Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):240-247
To compare the effect of high-dose vitamin A (HD Vit-A) use during postmolar follow-up of patients with low and plateauing (L&P) serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels, from the moment serum hCG plateaued (P-hCG) to the first normal serum hCG value (< 5IU/L).
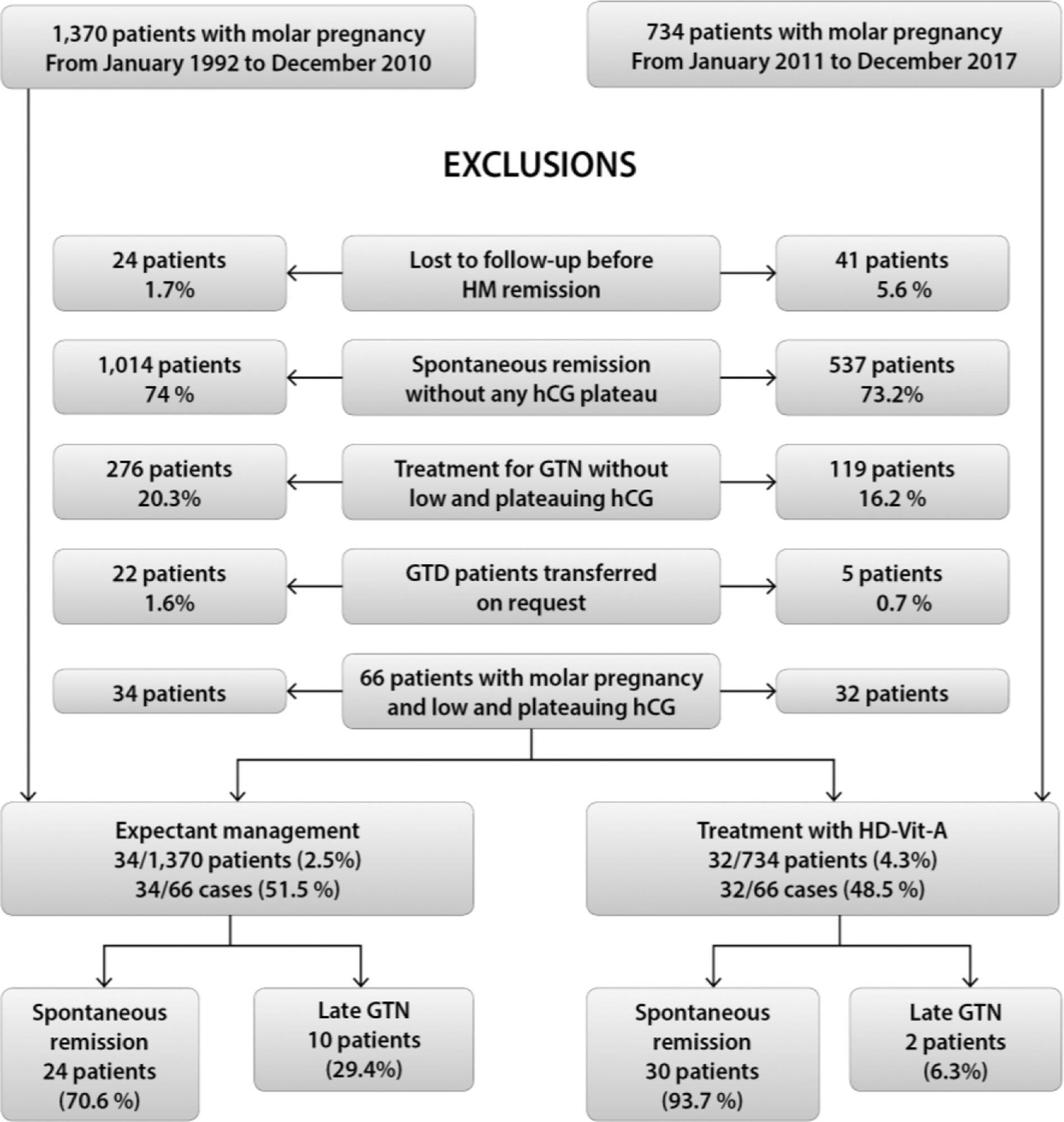
The present retrospective series case study compared two nonconcurrent cohorts of patients. Control group (CG): 34 patients with L&P serum hCG levels who underwent expectant management for 6 months after uterine evacuation, from 1992 to 2010; study group (SG): 32 patients in similar conditions who received 200,000 IU of Vit-A daily, from the identification of a P-hCG level to the first normal hCG value or the diagnosis of progression to gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN), from 2011 to 2017. The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the institution where it was conducted.
In both groups, the prevalence of persistent L&P serum hCG levels was < 5%. In the SG, hCG levels at plateau were higher (CG = 85.5 versus SG = 195 IU/L; p = 0.028), the rate of postmolar GTN was lower (CG = 29.4% versus SG = 6.3%, p = 0.034) and follow-up was shorter (CG = 14 versus SG = 10 months, p < 0.001). During GTN follow-up, there were no differences in GTN staging or treatment aggressiveness in both groups. High-dose Vit-A use did not have any relevant toxic effect. There were no GTN relapses or deaths.
The limited use of HD Vit-A seems to have a safe and significant effect on the treatment of postmolar patients with L&P serum hCG levels and may decrease the development of postmolar GTN in this population.
Search
Search in:


Comments