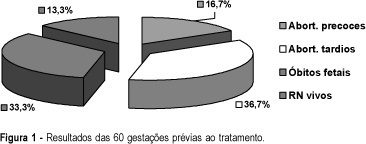
Purpose: to determine the effectiveness and the safety of treatment with heparin and low-dose aspirin in pregnant women with antiphospholipid syndrome, and to determine possible deteriorating factors for this syndrome. Methods: 17 patients with antiphospholipid syndrome were submitted to a rigorous antenatal care. Patients were treated with a fixed dose of heparin (10,000 IU/day) associated with low-dose aspirin (100 mg/day). We analyzed perinatal and maternal results, using chi² test and Fischer’s exact test. Results: the overall live birth rate was 88.2% in treated pregnancies of these patients versus 13.3% of their previous nontreated pregnancies. The incidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes was very significant: oligohydramnios (40%), fetal distress (33.3%), fetal growth retardation (33.3%), gestational diabetes (29.4%), preeclampsia(23.5%), and preterm delivery (60%). The presence of systemic lupus erythematosus was an indication of poor prognosis. No significant side effects were observed during the treatment. Conclusions: this treatment was effective to improve live birth rate, safe, but it was not able to avoid adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with antiphospholipid syndrome. Systemic lupus erythematosus was a deteriorating factor for this syndrome.
Search
Search in:


Comments