Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(12):586-591
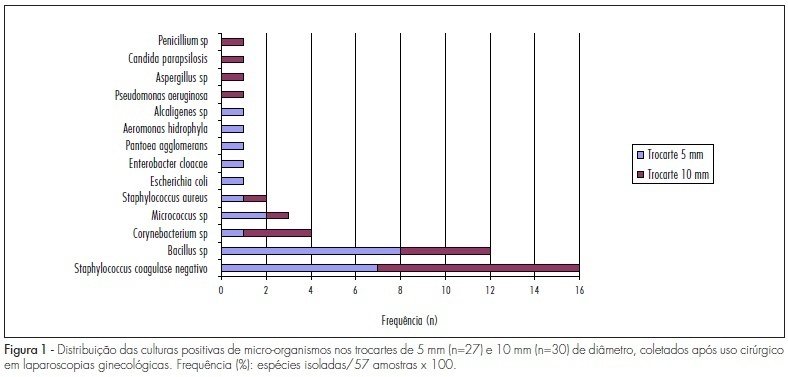
PURPOSE: to identify the microbial charge present in reusable trocars used in gynecological laparoscopies. METHODS: a descriptive exploratory study. An amount of 57 trocars, 30 with 10 mm of diameter and 27 with 5 mm, have been collected from the surgical unit, immediately after the surgery and placed in a sterilized recipient, in which 250 mL of sterile distilled water was added. Then, the trocars were agitated for the drainage of particles and to obtain a wash-out fluid to be analyzed. After being filtered through 0.22 µm cellulose membrane, the residue was placed on blood agar plates with a sterilized forceps. Following incubation, microbiological analysis has been done to count the number of colonies and further identify the microorganisms, using standard laboratorial techniques. RESULTS: microbial charge was recovered from 47.4% of the trocars analyzed. Among those, 45.6% presented 1 to 100 growing colonies. Fourteen types of microorganisms have been identified, among which the more frequently isolated were coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (28%) and Bacillus sp (21%), Aeromonas hydrophila, Alcaligenes sp, Candida parapsilosis, and enterobacteries were also identified. CONCLUSIONS: the study has demonstrated that the microbial challenge faced by the technician responsible for the cleaning and sterilization of trocars is low, as compared to the challenge imposed by biological markers. Nevertheless, it may be not inferred that the risks for infectious complications for patients are minimal.
Search
Search in:


Comments