Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-09-2025;47:e-rbgo26
A combination of chemotherapy and pelvic radiotherapy is recommended to treat locally advanced cervical cancer (CC), which has been associated with acute and chronic toxicities, especially radiation proctitis (RP). The objective of this study was to evaluate the frequency of RP and treatment management in females with CC who underwent pelvic radiotherapy at an oncology referral hospital.
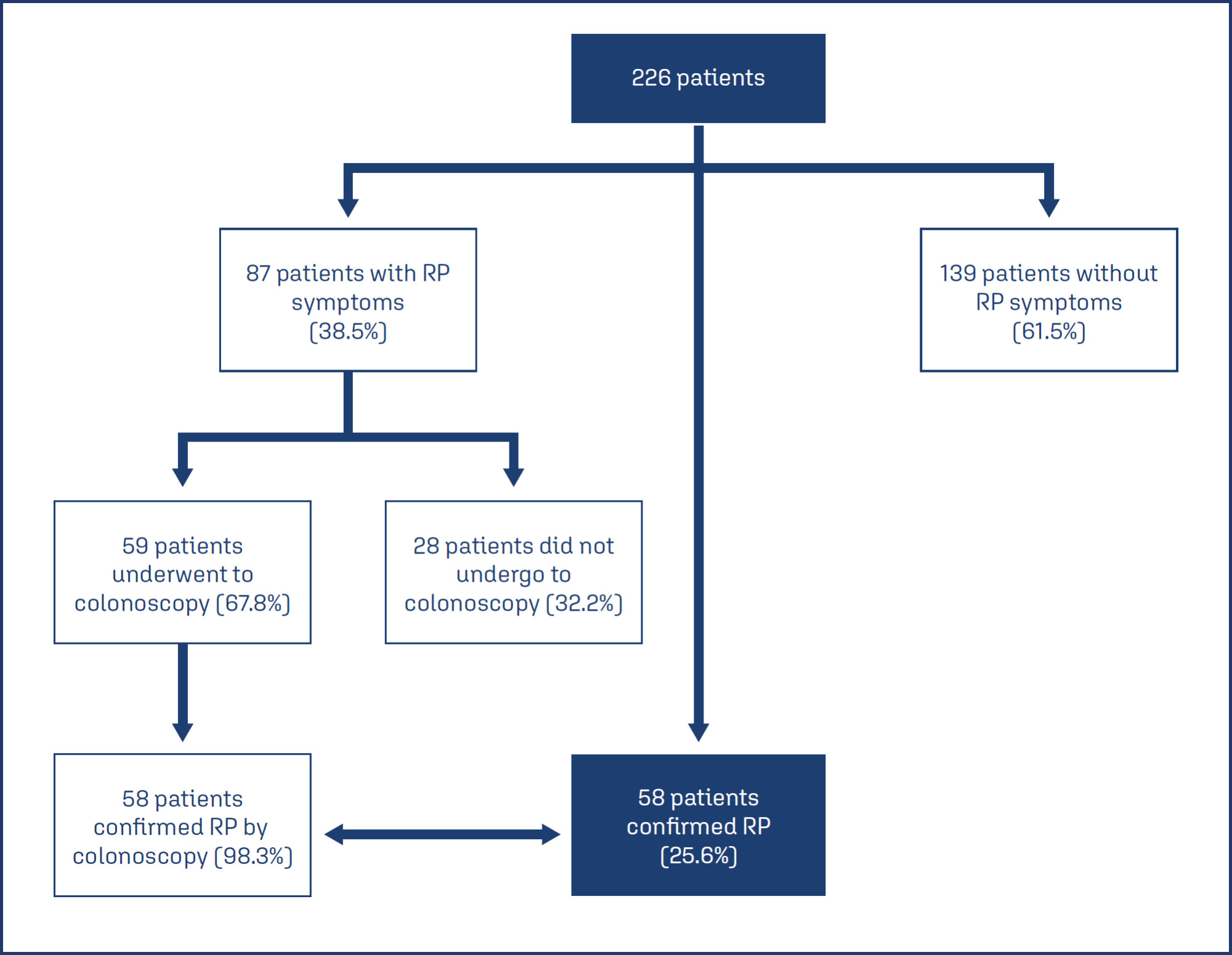
This cross-sectional study analyzed the medical records of patients treated with radiotherapy for CC between 2015–2017. We assessed sociodemographic, lifestyle, cancer, treatment, and clinical variables. We identified 298 records of females with CC who underwent pelvic radiotherapy during the defined period. Of these, 14 records were duplicates, 25 were excluded for lacking essential information, and 33 were missing in the archive. Accordingly, 226 relevant medical records were analyzed, with data regarding sociodemographic, clinical, cancer-related, treatment-related, and RP-related variables collected. Pearson’s chi-square test was used to compare symptomatic and non-symptomatic patients. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare chemotherapy doses. Statistical analysis was performed with Stata V12.1. A P-value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
The median patient age was 48 years (interquartile range 38–61). Patients predominantly had CC stages IIB and IIIB (>70%). Of the 226 females analyzed, 87(38.5%) experienced RP symptoms, represented by rectal bleeding; of these, 59 underwent colonoscopy, confirming RP in 58(98.3%). Accordingly, of the 226 females analyzed, 58(25.7%) had a confirmed diagnosis of RP. There was a statistically significant association between rectal bleeding and cumulative radiation dose (P < 0.001) and the presence of systemic arterial hypertension (P = 0.036). Regarding treatment, 38(65.5%) participants underwent argon plasma coagulation (APC), and of these, 22(57.9%) had no post-treatment macroscopic bleeding.
Patients with CC who received radiotherapy at an oncology referral service had a high frequency of RP, and APC helped control bleeding in certain patients.
Search
Search in:


Comments