Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 11-07-2019;41(10):607-612
Almost 80% of adolescent pregnancies are unplanned, and between 28 and 63% of adolescent mothers had a repeated pregnancy within 18 months. Among girls with repeated pregnancies, two-thirds reported that the pregnancy was unplanned. We aim to assess contraceptive use by adolescent mothers with increasing choice for long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) methods in postpartum consultation after a semistructured group intervention involving adolescent mothers.
Retrospective observational study conducted at the Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil, involving new antenatal and postpartum education groups for adolescents. At postpartum consultations, the adolescents chose their contraceptive. The datawas compared with previous series followed in a period before the implementation of the education group – a historical control group.
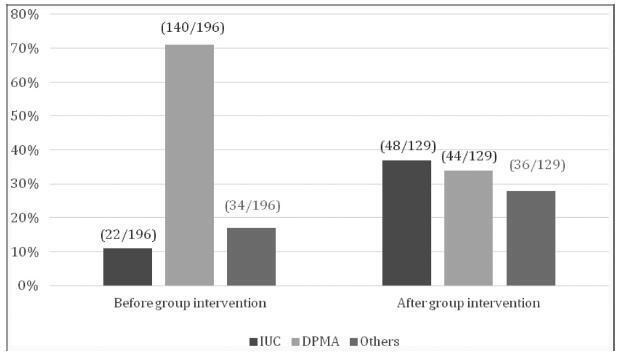
We included 129 adolescent after childbirth from January 1st, 2015 through July 31st, 2017. Out of this total, 63% had ever used contraceptive methods before pregnancy, and the most frequent method was combined oral contraceptives (33%) followed by condoms (21%). At the first postpartum consultation, the most common contraceptive chosen was intrauterine contraception (IUC) (37.2%) and depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) (34.1%).When comparing the rates before and after the education interventions, there was a 3-fold increase in the use of IUCs.
Antenatal and postpartum education have shown a significant increase in the choice for LARC methods among adolescent mothers, with very high acceptability after a period using the method. The educational groups performed during the antenatal care and beyond the gestational period are easy to be applied worldwide with low dependence on funding.
Search
Search in:


Comments