Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(6):401-406
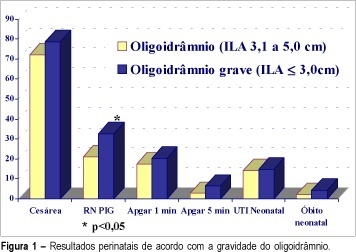
Purpose: to evaluate, in the high-risk pregnancies with oligohydramnios, the assessment tools for fetal well-being and perinatal results. Methods: five hundred seventy-two high-risk pregnancies were retrospectively analyzed. All of them presented with oligohydramnios established by AFI <=5.0 cm. Severe oligohydramnios was detected in 220 cases (AFI<=3,0 cm). The fetal well-being tests included: antepartum cardiotocography, biophysical profile score (BPS) and dopplervelocimetry of umbilical and middle cerebral arteries. Multiple gestation, fetal anomalies and premature rupture of membrane cases were excluded. Results: severe oligohydramnios was significantlly associated with abnormal and suspected cardiotocography results (23.2%), abnormal biophysical profile score (10.5%), abnormal results of middle cerebral artery dopplervelocimetry (54.5%), small for gestational age infants (32.7%) and meconial amniotic fluid (27.9%) when compared to pregnancies with AFI between 3.1 and 5.0 cm. This group presented: abnormal or suspected cardiotocography results (13.9%), abnormal biophysical profile score (4.3%), abnormal results of middle cerebral artery dopplervelocimetry (33.9%), small for gestational age infants (21.0%) and meconial amniotic fluid (16.8%). Conclusion: the oligohydramnios severity in high-risk pregnancies allows to discriminate the cases that are related to adverse perinatal outcome.
Search
Search in:


Comments