Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 04-08-2022;44(2):125-132
To investigate the expression of endothelin-1 (ET-1) and endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase (eNOS) in normal and preeclamptic (PE) placentae.
The present cross-sectional analytical study was performed in normal and PE primigravidae (n=10 in each group) who were admitted to the North Okkalapa General and Teaching Hospital from February 2019 to February 2020. Serum samples were collected immediately before delivery, and placental tissues were collected immediately after emergency or elective cesarean section. The expression of placental eNOS was measured by western blot, and the levels of ET-1 in placental tissue homogenates and in the serum were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
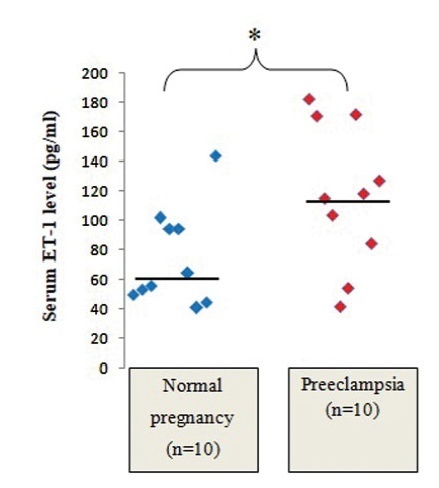
The PEgrouphadsignificantly higher serumlevelsof ET-1(median: 116.56 pg/mL; IQR: 89.14-159.62 pg/mL) than the normal group (median: 60.02 pg/mL; IQR: 50.89-94.37 pg/mL) (p<0.05). However, statistically significant differences were not observed in the levels of ET-1 in placental tissue homogenates between normal and PE placentae (median: 0.007 pg/μg of total protein; IQR: 0.002-0.0123 pg/μg of total protein; andmedian: 0.005 pg/μg of total protein; IQR: 0.003-0.016 pg/μg of total protein respectively). The median and IQR values of relative placental eNOS expression were significantly higher in the PE group than in the normal group (p<0.05). The serum levels of ET-1 level were not significantly correlated with placental ET-1 expression, and neither there was a significant correlation between placental ET-1 and eNOS expression in any of the groups.
The serum levels of ET-1 were significantly higher in PE pregnant women compared with normal pregnant women, while the ET-1 levels of placental tissue homogenates were not significantly different. Serum ET-1 rather than placental ET-1 might play a major role in the pathogenesis of PE.
Search
Search in:


Comments