Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):210-215
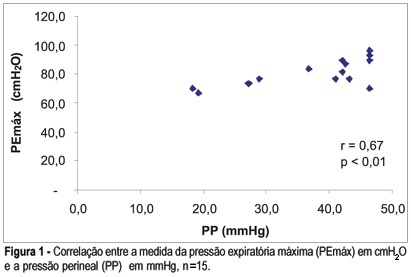
PURPOSE: to verify the behavior of the abdominal and perineal musculature in respiratory changes induced in 15 nulliparous women without previous history of perineal or respiratory failures, with age ranging from 20 to 26 years (22.9±1.83). METHODS: the electrical abdominal and perineal activities were analyzed simultaneously through surface electromyography and perineal pressure (PP) obtained through digital biofeedback. The volunteers were told to accomplish three types of respiratory maneuvers: maximum inspiration (PImax), maximum expiration (PEmax) and Valsalva (VM), at random. The electromyographic signs were collected by the AqDados® (4.4) software for binary language ASCII, being processed later using the Matlab® (6.5.1) software. The statistical analysis of the envoltory (EN) of the signal was accomplished through Spearman correlation and Kruskal-Wallis test, and the level of significance was set at 5% (p<0.05). RESULTS: it was observed that PP was larger in PImax (2.98±2,38), followed by VM (29.10±10.68), both being overcome by PEmax (38.22±9,98) (p<0.01). A positive correlation between PEmax and PP (p<0.01), as well as between EN of the perineal and abdominal musculature in PEmax and PImax (p<0.05 and p=0,03, respectively) could be shown. The results regarding VM were not significant, when PP and EN were analyzed. CONCLUSION: it was possible to identify the presence of abdomino-pelvic synergy during the execution of breathing maneuvers, especially in relation to PEmax.
Search
Search in:


Comments