Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(4):159-163
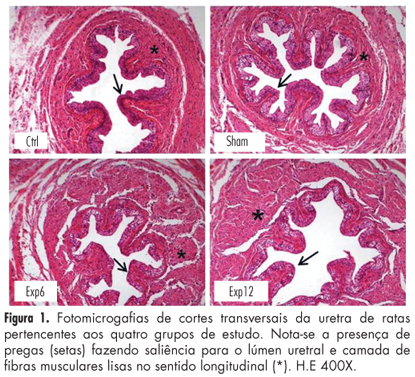
PURPOSE: To evaluate the effects of electrical stimulation (ES) of the pelvic floor on the urethra of female rats. METHODS: Forty adult rats were divided at random into four groups of ten animals each: Ctrl – without intervention; Sham – not submitted to ES, but with an electrode inserted into the vagina; Exp6 – submitted to six sessions of ES of the pelvic floor, and Exp12 – submitted to 12 sessions of ES of the pelvic floor. At the end of the experiment, all animals were anesthetized and the middle third of the urethra was removed, fixed in Bouin’s fluid and processed for histomorphometric study. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin for morphological and morphometric description, and others were stained with picrosirius red for the quantitation of total collagen. The thicknesses of the muscle layer and of the epithelium were determined, in 4 quadrants of the urethra, by performing 20 measurements per animal. The number of blood vessels present in the lamina propria was counted in the four quadrants over an area of 10³ µm² per quadrant and the images were obtained using the image analysis program AxioVision® REL 4.3 (Carl Zeiss). The collagen and muscle fiber ratios in the urethrae were calculated from two images per quadrant of every slice stained with picrosirius red, employing the Imagelab® Program. Data were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison test (p<0.05). RESULTS: The morphometry of the collagen, number of blood vessels and thickness of the epithelium showed no significant changes; however, the thickness of the periurethral muscle tissue increased significantly in Exp12 group, compared to the other groups (Exp12*>Exp6==Ctrl==Sham; *p<0.05). CONCLUSION: Prolonged functional electric stimulation of the pelvic floor induced an increase in periurethral muscle thickness in rats.
Search
Search in:


Comments