Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):207-215
The evaluation of the available evidence on vertical transmission by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV)-2.
An electronic search was performed on June 13, 2020 on the Embase, PubMed and Scopus databases using the following search terms: (Coronavirus OR COVID-19 OR COVID19 OR SARS-CoV-2 OR SARS-CoV2 OR SARSCoV2) AND (vertical OR pregnancy OR fetal).
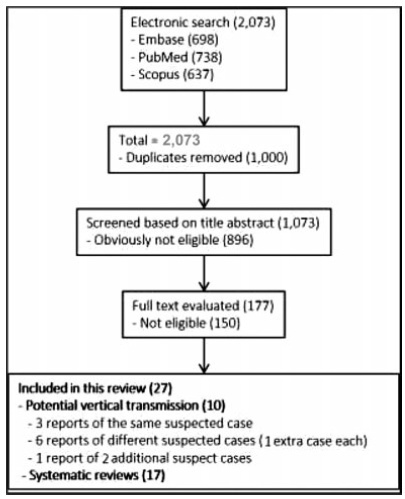
The electronic search resulted in a total of 2,073 records. Titles and abstracts were reviewed by two authors (WPM, IDESB), who checked for duplicates using the pre-established criteria for screening (studies published in English without limitation regarding the date or the status of the publication).
Data extraction was performed in a standardized way, and the final eligibility was assessed by reading the full text of the articles. We retrieved data regarding the delivery of the potential cases of vertical transmission, as well as themain findings and conclusions of systematic reviews.
The 2,073 records were reviewed; 1,000 duplicates and 896 clearly not eligible records were excluded. We evaluated the full text of 177 records, and identified only 9 suspected cases of possible vertical transmission. The only case with sufficient evidence of vertical transmission was reported in France.
The risk of vertical transmission by SARS-CoV-2 is probably very low. Despite several thousands of affected pregnant women, we have identified only one case that has fulfilled sufficient criteria to be confirmed as a case of vertical transmission. Well-designed observational studies evaluating large samples are still necessary to determine the risk of vertical transmission depending on the gestational age at infection.
Search
Search in:


Comments