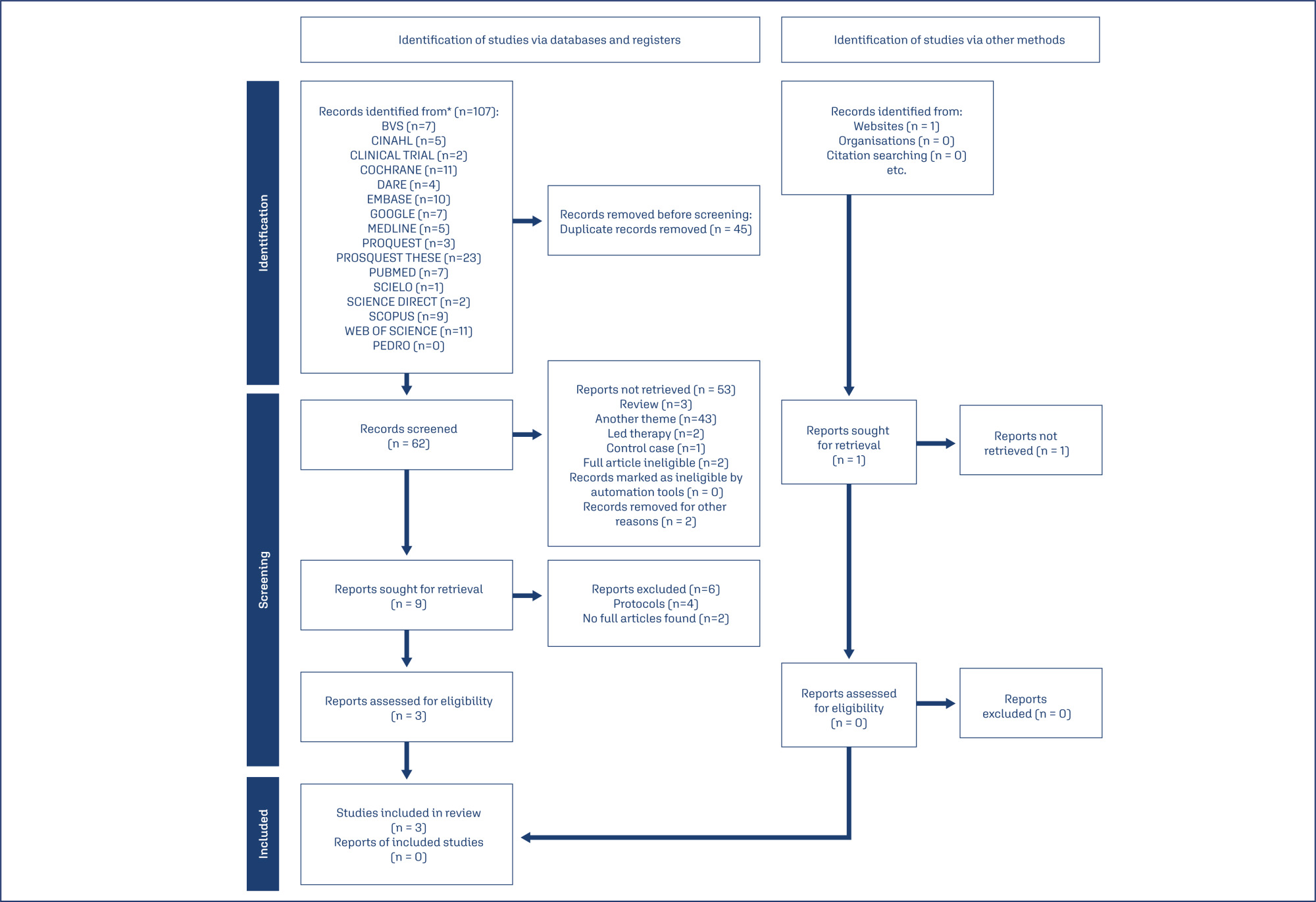
A thorough search was conducted on March 22, 2022, using the databases PubMed, SciELO, LILACS, PEDro, CINAHL, EMBASE, ScienceDirect, Scopus, Google Scholar, MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, Clinical Trials, Web of Science, TRIP, DARE, and ProQuest. The search terms included various combinations of low-level laser therapy, nipple pain, nipple trauma, and breastfeeding.
Out of 107 articles identified, only three controlled and randomized clinical trials was included. The extracted data encompassed breast and trauma characteristics, treatment types, outcomes (pain and healing process), evaluation tools, LLLT usage, laser brand, and parameters.
Data extraction was performed using RAYYAN for systematic reviews. The risk of bias in the studies was evaluated.
Pain was measured using the visual analog scale (VAS). The included studies did not use validated tools for assessing physical conditions. All studies employed LLLT with a 660-nm wavelength, though there were variations in equipment power, energy dose, and application methods. The meta-analysis revealed an average difference of −0.60 points (95% CI: −1.52 to 0.31) in the VAS pain scores between the LLLT and control groups. No heterogeneity was observed among the studies (I2=0%), indicating no significant difference in pain relief between LLLT (red light) and control groups.
LLLT may offer a promising option for managing breastfeeding-related complications, though further research is required.
Search
Search in:


Comments