Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS02
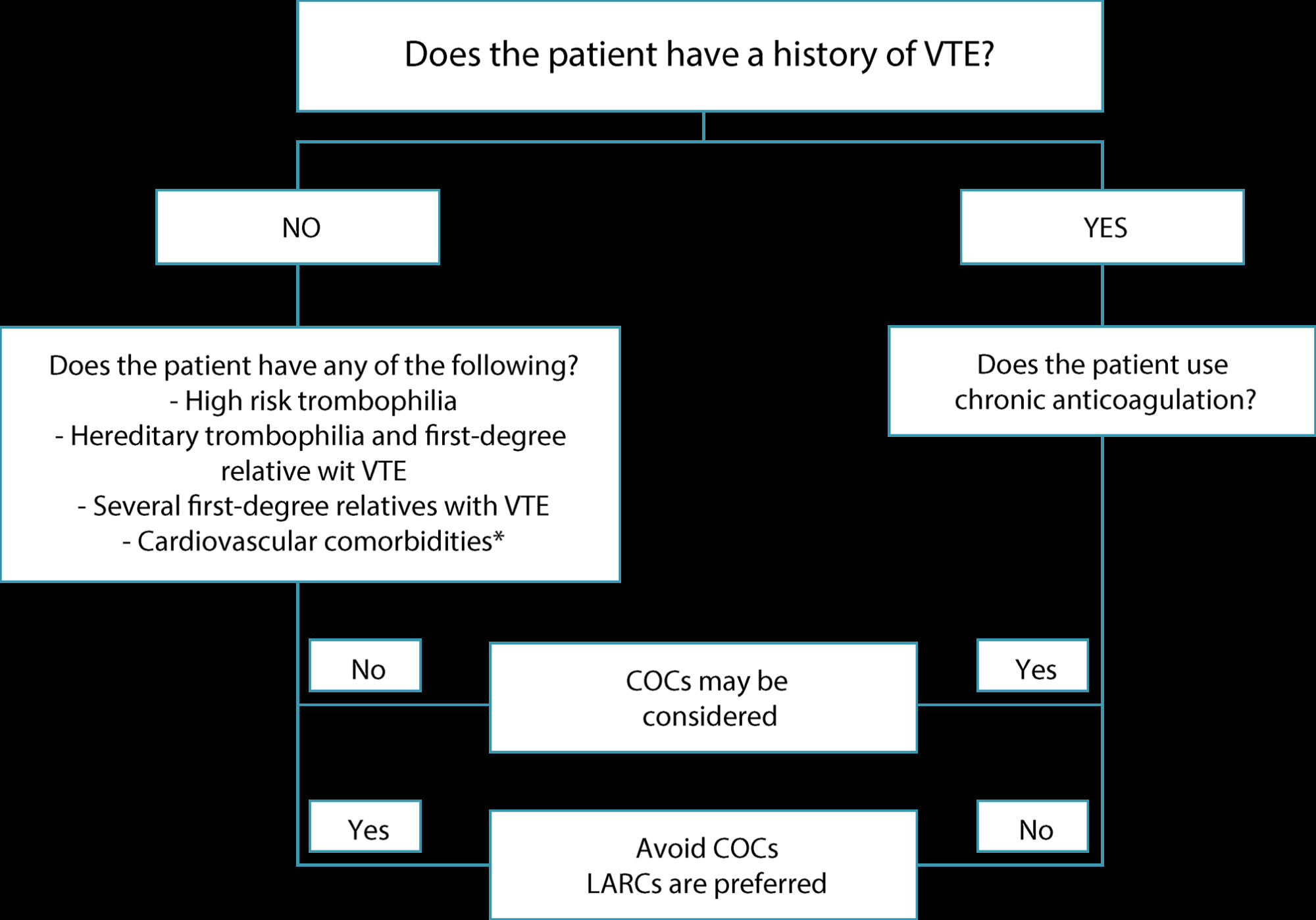
•The risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is not increased in women using long-acting reversible contraceptive methods (LARCs) with progestogens.
•Oral contraceptives with levonorgestrel or norgestimate confer half the risk of VTE compared to oral contraceptives containing desogestrel, gestodene or drospirenone.
•Progestogen-only pills do not confer an increased risk of VTE.
•Women using transdermal contraceptive patches and combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are at an approximately eight times greater risk of VTE than non-users of hormonal contraceptives (HCs), corresponding to 9.7 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Vaginal rings increase the risk of VTE by 6.5 times compared to not using HC, corresponding to 7.8 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Several studies have demonstrated an increased risk of VTE in transgender individuals receiving hormone therapy (HT).
•Hormone therapy during menopause increases the risk of VTE by approximately two times, and this risk is increased by obesity, thrombophilia, age over 60 years, surgery and immobilization.
•The route of estrogen administration, the dosage and type of progestogen associated with estrogen may affect the risk of VTE in the climacteric.
•Combined estrogen-progesterone therapy increases the risk of VTE compared to estrogen monotherapy.
•Postmenopausal HT increases the risk of thrombosis at atypical sites.
Search
Search in:


Comments